Lab 14 Problems with Key
advertisement

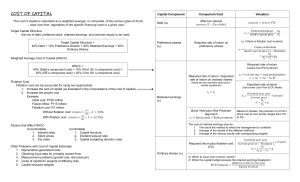
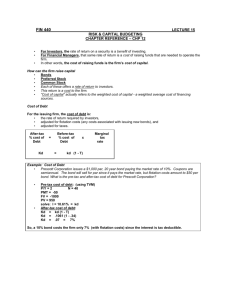
Chapter 13 problems (Ch. 12 in the 4th edition) 1. The cost of capital is used primarily in a. negotiations with banks because it reflects the company's overall borrowing power. b. setting the firm's basic risk level. c. capital budgeting because it reflects what the firm pays for the money it invests. d. negotiations with investment bankers because it establishes an overall return on which the market can base prices for the firm's securities. 2. A firm's cost of capital is the appropriate rate to use in the evaluation of a. its common stock. b. all capital budgeting proposals. c. average risk capital budgeting proposals. d. none of the above 27. To determine a firm's WACC, it is necessary to compensate for the effect of: a. transaction costs associated with doing business in financial markets b. the tax implications of debt c. none of the above d. both a and b 29. Flotation costs are administrative fees and expenses incurred in: a. the process of issuing and selling securities b. listing the company's stock on a stock exchange c. lawsuits alleging fraud in the issue of securities d. none of the above 37. Which of the following would increase the WACC? a. an increase in flotation costs b. a decrease in tax rates c. a decrease in preferred dividends d. Both a & b e. All of the above 42. The cost of retained earnings differs from the cost of new equity due to: a. flotation costs b. dividends c. capital gains yields d. Both a & c e. All of the above 55. Assume a firm’s bonds are currently yielding new investors 6%. The combined federal and state tax rate is 40%. What is the firm’s after-tax cost of debt is? a. 3.6% b. 4.0% c. 4.8% d. 6.0% 56. Assume the following information about a firm’s capital components. The firm’s WACC is? Capital Structure Cost Debt $20,000 8% Preferred stock $20,000 11% Common stock $60,000 14% a. 11.00% b. 11.90% c. 12.20% d. 12.05% 57. Determine the (after-tax) component cost of a $50 million debt issue that the Mattingly Corporation is planning to place with a large insurance company. Assume the company is subject to a 40% tax rate. This long-term debt issue will yield 12% to the insurance company. a. 4.8% b. 7.2% c. 12.0% d. none of the above 58. Calculate the cost of preferred stock for Ohio Valley Power Company, which is planning to sell $100 million of $3.25 cumulative preferred stock to the public at a price of $25 per share. Flotation costs are $1.00 per share. Ohio Valley has a marginal income tax rate of 40%. a. 13.0% b. 7.8% c. 8.12% d. 13.54% 71. Donoho Corp. issued 20-year, $1,000 par bonds eight years ago with a 10% coupon paying semiannually that are now selling for $1,152.47. Estimate the cost of retained earnings assuming investors generally demand a 5% risk premium on equity over the cost of debt. a. 8% b. 9% c. 11% d. 13% e. 15% 72. A firm's preferred stock is selling at $83 and pays a 9.5% annual dividend on a $100 par value. What is the cost of preferred if flotation costs are 12%? a. 10.64% b. 13.01% c. 10.79% d. 11.45% 1 d. none of the above 59. Allegheny Valley Power Company common stock has a beta of 0.80. If the current risk-free rate is 6.5% and the expected return on the stock market as a whole is 16%, determine the cost of retained earnings for the firm (using the CAPM). a. 14.1% b. 7.6% c. 6.5% d. none of the above 60. The following financial information is available on Rawls Manufacturing Company: Current per share market price $48.00 Most recent per share dividend $3.50 Expected long-term growth rate 5.0% Rawls can issue new common stock to net the company $44 per share. Determine the cost of retained earnings using the dividend growth model approach. (Compute answer to the nearest .1%). a. 12.3% b. 13.4% c. 13.0% d. 12.7% 65. Northeast Airlines has a current dividend of $1.80. Dividends are expected to grow at 7% into the foreseeable future. What is the firm’s cost of equity from new stock if its shares can be sold to net the company $46 after administrative expenses (flotation costs)? a. 10.9% b. 11.2% c. 7.2% 77. Use the dividend growth or Gordon model to develop the cost of equity from a new stock issue if last year’s dividend was $2.25, the anticipated constant growth rate is 5%, the stock’s selling price today is $36 per share, and flotation costs are estimated to be 11%? a. 12.4% b. 11.6% c. 10.9% d. 14.9% 85. Hatter Inc. has the following capital components and costs. Calculate Hatter’s WACC. Component Value Cost Debt 15,500 10% Preferred Stock 7,500 12% Common Equity 10,000 14% a. 11.67% b. 12.41% c. 13.73% d. 14.55% 101. Zylon Inc. plans net income of $10 million next year and typically pays 40% of its earnings in dividends. Its capital structure is one third equity and two thirds debt with no preferred stock. Zylon’s MCC curve will break at: a. $ 4,000,000 b. $ 6,000,000 c. $12,000,000 d. $18,000,000 Chapter 13 Equations: n 1. WACC wi sourcei ; (weights, w, and cost of source i) i 1 2. Cost of debt: Kd × (1 - tax rate) 3. Cost of preferred stock: 4. Cost of retained earnings from SML: Kx = KRF + bX (Km - KRF) 5. Cost of retained earnings from constant growth model: 6. Cost of new stock: K e K PF Dp (1 f )PP D 0 (1 g) g (1 f )P0 or = kp / (1 - f) Ke D 0 (1 g) g P0 2