Document
advertisement

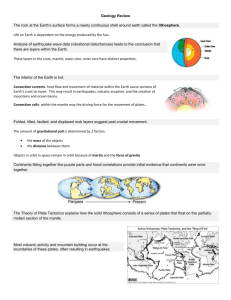
Name: ___________________________ VOCABULARY REVIEW (HINT – they are in order from the start of the 2nd semester) 1. __________ A push or a pull. Every motion starts with this. 2. __________ A force that is equal in size and opposite in direction. 3. __________ A force that change the motion of an object. They occur when one force is greater than the others. 4. __________ When two objects rub against each other. It makes an object slow down or stops moving. 5. __________ The friction between an object and air. 6. __________ The law of motion that states that an object in motion stays in motion and an object at rest stays at rest until acted on by and outside force. 7. __________ The law of motion that states that both the size of the force and the mass of the object itself affect the object’s acceleration. 8. __________ The law of motion that states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. 9. __________ The SI unit of force (N) 10. _________ The tendency of an object to keep its same motion. 11. __________ is how fast an object is moving. The formula is distance divided by time. 12. __________ is the speed and the direction of an object 13. __________ is how fast an object changes its velocity. This occurs when a moving object speeds up, slows down, or changes direction. 14. __________ is a property of motion. It depends on the mass and velocity of an object. 15. __________ is the SI unit of measurement for energy and work. 16. __________ is a machine with few or no moving parts that makes it easier to do work. 17. __________ is a machine made of two or more simple machines working together. 18. __________ is a simple machine made of a bar that rotates, or turns around a fixed point call the fulcrum. It is used to lift weight. 19. __________ is force applied to a simple machine. 20. __________ is force exerted by something you are trying to move. 21. __________is a point around which a lever pivots or rotates. 22. __________ is a simple machine made of a wheel with a groove around the outside. It needs a rope, cable or belt to make it do work by changing the direction of a force. 23. __________ is a simple machine made of a wheel fixed to a rod, or axle; both rotate together. The wheel turns on a post to help move things quickly and easily. 24. __________ is a simple machine made from a slanted/sloped surface that is higher on one end, used to make lifting easier. 25. __________ is a simple machine made from two inclined planes together used to raise an object, split an object, or hold an object in place. 26. __________ is a simple machine made from an inclined plane wrapped around a pole or shaft that is used to hold materials together or drill holes. 27. __________ the time it takes to spin on its axis (1day). 28. __________ the time it takes to orbit the sun once. 29. __________ the elliptical path an object takes in space while revolving around another object. 30. __________ a natural satellite of a planet. 31. __________ The force that governs the motion of our solar system. 32. __________ large bodies that orbit a star. 33. __________ A mixture of ices, rock, and dust loosely with an elliptical orbit around the sun. Radiation from the sun causes a tail to form, that points away from the sun. 34. __________The largest of the Jupiter’s moons. They are Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. 35. __________ Rocky fragments of comets, planets, moons, or asteroids without an orbit. 36. __________ Meteoroids that have entered an atmosphere. 37. __________ Any part of a meteoroid that survives passage through the atmosphere and lands on the surface of a planet or a moon. 38. __________ left over rocks or metals from the formation of the solar system that are smaller than a planet but larger than a meteor. 39. __________ the thin, outermost layer of the Earth. This layer consists of ocean plates and continental plates. 40. __________ Made of dense basaltic rock. These plates carry the continental plates across the surface of the Earth. 41. __________ Made of light granite rock. This crust rides on the oceanic crust. 42. __________ the crust and the upper rigid layer of the mantle move together and form the plates of the Earth. 43. __________ the largest layer of the Earth located directly under the crust. This layer is composed of very hot, dense, flowing rock. 44. __________ the middle layer of the mantle. This is the layer that flows and moves the plates of the Earth. 45. __________ the layer located directly under the mantle. This layer is composed of liquid nickel and iron. 46. __________ The center of the earth that is composed of nickel and iron under such great temperatures and pressures that the metals are in a solid state of motion. 47. __________ the thin, fragile, and rigid lithosphere is broken up into 12 main pieces. These pieces move very slowly at about 1 inch to 4 inches per year. 48. __________ the circular current caused by the difference in temperatures from the bottom to the top of the mantle. 49. __________ A theory that states that the Earth's surface is broken into pieces that move and have moved for millions of years. 50. __________ super continent 250 million years ago. The seven continents were all connected together into one huge land mass. 51. __________ A boundary in which two plates collide causing mountain building or a subduction zone. 52. __________ A boundary in which two plates are separating and moving in opposite directions. 53. __________ A boundary in which two plates scrape and slide past each other. 54. __________ is formed at a convergent plate boundary. One plate is lighter and thicker than the other causing the thinner denser plate to be driven down into the mantle. 55. __________ The molten rock under the Earth’s surface. It is full of gas and under extreme pressures. 56. __________ A fault in which the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall. 57. __________ is a fault in which the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall. 58. __________ is a fault in which the two fault blocks move past each other horizontally. 59. __________ The type of rock that forms when hot, liquid, or magma cool and hardens. 60. __________ is the type of rock that forms when particles of rock, or sediment, collect and harden into the new rock. 61. __________ is a type of rock that forms when existing rocks are heated or squeezed. 