Lab 9 problems
advertisement

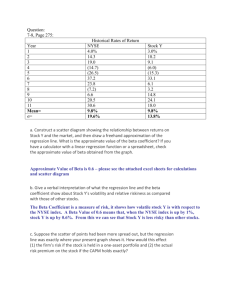
Lab 9 Problems Two stage growth problems. 1. Genestek Inc. just paid a $5.00 dividend. Due to a new product about to be released, analysts expect the company to grow at a supernormal rate of 15% for three years. After that it is expected to grow at a normal rate of 4% indefinitely. Stocks similar to Genestek are currently earning shareholders a return of 12%. a. The estimated selling price of the stock is: b. If everything goes as projected what will the price of the stock be one year from now, and what are the expected dividend and capital gains yield the first year assuming the stock is purchased for the price in part a. 2. Delta Company has some very exciting prospects in the near future. As a result it is expected to grow at a rate of 20% for the next year. After that it will grow at 7% indefinitely. The interest rate is currently 14% and Delta paid a dividend of $2.60 recently. What should Delta sell for today? a. $44.59 b. $39.45 c. $48.72 d. $41.67 Chapter 9 questions: 13. The Charming Co. manufactures decorating products. Treasury bills currently yield 5.4%, and the market is returning 8.1%. a. Calculate the Charming Co.'s beta from its characteristic line as depicted following (hint – think slope = rise over run): kCharming ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ 5.5 4.5 ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ 6.0 7.5 kM b. What expected return would an average investor require to buy shares of Charming? c. Would the answer to part b be a "fair" return? Why? 1 1.Modern portfolio theory suggests that: a. it is always wise to create a stock portfolio that captures a high average rate of return. b. the higher the expected return, the higher the portfolio’s risk. c. it is always wise to create a stock portfolio consisting of similar stocks. d. a riskless portfolio is always the wisest alternative. 2.Stocks that have high financial rewards are generally accompanied by: a. high dividend payments. b. low dividend payments because of internally generated growth. c. high risk. d. all of the above 3.The return on an investment in stock: a. is subject to risk but is generally non-negative like a savings account. b. has a standard deviation that has historically been small relative to its average value. c. consists of dividend and capital gains yields. d. is always very risky. 10.The risks associated with owning a single stock are called: a. systematic risk because all stocks in the system are affected. b. market risk because the stocks are purchased in the stock market. c. stand-alone risk because the stock stands alone outside of any portfolio. d. business risk because the stocks represent businesses. 11.Risk in finance: a. is variability in return. b. can be decomposed into business-specific and market components. c. will be accepted by some investors if higher expected returns are offered in compensation. d. all of the above 14.The underlying principles of portfolio theory include: a. diversifying business-specific risk away. b. basing decisions on stocks’ risk/return characteristics in a portfolio context rather than on a stand-alone basis. c. getting the highest available return for the amount of risk the investor is comfortable with. d. all of the above 19.Portfolio theory can be dangerous to a small investor because: a. he or she doesn’t have much money to lose. b. beta, the theoretical measure of risk, ignores business-specific risk, which is significant to an investor who doesn’t have a large enough portfolio to diversify it away. c. it makes investing seem more scientific than it really is. d. the stock market is very unforgiving. 23.Which of the following statements is false? a. Beta is meaningful only if an investor holds a well-diversified portfolio. b. You can completely eliminate risk if you hold a well diversified portfolio. c. A portfolio composed of only one stock will not be well diversified. d. A wise investor diversifies to capture the high average return of stocks while avoiding as much risk as possible. e. All of the above statements are correct. 2 27.Which of the following is not an example of a source of systematic or market risk? a. Interest rate changes b. Foreign competition with an industry’s products c. Changes in the overall economic outlook d. Changes in the inflation rate 34.Which of the following statements is false? a. The most commonly used index with which to measure risk is the standard deviation. b. The standard deviation measures the average deviation of the various outcomes from the expected rate of return. c. The variance is the square root of the standard deviation. d. The greater the volatility, the larger the standard deviation. e. All of the above statements are correct. 47.Market risk: a. is the degree to which a stock’s return moves with the market’s return. b. is caused by things that affect specific companies or industries. c. can be diversified away. d. is the chance of losing money in the stock market. 