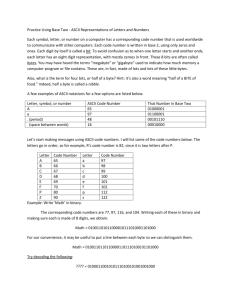
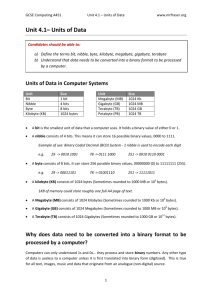
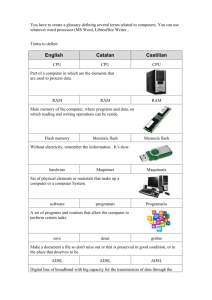
Quix 4 on Chapter 4
advertisement
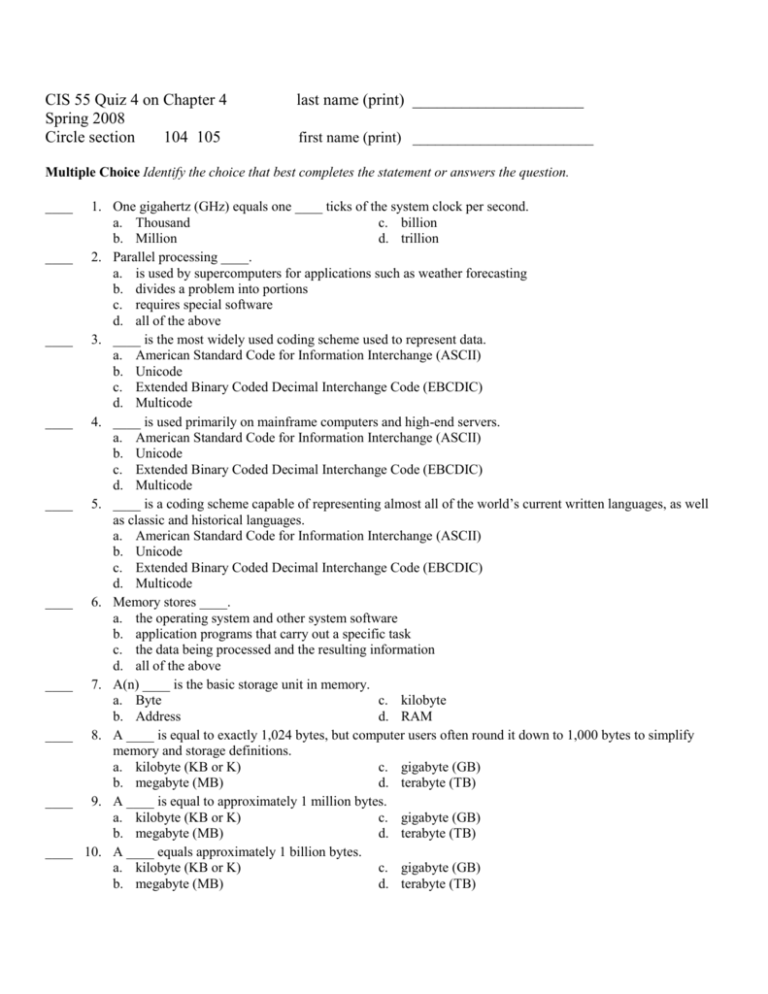
CIS 55 Quiz 4 on Chapter 4
Spring 2008
Circle section
104 105
last name (print) _____________________
first name (print) ________________________
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
____
____
____
____
____
____
____
____
____
____
1. One gigahertz (GHz) equals one ____ ticks of the system clock per second.
a. Thousand
c. billion
b. Million
d. trillion
2. Parallel processing ____.
a. is used by supercomputers for applications such as weather forecasting
b. divides a problem into portions
c. requires special software
d. all of the above
3. ____ is the most widely used coding scheme used to represent data.
a. American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII)
b. Unicode
c. Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBCDIC)
d. Multicode
4. ____ is used primarily on mainframe computers and high-end servers.
a. American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII)
b. Unicode
c. Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBCDIC)
d. Multicode
5. ____ is a coding scheme capable of representing almost all of the world’s current written languages, as well
as classic and historical languages.
a. American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII)
b. Unicode
c. Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBCDIC)
d. Multicode
6. Memory stores ____.
a. the operating system and other system software
b. application programs that carry out a specific task
c. the data being processed and the resulting information
d. all of the above
7. A(n) ____ is the basic storage unit in memory.
a. Byte
c. kilobyte
b. Address
d. RAM
8. A ____ is equal to exactly 1,024 bytes, but computer users often round it down to 1,000 bytes to simplify
memory and storage definitions.
a. kilobyte (KB or K)
c. gigabyte (GB)
b. megabyte (MB)
d. terabyte (TB)
9. A ____ is equal to approximately 1 million bytes.
a. kilobyte (KB or K)
c. gigabyte (GB)
b. megabyte (MB)
d. terabyte (TB)
10. A ____ equals approximately 1 billion bytes.
a. kilobyte (KB or K)
c. gigabyte (GB)
b. megabyte (MB)
d. terabyte (TB)
____ 11. ____ is the most common type of volatile memory.
a. ROM
c. CMOS
b. Flash memory
d. RAM
____ 12. A nanosecond (abbreviated ns) is one ____ of a second.
a. thousandth
c. billionth
b. millionth
d. trillionth
____ 13. A computer ____ is a small piece of semi-conducting material, usually silicon, on which integrated circuits
are etched.
a. plug
c. chip
b. port
d. roster
____ 14. Together, four operations (fetching, decoding, executing, and storing) comprise a(n) ____ cycle.
a. baseline
c. registration
b. machine
d. pipelined
____ 15. With ____, the processor begins fetching a second instruction before it completes the machine cycle for the
first instruction.
a. clocking
c. pipelining
b. multi-core processing
d. recatching
____ 16. A(n) ____ processor is a chip with two or more separate processors.
a. parallel
c. multi-core
b. compressed
d. binary
____ 17. When 8 bits are grouped together as a unit, they form a(n) ____.
a. key
c. index
b. cache
d. byte
____ 18. ____ refers to memory chips storing permanent data and instructions.
a. ROM
c. PRAM
b. RAM
d. MRAM
What will the following JavaScript program
j = 1;
k = 2;
while (j <= 10)
{
document.writeln(j);
k = k + 3;
j = j + k;
}
____ 19. First number printed.
____ 20. Second number printed