Production II
advertisement

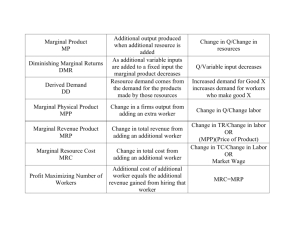
Production II Farm and Ranch Management o Decision-making process whereby limited resources are allocated to a number of production alternatives to obtain some objective Types of problems faced o How much to produce? How to produce? What to produce? Three primary functions of management o Planning, implementation, and control Marginal o Refers to incremental changes, increases or decreases, which occur at edge Planning o Primarily making choices, but also organizing Production Function o Systematic way of showing the relationship between different amounts of a resource or input that can be used to produce a product and the corresponding output, also call response curve, yield curve, or input/output curve TPP o Total physical product, output or yield APP o Average physical product, average amount of output produced by each unit of input, TPP/input level MPP o Marginal physical product, the additional TPP produced by using an extra unit of input, change in TPP divided by change in input level, also derivative Stages of Production o Classic 3 stage production function o Stage one- TPP increasing at an increasing rate, APP increasing, MPP increasing and decreasing o Boundary Stage 1 and Stage 2, MPP = APP, APP is at its maximum o Stage 2- TPP increasing at decreasing rate, APP and MPP decreasing, logical stage of production o Boundary Stage 2 and Stage 3- MPP= zero, TPP is at its maximum o Stage 3 – TPP and APP decreasing, MPP is negative Law of diminishing returns o As additional units of a variable input are used in combination with one or more fixed inputs, the marginal physical product will eventually begin to decline TVP o Total value product, the quantity of output (TPP) multiplied by the selling price, same as gross income MVP o Marginal value product, the additional revenue received from using an additional unit of input, MVP = change inTVP divided by change in input level AVP o Average value product, average gross revenue per unit of input used, TVP/input level MIC o Marginal input cost, change in total input cost or the addition to total input cost caused by using an additional unit of input, MIC – change in total input cost/ change in input level Profit maximizing point o where MVP = MIC MR o Marginal revenue, the additional income received from producing another until of output, MR = change in total revenue/ change in total physical product MC o Marginal cost, the additional cost incurred from producing another unit of output, MC = change in total input cost/ change in total physical product o MR + MC o Output level where profits will be maximized o Input substitution ratio o Amount of input A replaced divided by amount of input B added, the rate at which one input will substitute for another o Constant rate of substitution o The input substitution ratio is constant over the full range of possible input combinations Decreasing rate of substitution o as more of one input is substituted for another, it becomes increasingly difficult to make the substitution and still maintain the same level of output Price ratio for inputs o Price of input A divided by price of input B Least-cost combination of inputs o The substitution ratio and price ratio are equal Production Possibility Curve o PPC, shows all possible combinations of two outputs that can be produced from a given fixed input Substitution ratio between products o Quantity of output lost divided by quantity of output gained Where is profit maximized? o Where substitution ratio between products is equal to the price ratio for the products, price ratio is the unit of output being gained divided by the unit price of the output being lost, opposite of the substitution ratio Enterprise relationships o Competitive- given a limited input output of one enterprise can only be increased if the output of the other is decreased o Supplementary- the production form one enterprise can be increased without affecting the production level of the other o Complementary- increasing the production level of one enterprise causes the production of the other enterprise to increase Equal marginal principle o A limited input should be allocated among alternative uses in such a way that the marginal value products of the last unit are equal in all uses What is required to maximize profits from the total business? o The proper allocation of limited inputs, which will not necessarily result in maximizing the profit from any single enterprise Opportunity cost o The value of the next best alternative Cost concepts o TFC-total fixed costs o AFC- average fixed costs o TVC- total variable costs o o o o o o o o AVC-average variable costs TC- total costs ATC- average total costs MC- marginal costs Short Run- at least one fixed input level Long Run- all inputs are variable Fixed costs- incurred if no production Variable costs- costs associated with the level of production DIRTI 5 o Fixed costs, depreciation, insurance, repairs, taxes (property), and interest Any elasticity o % change of one item divided by % change of some other item Cost curve relationships o Total Cost Curves Fixed- constant and unaffected by output level, horizontal line Variable- always increasing first at a decreasing rate then at an increasing rate Total- sum of fixed and variable, always higher than variable by a vertical distance Fixed costs- same shape as variable costs curve o Averages and Marginal Cost curves Average fixed Cost- always declining but at a decreasing rate Average Variable Cost- U shaped Average Total Cost- U shaped, average variable and total cost curves approach each other as output decreases Marginal Cost- generally increasing, crosses average cost curves at their minimum values Economies of Size o Increasing returns to size, exists when the long run average cost curve is decreasing ,LRAC is decreasing Constant returns to size o LRAC is constant Decreasing returns to size o Increasing LRAC Principle of Comparative Advantage o States that individuals or regions will tend to specialize in the production of those commodities for which their resources give them a relative or comparative advantage, it is relative not absolute yields, costs and profits are importuning in this principle Enterprise Budget o A listing of all estimated income and expenses associated with a specific crop or livestock commodity to provide an estimate of its profitability What does an enterprise budget represent? o Any enterprise budget represents only one point on the production function, not the max. pt. changing component changes the profit associated with the enterprise Break Even Analysis: o Break-even yield = total costs/ output price o Break-even price = total costs/ expected yield Cost of production o The average cost of producing one unit of a given product Partial budgets o Used to calculate expected change in profit for a proposed change in the farm business, differs from an enterprise in that several enterprises might be involved in the change, contains only those income and expenses which will change because of the proposed modification or change Whole farm Budget o Involves plans for the entire operation, detailed physical and financial plan for the organization and operation of the total business, summary of the expected income, expenses, and profits Gross margin o Income above variable cost for an enterprise Linear programming o Mathematical technique to solve a problem with linear objective function, linear constraints, and alternative ways to produce Cash Flow Budget o A summary of cash inflows and outflows for a business over a given period of time Balance Statement o Summarizes the financial condition of the business at a point in time Income Statement o Summarizes the financial condition of the business at a point in time Depreciation o Noncost expense, accounting procedure to spread the original cost of an item over its useful life Depreciation Methods o Straight line, double declining balance, modified accelerated cost recovery system (MACRS), sum of the year’s digits Ratio analysis o See finance review Forms of business organization o Sole proprietorship, partnerships, corporations Capital and use of credit o See finance review Principle of increasing risk (use of credit) o As the debt/equity ratio leverage increases, the borrower has a greater risk of losing equity capital See acronyms for government agencies associated with farm management Cost of borrowing o Interest rate paid, interest is tax deductible, principle payment is not Investment analysis o Time value of money, see finance review Cash vs. Accrual methods o See finance review Tax basis & capital gains o See finance review Short-run situations o Expected selling price > ATC, a profit can be made and is maximized by producing where MR = MC o Expected price < ATC but > AVC, a loss is expected, but the loss will be less than total fixed cost and is minimized by producing at the point MR = MC o Expected Price < AVC, minimize loss by not producing, loss will equal TFC