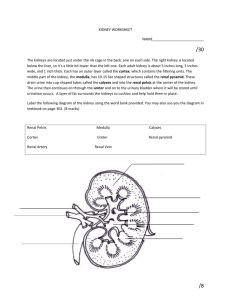
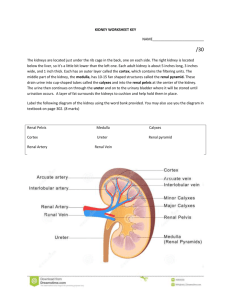
Answers
advertisement
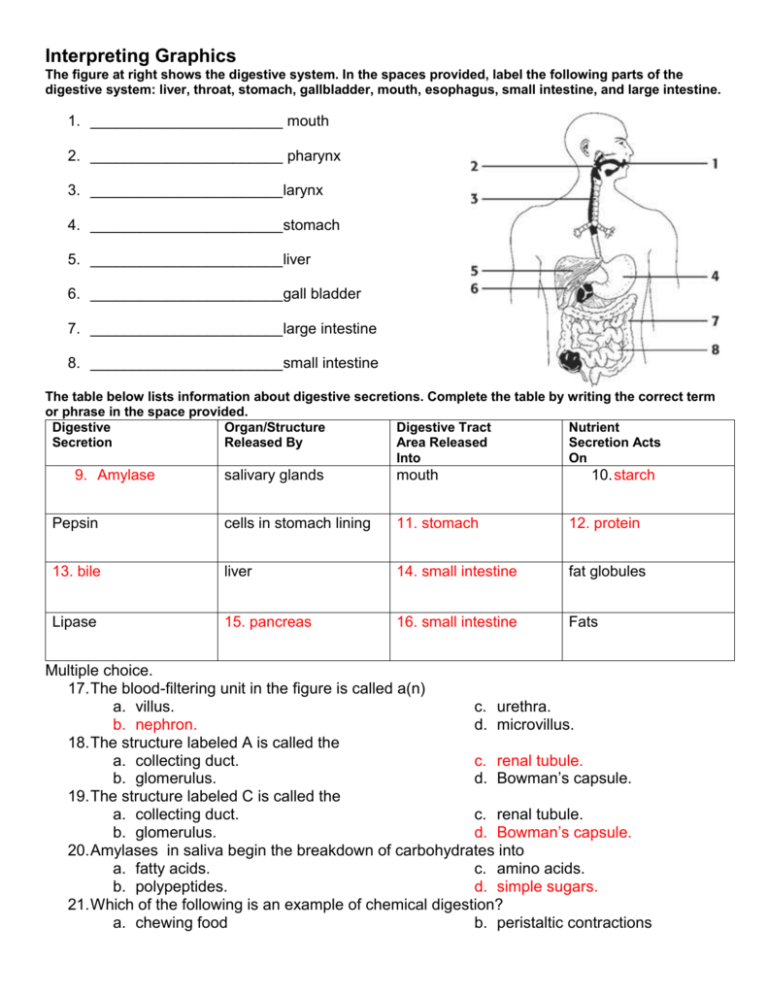
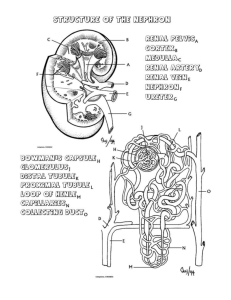
Interpreting Graphics The figure at right shows the digestive system. In the spaces provided, label the following parts of the digestive system: liver, throat, stomach, gallbladder, mouth, esophagus, small intestine, and large intestine. 1. _______________________ mouth 2. _______________________ pharynx 3. _______________________larynx 4. _______________________stomach 5. _______________________liver 6. _______________________gall bladder 7. _______________________large intestine 8. _______________________small intestine The table below lists information about digestive secretions. Complete the table by writing the correct term or phrase in the space provided. Digestive Organ/Structure Digestive Tract Nutrient Secretion Released By Area Released Secretion Acts Into On 9. Amylase salivary glands mouth 10. starch Pepsin cells in stomach lining 11. stomach 12. protein 13. bile liver 14. small intestine fat globules Lipase 15. pancreas 16. small intestine Fats Multiple choice. 17. The blood-filtering unit in the figure is called a(n) a. villus. c. urethra. b. nephron. d. microvillus. 18. The structure labeled A is called the a. collecting duct. c. renal tubule. b. glomerulus. d. Bowman’s capsule. 19. The structure labeled C is called the a. collecting duct. c. renal tubule. b. glomerulus. d. Bowman’s capsule. 20. Amylases in saliva begin the breakdown of carbohydrates into a. fatty acids. c. amino acids. b. polypeptides. d. simple sugars. 21. Which of the following is an example of chemical digestion? a. chewing food b. peristaltic contractions c. breaking bonds d. churning food 22. In the stomach, single protein strands are cut into smaller amino acid chains by the digestive enzyme called a. amylase. c. lipase. b. pepsin. d. gastrin. 23. The products of digestion are absorbed into the bloodstream through the a. villi and microvilli of the small c. stomach and colon. intestine. d. liver and gallbladder. b. rectum of the large intestine. 24. Bile, which breaks fat globules into tiny fat droplets, is produced by the a. pancreas. c. liver. b. gallbladder. d. duodenum. 25. The end result of the filtration, reabsorption, and secretion processes in the nephrons is a. water. c. urine. b. carbon dioxide. d. urea. 26. Urine leaves the bladder and exits the body through a tube called the a. urethra. c. kidney. b. ureter. d. nephron. 27. Within each Bowman’s capsule is a fine network of capillaries called a a. glomerulus. b. collecting duct. a. renal tubule. c. nephron. The figure at right shows a nephron from a kidney. In the spaces provided, label the following structures: Bowman’s capsule, capillaries, renal tubule, collecting duct, and glomerulus. 28. ______________________ glomerulus 29. ______________________ Bowman’s capsule 30. ______________________ renal tubule 31. ______________________ capillaries 32. ______________________ collecting duct 33. ______________________ loop of Henle 34. Explain why there are different lengths of the loop of Henle in these organisms. a. Beaver (aquatic): aquatic environment will decrease the need for water absorption so the loop will be smaller. b. Human (terrestrial): This is the standard being measured from. Humans have a relatively high need to reabsorb water considering the aridness of the environment. c. Kangaroo rat (arid/terrestrial): kangaroo rats live in very arid environments so their needs to reabsorb water is high. Therefore, their loop will be larger, respectively.