MicroProb4
advertisement

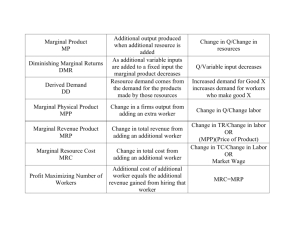
Problem Set 4 Econ 1200, Principle of Microeconomics, Mankiw’s Book Dr. G. Chang 1) Exercises from Study Guide to Accompany Mankiw, UT edition. (The Study Guide is the second half part of the UT edition textbook) Chapter 11: Public Goods and Common Resources Terms and Definitions: All Practice Problems: 1: all. Multiple-Choice Questions: All Chapter 12: The Design of Tax System Terms and Definition: All Practice Problems: 1 all, 2 all Multiple-Choice Questions: All Chapter 13: The Costs of Production Chapter Review Terms and Definitions: All Practice Problems: 3 True/False Questions: All Multiple-Choice Questions: All Answer the following questions: 1. A graph of total product shows how output changes as a. all inputs are increased simultaneously. b. the firm adopts new technologies. c. the scale of production varies. d. one input is increased, holding all others constant. 2. For a production process that uses just one input, average product is found by a. graphing total output against the number of units of input. b. computing the change in output for a unit change in input. c. dividing total output by the number of units of input. d. multiplying the number of units of input by their cost. 3. The "law" of diminishing marginal returns (diminishing marginal product) a. says that eventually the marginal product of any input must become negative. b. applies to only a simultaneous increase in all inputs. c. can only be true for a production function with decreasing returns to scale. 1 d. refers to what happens to output as only one factor is increased, all other inputs being held constant. 4. Marginal product refers to a. the increased revenue from employing an additional worker. b. the change in total output from a one-unit increase in a variable input. c. total output divided by total input. d. total output divided by total cost. 5. When looking at the curve for total product, the region of diminishing marginal returns is given by the region where marginal physical product is a. negative. b. positive. c. positive and increasing. d. positive and decreasing. 6. Consider the following data on workers and output. Workers 1 2 3 4 5 Output 10 25 35 42 40 Where do diminishing marginal returns to workers begin to set in? a. After the first worker. b. After the second worker. c. After the third worker. d. After the fourth worker. 7. For a production process that uses just one input, a firm should expand using the input as long as a. marginal revenue product is greater than the price of the input. b. marginal product is positive. c. average cost is declining. d. marginal physical product is greater than average physical product. 8. The rule for optimal input use implies that a firm should use additional units of an input until a. average cost equals the price of the input. b. marginal product is maximized. c. marginal revenue product equals the price of the input. d. increasing returns to scale are exhausted. 9. The optimal choice of input combinations a. is a purely technological decision, unaffected by input prices, and better left to engineers 6 economists. b. can be determined by looking at information on the marginal physical product and price of various inputs. c. will always be the same in both the short and long run. d. is likely to include more of an input if its price rises and if other input prices are unchanged. 10. Marginal revenue product (MRP) is equal to 2 a. MP/Poutput b. MP x Pinput c. Poutput/MPP d. MP x Poutput 11. To maximize profits, firms should increase the use of the input with MRP is _______ than the input price and reduce the use of the input when the MRP is ________ than the input price. a. high; low b. low; high 12. Consider the following data on workers and output. Workers 1 2 3 4 5 Output 10 25 35 42 40 Suppose output price = $2, and the wage rate is $16, how many workers should be hired? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 e. 5 Table 2 On Taxable Income ... Up to $10,000 From $10,000 to $50,000 From $50,000 to $80,000 From $80,000 to $165,000 Over $165,000 The Tax Rate is ... 10% 15 20 30 40 13. Refer to Table 2. If Chris has $30,000 in taxable income, his marginal tax rate will be a. 10%. b. 15% c. 20% d.30% e. 40% 14. Refer to Table 2. If Chris has $30,000 in taxable income, his tax liability will be a. $3000. b. 4000 c. 4,500 d. 5,000 e. None of the above 15. Refer to Table 2. If Chris has $30,000 in taxable income, his average tax rate will be a. 10%. b. 15% c. 20% d.30% e. None of the above Table 3: Consider the following data on workers and output. Workers 1 2 3 4 5 Output 10 25 35 42 40 16. In Table 3, what is the marginal product for the third worker? _____ 17. In Table 3, what is the average product of the third worker? ______ 18. In Table 3, what is the total product of three workers? ______ 3 Key for the above multiple choice questions 1d, 2c; 3d; 4b; 5d; 6b; 7a; 8c; 9b; 10 d; 11a, 12c, 13b, 14b, 15e 16. 10 17. 35/3=11.67 18. 35 4