Thermochemistry Review Worksheet1
advertisement

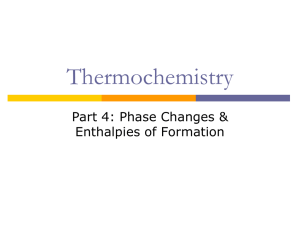
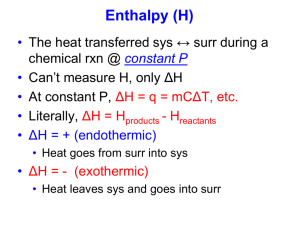
Thermochemistry Review Part 1 Definition Questions: you should be able to use or apply the following terms. Be able to write complete definitions for, energy potential energy kinetic energy enthalpy thermal 1. temperature heat specific heat capacity endothermic Hess’s Law standard state standard heat of formation exothermic Law of conservation of Energy isolated, closed, open system The specific heat capacity of diamond is 0.5050 J/gºC. How much energy is required to heat 25.0 g of diamond from 10.5ºC to 15.6ºC? 2. A piece of aluminum with a mass of 50g and an initial temperature of 90oC is placed into 100mL of water at a temperature of 25oC. The temperature of water rises to 31.30C. Determine the specific heat capacity of aluminum. 3. How much energy is absorbed by 300g of methanol, CH3OH, as it evaporates? Given: The molar heat of vaporization is 35.3kJ/mol. 4. What is the molar enthalpy of the formation of 1mol H2SO4(l) given the following information? H2O(g) + SO3(g) H2SO4(l) ΔHrxn = ___kJ 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(g) 2S(s) + 3O2(g) 2SO3(g) H2(g) + 2O2(g) + S(s) H2SO4(l) ΔHrxn = -484kJ ΔHrxn = -890kJ ΔHrxn = -814kJ a. 4. What is the molar enthalpy of the formation of 1mol C2H6 gas given the following information? C2H4(g) + H2(g) C2H6(g) ΔHrxn = xkJ C2H4(g) + 3O2(g) 2CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) 2C2H6(g) + 7O2(g) 4CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(l) ΔHrxn = -1401kJ ΔHrxn = -3100kJ ΔHrxn = -572kJ 5. The reaction for the fermentation of glucose is Fe3O4(s) + CO(g) → 3 FeO(s) + CO2(g) a. Using standard enthalpies of formation, determine ΔHrxn . b. Is this reaction endothermic or exothermic? Explain in terms of bonds breaking/forming. 6. Answer the following questions with regards to the Heating Curve. 1) What is happening to the average potential energy of the molecules in the sample during section 3? 2) As a substance goes through section (2), what happens to the distance between the particles? 3) What is the name of the process happening during section (2)? 4) What would be the name of the process happening during section (2) if time were going the other way? 5) What is the boiling point of this substance? 6) At what temperature would this sample finish freezing? 7) When this substance is melting, the temperature of the ice-water mixture remains constant because: Heat is not being absorbed The ice is colder that the water Heat energy is being converted to potential energy Heat energy is being converted to kinetic energy a. b. c. d.