Geology Review The rock at the Earth`s surface forms a nearly
advertisement
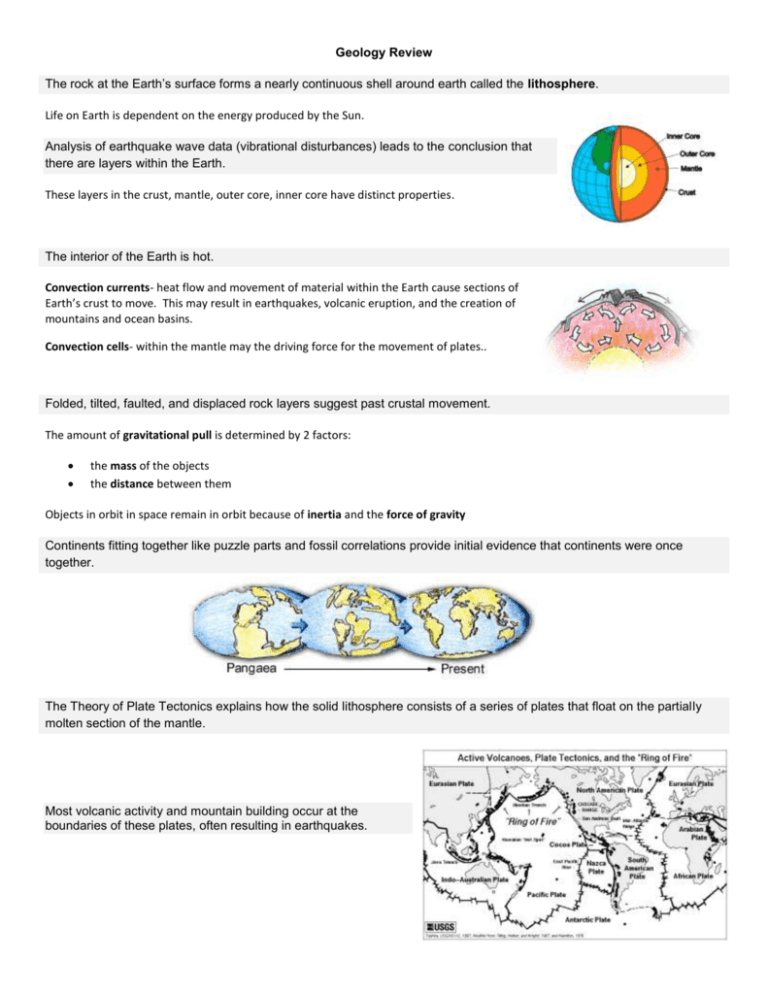
Geology Review The rock at the Earth’s surface forms a nearly continuous shell around earth called the lithosphere. Life on Earth is dependent on the energy produced by the Sun. Analysis of earthquake wave data (vibrational disturbances) leads to the conclusion that there are layers within the Earth. These layers in the crust, mantle, outer core, inner core have distinct properties. The interior of the Earth is hot. Convection currents- heat flow and movement of material within the Earth cause sections of Earth’s crust to move. This may result in earthquakes, volcanic eruption, and the creation of mountains and ocean basins. Convection cells- within the mantle may the driving force for the movement of plates.. Folded, tilted, faulted, and displaced rock layers suggest past crustal movement. The amount of gravitational pull is determined by 2 factors: the mass of the objects the distance between them Objects in orbit in space remain in orbit because of inertia and the force of gravity Continents fitting together like puzzle parts and fossil correlations provide initial evidence that continents were once together. The Theory of Plate Tectonics explains how the solid lithosphere consists of a series of plates that float on the partially molten section of the mantle. Most volcanic activity and mountain building occur at the boundaries of these plates, often resulting in earthquakes. Plates may collide, move apart, or slide past one another. continental plates-beneath continents, more dense. oceanic plates- beneath the oceans, less dense. Rocks are composed of minerals. Minerals are naturally occurring, inorganic, solids with a crystal structure and definite chemical composition. Rock forming minerals - only a few rock-forming minerals make of most of the rocks of Earth Identification of minerals – Minerals are identified based on physical properties such as streak, hardness, and reaction to acid The rock cycle model shows how types of rock or rock material may be transformed from one type of rock to another. Rocks are classified according to their method of formation. Igneous rock forms when molten rock solidifies. Intrusive-forms inside the Earth, coarse texture Extrusive- forms outside the Earth, fine texture Sedimentary forms when sediments are carried, deposited, and pressed together. May contain fossils! Metamorphic forms when rocks are changed as a result of heat and/or pressure. Fossils can be used to study past climates and environments. The dynamic processes that wear away at Earth’s surface include weathering and erosion. Weathering is the process of breaking rocks into sediments. Erosion is the transportation of sediment. Gravity is the driving force behind erosion. Gravity can act directly or through agents such as moving water, wind, and glaciers.