File - Mr. Schmitt - Biology 12
advertisement
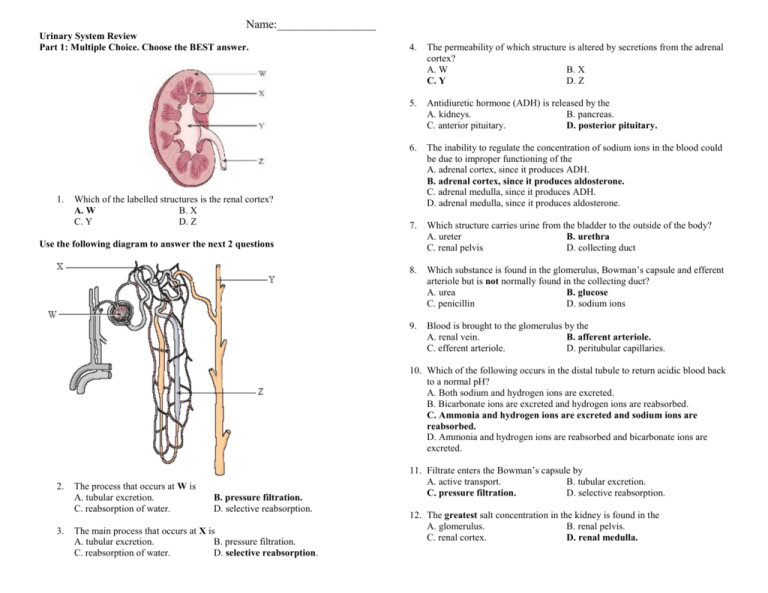
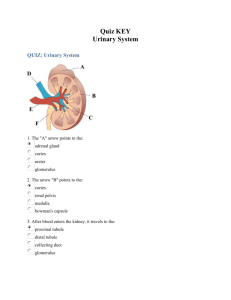
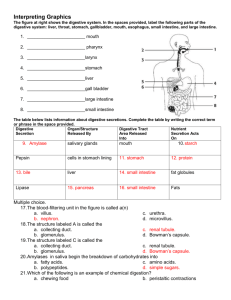
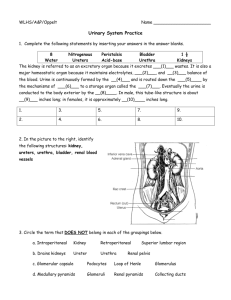
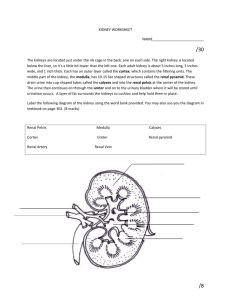
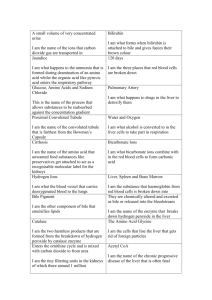
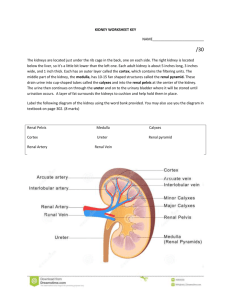
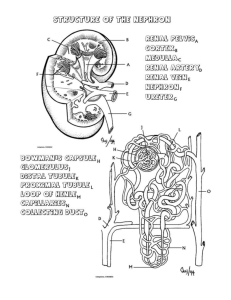
Name:_________________ Urinary System Review Part 1: Multiple Choice. Choose the BEST answer. 1. Which of the labelled structures is the renal cortex? A. W B. X C. Y D. Z 4. The permeability of which structure is altered by secretions from the adrenal cortex? A. W B. X C. Y D. Z 5. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is released by the A. kidneys. B. pancreas. C. anterior pituitary. D. posterior pituitary. 6. The inability to regulate the concentration of sodium ions in the blood could be due to improper functioning of the A. adrenal cortex, since it produces ADH. B. adrenal cortex, since it produces aldosterone. C. adrenal medulla, since it produces ADH. D. adrenal medulla, since it produces aldosterone. 7. Which structure carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body? A. ureter B. urethra C. renal pelvis D. collecting duct 8. Which substance is found in the glomerulus, Bowman’s capsule and efferent arteriole but is not normally found in the collecting duct? A. urea B. glucose C. penicillin D. sodium ions 9. Blood is brought to the glomerulus by the A. renal vein. B. afferent arteriole. C. efferent arteriole. D. peritubular capillaries. Use the following diagram to answer the next 2 questions 10. Which of the following occurs in the distal tubule to return acidic blood back to a normal pH? A. Both sodium and hydrogen ions are excreted. B. Bicarbonate ions are excreted and hydrogen ions are reabsorbed. C. Ammonia and hydrogen ions are excreted and sodium ions are reabsorbed. D. Ammonia and hydrogen ions are reabsorbed and bicarbonate ions are excreted. 2. 3. The process that occurs at W is A. tubular excretion. C. reabsorption of water. B. pressure filtration. D. selective reabsorption. The main process that occurs at X is A. tubular excretion. B. pressure filtration. C. reabsorption of water. D. selective reabsorption. 11. Filtrate enters the Bowman’s capsule by A. active transport. B. tubular excretion. C. pressure filtration. D. selective reabsorption. 12. The greatest salt concentration in the kidney is found in the A. glomerulus. B. renal pelvis. C. renal cortex. D. renal medulla. 17. The structure labelled Y is the A. glomerulus. C. Bowman’s capsule. 13. 10. Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce urea B. to excrete metabolic wastes C. to regulate the acidity of the blood D. to maintain a constant blood volume B. loop of Henle. D. proximal convoluted tubule. 18. Which of the following is the correct sequence of structures from highest to lowest concentration of urea? A. 2, 1, 3 B. 2, 3, 1 C. 3, 1, 2 D. 3, 2, 1 14. Consuming alcohol inhibits the release of a hormone, resulting in the production of dilute urine. This occurs because the alcohol is affecting the A. thyroid gland. B. adrenal cortex. C. adrenal medulla. D. posterior pituitary. 15. Which of the following would cause increased water reabsorption by the kidneys? A. increased blood volume B. increased cardiac output C. decreased blood pressure D. decreased ADH secretion 19. Which of the following statements comparing blood in X to blood in Y is true? A. The concentration of urea is higher in X. B. The concentration of oxygen is lower in X. C. The concentration of glucose is higher in Y. D. The concentration of carbon dioxide is lower in Y. 20. After the drug penicillin is administered for an infection in the urinary bladder, what pathway would penicillin take out of the body? renal arte 16. Which process occurs at X? A. tubular excretion C. selective