Biochemistry Packet
advertisement
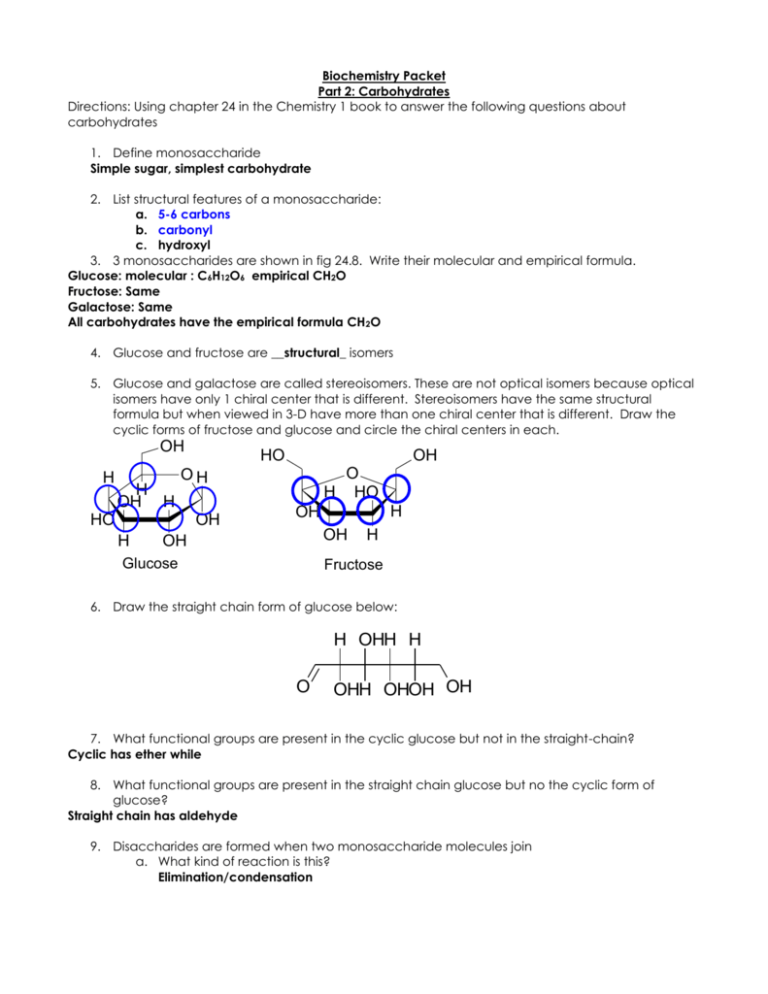
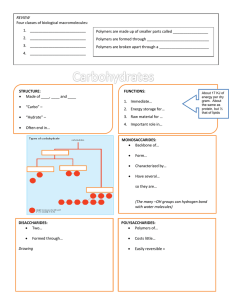
Biochemistry Packet Part 2: Carbohydrates Directions: Using chapter 24 in the Chemistry 1 book to answer the following questions about carbohydrates 1. Define monosaccharide Simple sugar, simplest carbohydrate 2. List structural features of a monosaccharide: a. 5-6 carbons b. carbonyl c. hydroxyl 3. 3 monosaccharides are shown in fig 24.8. Write their molecular and empirical formula. Glucose: molecular : C6H12O6 empirical CH2O Fructose: Same Galactose: Same All carbohydrates have the empirical formula CH2O 4. Glucose and fructose are __structural_ isomers 5. Glucose and galactose are called stereoisomers. These are not optical isomers because optical isomers have only 1 chiral center that is different. Stereoisomers have the same structural formula but when viewed in 3-D have more than one chiral center that is different. Draw the cyclic forms of fructose and glucose and circle the chiral centers in each. OH H H OH H HO O H HO OH HO OH H OH H OH OH OH Glucose H Fructose 6. Draw the straight chain form of glucose below: H OHH H O OHH OHOH OH 7. What functional groups are present in the cyclic glucose but not in the straight-chain? Cyclic has ether while 8. What functional groups are present in the straight chain glucose but no the cyclic form of glucose? Straight chain has aldehyde 9. Disaccharides are formed when two monosaccharide molecules join a. What kind of reaction is this? Elimination/condensation b. What kind of functional group is formed? ether 10. Important carbohydrates: Di/polysaccharide Sucrose Made from: Glucose and fructose lactose Glucose and Galactose Starch Glucose only 11. What is the primary role of carbohydrates in humans? As an energy source – stored in liver as glycogen