62. __________ The process by which water, ice, heat, and wind act to break down rocks. 63. __________ is the process by which particles of rock are removed from their source the removal and transport of rock and soil by the flow of water and by the actions of gravity, wind, and ice. 64. __________ is the process in which water, ice wind and gravity drop newly formed sediments. 65. __________ The basic unit of structure and function in living things. 66. __________ A cell structure that contains the genetic information the cells need. 67. __________ The hereditary material that controls all the activities of a cell, contains the information to make new cells, and provides instructions for making proteins. 68. __________ A segment of DNA that carries hereditary instructions and is passed from parent to offspring. 69. __________ Cells with a nucleus. eu = true karyote = nucleus 70. __________ An organism whose cells do not contain a nucleus. pro = before karyote = nucleus 71. __________ Many celled organisms. Examples: plant, animal, fungi 72. __________ One celled organisms. 73. __________ An organism that can make its own food. (producers) 74. __________ Organisms that must eat in order to survive. (consumers) 75. __________ A field of biology that study how living things are classified. 76. __________ A further broken-down level of classification found within each kingdom according to similarities. They include Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus and Species. 77. __________one celled organisms that live in extreme environments. 78. __________ consists of most bacteria. They are single-celled organisms. 79. __________ consists of simple eukaryotes, multi-cellular organisms. 80. __________ consists of yeast and fungus members. These break down organic materials to obtain food. 81. __________ houses all plant members. (ex. flowers, corn, moss, ferns and trees) 82. __________ consists of humans and all animals. (ex. insects, mammals, reptiles, birds and amphibians) 83. __________ living components in the environment. 84. __________ non-living components in the environment. 85. __________ All members of a species living together in the same area at the same time. 86. __________ All of the populations of different species that live in the same area. 87. __________ A community of organisms and their nonliving environment. 88. __________ Any living thing that can carry out all of the basic life activities. 89. __________ The broadest group in the modern classification system. MOTION REVIEW 1. Write Newton’s 1st Law of Motion 2. The 1st law of motion is also called the law of ______________. 3. Newton’s 2nd law shows how 3 things are linked together. What are those 3 things? • • • 4. Force is measured in a unit called ____________. 5. What is the formula for the 2nd law? 6. Write Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion 7. What 2 things do you have to know before you can find the speed of something? • • 8. What is the formula for finding speed? Calculate the speed for questions 9 - 12 below. 9. A football field is about 100m long. If it takes a person 20 seconds to run its length, how fast were they running? 10. If you drive at 100 km/hr for 6 hours, how far will you go? 11. If you run at 12m/min for 15 minutes, how far will you go? 12. The fastest train in the world moves at 500 km/hr. How far will it go in 3 hours? 13. What is the formula for work? 14. The unit of force is measured in ____________________. 15. The unit of distance is measured in ____________________. 16. The unit of work is measured in ____________________ 17. List the 6 types of simple machines AND list the reason why you would use that type of simple machine. • Use: • Use: • Use: • Use: • Use: • Use: 18. What is the advantage of using each of the below pulleys? Fixed Pulley - Moveable Pulley - Compound Pulley – SPACE SECTION REVIEW 19. What is the center of our solar system? 20. What 2 gasses is the sun made of? • • 21. Name the planets in order starting with the planet closest to the sun and working out. • • • • • • • • • 22. The Sun is the center of our solar system, and creates a large amount of gravitational force. If this system lost the Sun, what would happen to the planets? 23. A probe is a vehicle designed to carry instruments, but not crew. List some places we could most likely send a probe. 24. The space shuttle differed from previous space vehicles because it …… 25. What are the orbit paths of most of the planets in our solar system? EARTH SYSTEMS, ROCKS and TECTONICS SECTION REVIEW 1. The planet we call Earth has how many layers? 2. Write them in order from the center to the outside of the planet. • • • • 3. Name the 2 different crusts found on our Earth. • • 4. The crust and the upper layer of the mantle together make up a zone of rigid, brittle rocks called? 5. Name the layer of the Earth that flows and moves the plates of the Earth. 6. 7. What are the 3 general classes of rocks? • • • What does “igneous” mean? 8. What is the difference between lava and magma? 9. What are the 4 ways Sedimentary Rock can be formed? • • • • 10. ___________________ are formed when an existing rock is partially melted, squeezed, or both. 12. What is weathering? 13. What is erosion? 14. What is deposition? 15. Explain how weathering, erosion and deposition processes are tied together. CELLS, LIVING THINGS AND ECOSYSTEMS SECTION REVIEW Label the 3 types of cells. A. _____________________ B. ________________________ C. _________________________ 1. What is found in the nucleus of a plant and animal cell? 2. What are the 6 Kingdoms of Life? • • • • • • 3. There are 7 levels in the classification system of organisms. Start with the broadest level first: • • • • • • • 4. ____________________ kingdom consists of most bacteria. 5. ____________________ kingdom consists of simple eukaryotes, multicellular organisms. (mold) 6. ____________________ kingdom consists of fungus & yeasts members. These break down organic materials to obtain food. 7. ____________________ kingdom consists of all plants. 8. ____________________ kingdom consists of Humans and ALL animals. 9. What is the difference between biotic and abiotic? 10. ____________________ is the kingdom that consist of bacteria found in extreme environments. 11. Which is Abiotic and Biotic? a. _______________ b. ________________ c. ________________ d. _______________ e. _____________________ f. _______________