reabsorption urethra B. pressure filtration D. antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secretion convoluted tubule 21. When proteins are broken down, urea is produced and enters the blood plasma. Which of the following processes would account for the presence of urea in the nephron? A. pressure filtration at the glomerulus B. tubular excretion in the distal tubule C. active transport in the collecting duct D. facilitated transport in the proximal tubule 22. Which of the following structures would have cells with the greatest concentration of mitochondria in their cytoplasm? A. glomerulus B. collecting duct C. Bowman’s capsule D. proximal convoluted tubule 23. Low levels of sodium ions (Na+) in the body result in the secretion of A. adrenalin. B. aldosterone. C. insulin. D. thyroxin. 25. Which of the following structures has receptor sites for ADH and aids in the reabsorption of water? A. W B. X C. Y D. Z 24. 27. Where in the kidney could the conditions indicated in the table above be found? A. distal tubule B. proximal tubule C. afferent arteriole D. Bowman’s capsule 26. Active transport of glucose into the blood occurs in the A. glomerulus. B. collecting duct. C. Bowman’s capsule. D. proximal convoluted tubule. 27. What is the correct order of the processes which would modify blood plasma as it passes through the nephron? excretion 28. Homeostasis is maintained on day 2 by a hormone that is produced in the A. hypothalamus and acts on the collecting duct. B. adrenal cortex and acts on the collecting duct. C. posterior pituitary and acts on the loop of Henle. D. anterior pituitary and acts on the distal convoluted tubule. 29. 35. Why is the loop of Henle important to the maintenance of blood volume? A. It reabsorbs glucose. B. It synthesizes blood proteins. C. It adjusts the pH of the urine. D. It produces a hypertonic renal medulla. 30. What is the structure labelled X? A. ureter C. renal pelvis B. urethra D. urinary bladder 31. Which of the following is not a function of structure Y? A. control of blood pH B. production of glycogen C. excretion of histamines D. maintenance of blood volume 32. Which structure is most likely the collecting duct? A. W B. X C. Y D. Z 33. The concentration of solutes in the urine was measured over a one-day period. What might have caused the change that occurred at time X? A. The blood became more acidic. B. Excess sodium ions were excreted. C. The secretion of ADH was inhibited. D. Aldosterone production was stimulated. 34. Tubular excretion occurs when molecules move from the A. loop of Henle to the renal medulla. B. Bowman’s capsule into the glomerulus. C. proximal tubule into the peritubular capillary network. D. peritubular capillary network into the distal convoluted tubule. 35. Which of the labelled arrows points to the renal cortex? A. W B. X C. Y D. Z 36. The function of which of the following is most dependent upon adequate blood pressure? A. the glomerulus B. the loop of Henle C. the collecting duct D. the proximal convoluted tubule 37. Which labelled structure is the efferent arteriole? A. W B. X C. Y D. Z 38. Which of the following correctly compares the relative concentrations of the given substances in urine and blood in the renal vein? Part B Written Response - Write in complete sentences, using concise, detailed writing with the appropriate vocabulary to receive full marks. 1. a) Explain why it would be abnormal to find glucose in structure Y. (1 mark) b) Explain why structure X is longer in an animal that lives in the desert. (1 mark) 2. Describe what happens to urine production when you drink alcohol. (4 marks) 3. Identify two components of blood that cannot move into the filtrate under normal conditions. (2 marks) i) ii) Bonus Question #1: Describe the major differences between the ascending and descending loops of Henle and explain the reason for this difference.