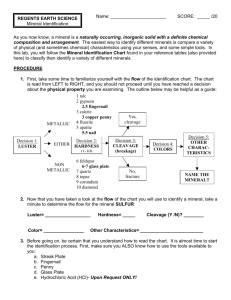
Mineral: A naturally occurring, inorganic solid substance with a fixed
advertisement

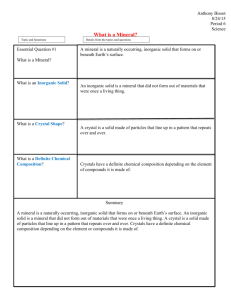
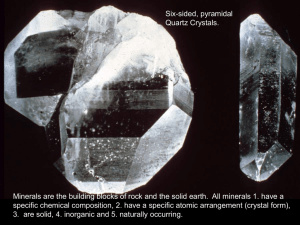
Mineral: A naturally occurring, inorganic solid substance with a fixed chemical composition and crystal structure. Building blocks of rocks. Crystalline structure : made of crystal; containing a repeating structure of atoms. Examples Cubic, hexagonal and monoclinic (three dimensional parallelogram) Luster: a description of a mineral based on how much light reflects off it. Color: can be used to help identify the mineral. For example: streak a line of finely powdered mineral of characteristic color left when the mineral is rubbed across an unglazed porcelain tile. Cleavage: the tendency of a mineral to split, when struck, along specific planes of the crystal structure Fracture: breakage of a mineral, when struck, in a way that is not along cleavage planes of the crystal structure. (broken unevenly) Hardness: the ability of a mineral to resist being scratched on a scale of 1 to 10. 1 being very soft and ten being really hard. chemical properties: properties of a substance relating to the chemical nature and reactivity of a substance. Does it fizz? Magnetic test: Does the mineral attract?