Chapter 11 - Flexible Budgeting and Analysis of Overhead Costs
EXERCISE 11-23 (15 MINUTES)
Variable-overhead spending variance
= actual variable overhead – (AQ SVR)
= $520,000 – (20,000 direct-labor hrs $20.00)
= $120,000 U
Variable-overhead efficiency variance = SVR (AQ – SQ)
= $20.00 (20,000 – 25,000*)
= $100,000 F
*SQ = 10,000 units 2.5 direct-labor hours per unit
Fixed-overhead budget variance
= actual fixed overhead – budgeted fixed overhead
= $1,050,000 – $937,500*
= $112,500 U
*Budgeted fixed overhead = 37,500 direct-labor hours $25 per hour
Fixed-overhead volume variance = budgeted fixed overhead – applied fixed overhead
= $937,500 – $625,000*
= $312,500 U†
*Applied fixed overhead = $25 per hour 2.5 direct-labor hours per unit 10,000 units
†Some
accountants would designate a positive volume variance as “unfavorable.”
EXERCISE 11-24 (10 MINUTES)
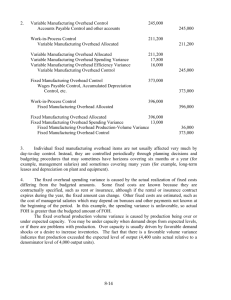
1.
Product
Field ..................................................
Professional .....................................
Total .................................................
Std Direct
Labor Hrs/Unit
4
6
Number
of Units
300
400
Total Std Direct
Labor Hours
1,200
2,400
3,600
The total standard allowed direct-labor hours in May is 3,600 hours.
2.
Basing the flexible budget on the number of binoculars produced would not be
meaningful. Production of 700 binoculars could mean 100 field models and 600
professional models, or 200 field models and 500 professional models, and so forth.
Depending on the composition of the 700 units, in terms of production type, different
amounts of direct labor would be expected. More to the point, different amounts of
variable-overhead costs would be expected.
11-1
Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education.
Chapter 11 - Flexible Budgeting and Analysis of Overhead Costs
EXERCISE 11-25 (20 MINUTES)
1.
Variable-overhead spending variance
= actual variable overhead – (AQ SVR)
= $120,000 – (5,000 $20.00)
2.
= $20,000 U
Variable-overhead efficiency variance = SVR(AQ – SQ)
= $20.00(5,000 – 4,000*)
3.
= $20,000 U
*SQ = 4,000 direct-labor hrs. = 2,000 units 2 direct-labor hrs. per unit
Fixed-overhead budget variance = actual fixed overhead – budgeted fixed overhead
= $28,500 – $30,000
4.
Fixed-overhead volume variance
= $1,500 F
= budgeted fixed overhead – applied fixed overhead
= $30,000 – $24,000†
†Applied
fixed overhead
=
=
= $6,000 U**
predetermined fixed standard allowed
overheadrate direct labor hours
$30,000
(2,000 2)
2,500 2
= $24,000
** Some accountants would designate a positive volume variance as "unfavorable."
EXERCISE 11-31 (45 MINUTES)
Budgeted fixed overhead .........................................................................................
$ 25,000
Actual fixed overhead ..............................................................................................
$ 32,500a
Budgeted production in units ..................................................................................
12,500
Actual production in units ......................................................................................
12,000c
Standard machine hours per unit of output ...........................................................
4 hours
Standard variable-overhead rate per machine hour ..............................................
$8.00
Actual variable-overhead rate per machine hour ...................................................
$9.00b
Actual machine hours per unit of output ................................................................
3d
Variable-overhead spending variance ....................................................................
$ 36,000 U
Variable-overhead efficiency variance ....................................................................
$ 96,000 F
Fixed-overhead budget variance .............................................................................
$ 7,500 U
Fixed-overhead volume variance ............................................................................
$ 1,000g U*
Total actual overhead ...............................................................................................
$356,500
Total budgeted overhead (flexible budget) .............................................................
$409,000e
Total budgeted overhead (static budget) ................................................................
$425,000f
Total applied overhead .............................................................................................
$408,000
11-2
Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education.
Chapter 11 - Flexible Budgeting and Analysis of Overhead Costs
*Some accountants would designate a positive fixed-overhead volume variance as
unfavorable.
Explanatory Notes:
a.
Fixed-overhead budget variance = actual fixed overhead – budgeted fixed overhead
$7,500 U = X – $25,000
X = $32,500 = actual fixed overhead
b.
Total actual overhead = actual variable overhead + actual fixed overhead
$356,500 = X + $32,500
X = $324,000 = actual variable overhead
Variable-overhead spending variance
= actual variable overhead – (AQ SVR)
$36,000 U = $324,000 – (AQ $8)
$8AQ = $288,000
AQ = 36,000
Actual variable-overhead
rate per machine hour
=
actual variable overhead
actual machine hours
$324,000
$9 per machine hour
36,000
budgeted fixed overhead
budgetedmachine hours
=
c.
Fixed-overhead rate
=
=
$25,000
(12,500 units)(4 hrs. per unit)
= $.50 per machine hr.
Total standard
overhead rate = standard variable overhead rate + fixed-overhead rate
$8.50 = $8.00 + $.50
Total applied
overhead
= total std machine hours total std overhead rate
$408,000 = X $8.50
X = 48,000 = total standard machine hrs.
