diebetes2 - Forest Hills High School
advertisement

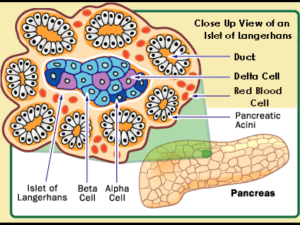
Diabetes is a disease that is characterized by abnormally high glucose levels in the blood Diabetes (Diabetes Mellitus) is a metabolism disorder. Many things that we eat is broken down into Glucose. Glocose is a sugar that can be found in the blood stream, it is the "fuel" for humans. Insulin is very importanat to the body. Insulin is responsible for letting the glucose into the cells. When you finish eating, the pancreas excretes a certain amount of insulin to allow the glocose into the cell which eventually lowers the blood suger level. A person who has diabetes has too much glucose in their blood (hyperglycemia), because either insulin is not produced, too little is produced, or the insulin is rejected by the cells. The extra blood glucose passes out of the body through urine. Even if you have a lot of glucose the cells are not recieving it. There are three different types of Diabetes: Diabetes Type 1 is where the body produces no insulin at all. Diabetes Type 2 is where the body doesn't produce enough insulin, or your insulin is not working properly. Gestational Diabetes is something that some women develop during their pregnancy. *Diabetes Type 1 and 2 are chronic where as Gestational Diabetes usually goes away after the child is born. -Always tired -Wounds that wont heal -Frequent Urination -Always Hungry -Sudden Weight loss -Blurry Vision - Urinalysis -Blood Glucose Test -Insulin shots are mostly used -Some dieting and excersize -Usually tablets, excersize and a special diet -Sometimes Insulin shots -Small amounts of Sugar -Small amount of Salt (Salt can cause High Blood Pressure) -Foods Rich in Fiber -Less fat (Fat can cause Heart Disease) High Risks of: -Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) -Ketoacidosis (Chemical balance of body is too acidic) -Nonketotic Hyperosmolar Coma (Type two only- High blood sugar, very dehydrated, results in loss of consciousness) Long Term: -Cardiovascular Disease -Retinal Damage -Chronic Kidney Failure Cleveland Clinic Foundation. (2009). Diabetes and the Foods You Eat. Date Retrieved September 30, 2009 from, http://my.clevelandclinic.org/disorders/Diabetes_Mellitus/hic_Di abetes_and_the_Foods_You_Eat.aspx MediLexicon International Ltd. (2009). All About Diabetes. Date Retrieved September 30, 2009 from, http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/info/diabetes/whatisdiabetes. php Introduction: http://img.webmd.com/dtmcms/live/webmd/consumer_assets/site _images/articles/health_tools/diabetes_type2_slideshow/istock_photo_of_diabetic_treatments.jpg Types of Diabetes: http://www.topnews.in/health/files/type1diabetes.jpg Chart of Effects: http://www.nurseminerva.co.uk/diabet1.gif Age Chart (Bar Graph): http://seniorjournal.com/images/Symbols/Health/Diabetes-graphage-diagnosed.JPG