56.A statistic known as a stock’s beta coefficient measures: a. total risk. b. systematic or market risk. c. unsystematic or business-specific risk. d. none of the above 57.Which of the following statements about the beta coefficient is not true? a. A beta of > 1 implies that the stock’s volatility is greater than that of the market. b. A beta of < 0 implies that the stock tends to move against the market. c. A beta of 1 implies a volatility equal to that of the market. d. All of the above are true. 66.The security market line proposes that the required rates of return are determined by the following formulation: a. km = krf + (kx – krf)bx c. krf = kx + (km – kx)bx b. kx = krf + (km – krf)bx d. kx = krf + (km – krf)bm 75. A stock has an expected return of .10 (10%) and a variance of .25. Its coefficient of variation is: a. 2.5 c. 5 b. .4 d. 2.0 83. The only component of the CAPM equation that relates specifically to a company is: a. βX b. kM c. kRF d. (kM – kRF) 84. A classic example of a negative beta investment is the stock of a: a. steel mill because the industry is subject to intense international competition. b. gold mining company because it’s profitability runs opposite to the state of the economy. c. financial services company because it’s in the stock business itself. d. company in the defense industry because war is always a possibility. 87.If you invest 30% of your funds in AT&T stock with an expected rate of return of 10% and the remainder in GM stock with an expected rate of return of 15%, the expected return on your portfolio is: a. 12.5%. 3 b. c. d. e. 13.0%. 13.5%. 14.5%. none of the above 88.Phoenix Company common stock is currently selling for $20 per share. Security analysts at Smith Blarney have assigned the following probability distribution to the price of (and rate of return on) Phoenix stock one year from now: Price Rate of Return Probability $16 –20% 0.25 20 0% 0.30 24 +20% 0.25 28 +40% 0.20 Assuming that Phoenix is not expected to pay any dividends during the coming year, determine the expected rate of return on Phoenix Stock. a. 8% b. 0% c. 10% d. 40% 89.Don has $3,000 invested in AT&T with an expected return of 11.6 percent; $10,000 in IBM with an expected return of 12.8 percent; and $6,000 in GM with an expected return of 12.2 percent. What is Don’s expected return on his portfolio? a. 12.42% b. 12.20% c. 11.81% d. cannot be determined 91.Determine the beta of a portfolio consisting of equal investments in the following common stocks: Security Beta a. 1.05 Apple Computer 1.15 b. 1.00 Coca-Cola 1.05 c. 1.10 Harley-Davidson 1.50 d. 0.95 Homestake Mining 0.50 106. Elephant Company common stock has a beta of 1.2. The risk-free rate is 6 percent and the expected market rate of return is 12 percent. Determine the required rate of return on the security. a. 7.2% b. 14.4% c. 19.2% d. 13.2% 108. Charlie Dobbs is considering investing in Astrotech. His research has revealed the following: The market is returning 11%. Three month treasury bills are yielding 5%. Astrotech’s beta is 1.2. Astrotech recently paid a dividend of $1.50. Analysts expect Astrotech to grow at 4% indefinitely. How much should Charlie be willing to pay for a share of Astrotech? a. $19.02 b. $12.00 4 c. $10.26 d. $18.29 108b. What is the Market Risk Premium (MRP) in problem 108? 110.Ken Howard has a two stock portfolio consisting of Acton Inc. and Boron Corp. Assume the following conditions exist. Return on the market 3 month Treasury bill rate Acton’s beta Boron’s beta Market value of Ken’s investment in Acton Market value of Ken’s investment in Boron = 13% = 6% = 1.15 = 1.40 = $125,000 = $250,000 $375,000 What does the SML predict is Ken’s required rate of return for the overall portfolio? a. 15.24% b. 14.93% c. 23.12% d. 20.90% 110b. What is the MRP in problem 110? 112.Frazier Manufacturing paid a dividend last year of $2, which is expected to grow at a constant rate of 5%. Frazier has a beta of 1.3. If the market is returning 11% and the risk-free rate is 4%, calculate the value of Frazier’s stock. a. $25.93 b. $31.33 c. $38.53 d. $41.63 112b. What is the MRP in problem 112? 97.Stock A has a required return of 18% and a beta of 1.4. The expected market return is 14%. What is the risk-free rate? a. .6% b. 1.2% c. 3.0% d. 4.0% e. 6.0% 98. Stock X paid a dividend of $2.50 yesterday. It is expected to grow at 7% indefinitely. X’s return generally responds to market changes twice as much as does the average stock. Treasury bills currently yield 8%. The market is yielding 11%. What should X sell for today? a. $38.21 c. $17.21 b. $32.14 d. $35.71 99. PDQ stock has a required return of 20%. The expected market return is 15% and the risk-free rate is 5%. Solve for the beta of PDQ stock. a. 1 d. 2.5 b. 1.5 e. 3 c. 2 5 21. Weisman Electronics just paid a $1.00 dividend, the market yield is yielding 10%, the risk-free rate is 4%, and Weisman’s beta is 1.5. How fast do investors expect the company to grow in the future if its stock is selling for $27.25? 101. Use the following information to calculate your company’s expected return. State Probability Return a. 11% Boom 20% 40% b. 13% Normal 60% 15% c. 15% Recession 20% (20%) d. 17% 102. Use the following information to calculate the variance, standard deviation, and coefficient of variation of Macadam Corp.’s returns. (mean is from problem 101) State Probability Return a. 8.6% Boom 20% 40% b. 11.4% Normal 60% 15% c. 19.2% Recession 20% (20%) d. 19.8% 5. Conestoga Ltd. has the following estimated probability distribution of returns. Return Probability 4% .20 12% .50 14% .30 Calculate Conestoga’s expected return, the variance and standard deviation of its expected return and the return’s coefficient of variation. 3.The following information is available in general and about investments in stocks J and K. The market return (kM) The risk free rate (kRF) Stock J’s beta Expected constant growth rate for Stock J Investment in Stock J Stock K’s beta Expected constant growth rate for Stock K Investment in Stock K a. b. c. = 9% = 5% = 0.8 = 6% = $80,000 = 1.4 = 7% = $120,000 What are the expected returns on Stock J and Stock K individually? What is the expected return on the portfolio? If Stock K just paid a dividend of $2.50, what is Stock K’s intrinsic value? 6