Thermochemistry Review Worksheet - High School Chemistry
advertisement

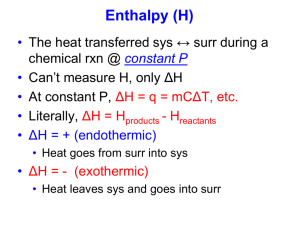
Name: Per: Date: _________________Row Thermochemistry Review Worksheet 1.Definitions: -Endothermic: -Exothermic: -Enthalpy: -Law of Conservation of Energy -Heat of Reaction: -Heat of Fusion -Specific Heat 2. Explain why water is used in a calorimeter? What unique properties does water have? Calculations: 1. How many Joules of heat energy would be required to raise the temperature of 16.0g of lead from 25˚C to its melting point of 327˚C for a length of time long enough to completely melt the lead. Given: The specific heat capacity of lead is 0.159J/gK and the molar enthalpy of fusion is 24.7J/g. Specific heat is in Kelvin. Must convert C to Kelvin. Q=mcΔT Q=1460J 2. How much energy is absorbed by 300g of methanol, CH3OH, as it evaporates? Given: The molar heat of vaporization is 35.3kJ/mol. 300 * (1/45.02) * (35.3/1) = 200 J (1 sigfig) 3. If 540g of water condenses on a car during a cool night, calculate the amount of energy released to the air during this condensation. Given: The molar heat of vaporization of water is 40.79kJ/mol. 540 * (1/18.02) * (40.79/1) = 1200kj 2 sig figs 4. Calculate the amount of energy that is needed to change 125g of ice at -25˚C to water at 75˚C. Be sure to sketch a Phase Diagram of this process before beginning the work. Given: Molar enthalpy of fusion is 6.009kJ/mol, molar enthalpy of vaporization is 40.79kJ/mol, the specific heat of solid H2O is 2.1J/gK, the specific heat of liquid H2O is 4.186J/gK, and the specific heat of gas H2O is 1.7J/gK. 125 * 2.1 * 100 = 26000kj 5. What is the molar enthalpy of the formation of 1mol H2SO4(l) given the following information? 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(g) ΔHrxn = -484kJ 2S(s) + 3O2(g) 2SO3(g) ΔHrxn = -890kJ H2(g) + 2O2(g) + S(s) H2SO4(l) ΔHrxn = -814kJ H2O(g) + SO3(g) H2SO4(l) ΔHrxn = xkJ 115KJ 6. What is the molar enthalpy of the formation of 1mol C2H6 gas given the following information? C2H4(g) + 3O2(g) 2CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) ΔHrxn = -1401kJ 2C2H6(g) + 7O2(g) 4CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) ΔHrxn = -3100kJ 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(l) ΔHrxn = -572kJ C2H4(g) + H2(g) C2H6(g) ΔHrxn = xkJ -137KJ 7. The reaction for the fermentation of glucose is … C6H12O6 (aq) 2CO2(g) + 2C2H5OH(aq) ΔHrxn = -67kJ a. Is this reaction endothermic or exothermic? b. Calculate the energy released when 250g of glucose C6H12O6 (aq) ferments. 250 * (1/180.07) * (-67/1) = -93KJ