Actual production =
=
total standardmachine hrs.
standardmachine hrs. per unit
48,000
12,000 units
4
11-3
Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education.
Chapter 11 - Flexible Budgeting and Analysis of Overhead Costs
d.
Actual machine hrs. per
unit of output
=
total actual machine hrs.
actual production
36,000 machine hrs.
3 machine hrs. per unit
12,000 units
Total budgeted overhead (flexible budget)
=
e.
= budgeted fixed overhead + (SVR SQ)
= $25,000 + ($8.00 12,000 units 4 machine hrs. per unit)
= $409,000
f.
Total budgeted overhead (static budget)
=
total standard budgeted standardmachine hrs.
per unit
overheadrate production
= ($8.50)(12,500)(4)
= $425,000
g.
Fixed overhead volume variance
= budgeted fixed overhead – applied fixed overhead
= $25,000 – ($.50)(12,000 4)
= $1,000 U*
* Some accountants would designate a positive volume variance as "unfavorable."
EXERCISE 11-32 (15 MINUTES)
1.
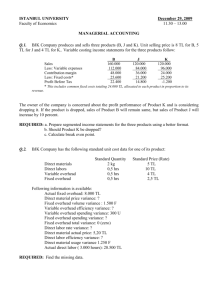
Formula flexible budget:
Total budgeted monthly electricity cost = (€25 euros* number of patient days)
+ €40,000 euros
*€25 per patient day = 50 kwh per patient day €.50 per kwh
2.
Columnar flexible budget:
10,000
€ 250,000
40,000
€ 290,000
Variable electricity cost ............
Fixed electricity cost.................
Total electricity cost .................
Patient Days
20,000
€ 500,000
40,000
€ 540,000
11-4
Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education.
30,000
€ 750,000
40,000
€ 790,000
Chapter 11 - Flexible Budgeting and Analysis of Overhead Costs
PROBLEM 11-38 (20 MINUTES)
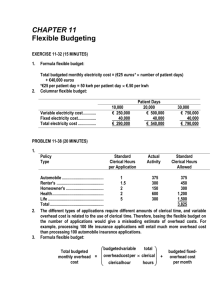
1.
Policy
Type
Standard
Clerical Hours
per Application
Actual
Activity
1
1.5
2
2
5
375
300
150
600
300
Automobile .......................................
Renter's ............................................
Homeowner's ...................................
Health ................................................
Life ....................................................
Total ..................................................
Standard
Clerical Hours
Allowed
375
450
300
1,200
1,500
3,825
2.
The different types of applications require different amounts of clerical time, and variable
overhead cost is related to the use of clerical time. Therefore, basing the flexible budget on
the number of applications would give a misleading estimate of overhead costs. For
example, processing 100 life insurance applications will entail much more overhead cost
than processing 100 automobile insurance applications.
3.
Formula flexible budget:
total
budgeted variable
Total budgeted
overhead
cost
per
clerical
+
monthly overhead =
cost
hours
clerical hour
Total budgeted monthly overhead cost = ($5.00 X) + $3,000
where X denotes total clerical time in hours.
4.
Budgeted overhead cost for May
= ($5.00 3,825) + $3,000
= $22,125
PROBLEM 11-39 (25 MINUTES)
1.
Let X = budgeted fixed overhead
X ÷ 2,000 machine hours = $20.00 per hour
X = $40,000
2.
Variable-overhead spending variance:
Actual machine hours x actual rate
2,200 hours x $11.50*…………………... $ 25,300
11-5
Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education.
budgeted fixedoverhead cost
per month
Chapter 11 - Flexible Budgeting and Analysis of Overhead Costs
Actual machine hours x standard rate
2,200 hours x $12.00…………………….
26,400
Variable-overhead spending variance…... $ 1,100 Favorable
* $25,300 ÷ 2,200 hours
3.
Fixed-overhead volume variance:
Budgeted fixed overhead………………………………
Standard machine hours allowed x standard rate
750 hours* x $20.00………………………………
Fixed-overhead volume variance……………………
$ 40,000
15,000
$ 25,000 U†
* 1,500 units x .5 machine hours per unit
†The
fixed-overhead volume variance is positive;
some managerial accountants would interpret it as
an unfavorable variance.
4.
Lackawanna Licorice Company spent more than anticipated. Actual fixed
overhead amounted to $50,500 ($75,800 - $25,300) when the budget was
set at $40,000. The fixed-overhead budget variance is $10,500 unfavorable
($50,500 - $40,000).
5.
Variable overhead is underapplied by $16,300:
Actual overhead: Actual machine hours x actual rate
2,200 hours x $11.50………………………………………….. $ 25,300
Applied overhead: Standard machine hours allowed x
standard rate
750 hours x $12.00…………………………………………….
9,000
Underapplied variable overhead………………………………... $ 16,300
6.
Without having complete information, it is difficult to be 100% certain.
However, by an analysis of data related to the volume variance, a lengthy
strike appears to be a strong possibility. Lackawanna had planned to
work 2,000 machine hours during the period, giving the company the
capability of producing 4,000 finished units (2,000 hours x 2 units per
hour). Actual production amounted to only 1,500 units, leaving the firm far
shy of its production goal. A strike is a plausible explanation.
11-6
Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education.