Chapter 2
advertisement

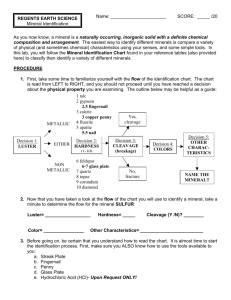
Earth Science Chapter 2 Section 1 A. What is a Mineral: A mineral is a naturally occurring, inorganic solid that has a crystal structure and a definite chemical composition. 1. Naturally Occurring – Not man-made. 2. Inorganic – A material that was never living. 3. Solid – A material that has a definite shape and volume, particles are not free flowing 4. Crystal Structure – Particles of a crystal line up in a pattern that repeats over and over. The repeating pattern of a solid forms a crystal. A crystal has flat sides called faces and sharp edges called corners. 5. Definite Chemical Composition - A mineral always contains elements in definite proportions, it never varies. 1. Element - a substance made up of a single kind of atom. 2. Compounds – two or more elements combined so that the elements no longer have distinct properties. B. Identifying Minerals: Each mineral has its own specific properties that can be used to identify it. Properties of a Mineral: 1. Hardness – One of the identifying factors of a mineral is how hard it is. A scale has been devised to identify the hardness of a mineral. a. Mohs hardness scale – This scale ranks minerals from softest to hardest. 2. Color – The color of a mineral is a physical property that can be used , but can only be used when the color of a mineral never changes. Many mineral colors change due to impurities in the compound. 3. Streak - The color of a minerals powder. 4. Luster – How a mineral reflects light from its surface. Luster can be identified as metallic, glassy, earthy, waxy and pearly. 5. Density – The mass is a given space or the mass per unit volume. No matter the size of a mineral the density remains the same. 6. Crystal System - Property based on the number of crystal faces. 7. Cleavage and Fracture – The way the mineral breaks apart. a. A mineral that splits along flat plains has cleavage b. A mineral that breaks apart in an irregular pattern. For Example: Quartz – Shell-like break Copper and Iron- hackly, From jagged points, soft minerals crumble like clay. 8. Special Properties – a. Fluorescence- Glow under UV light. b. Magnetic – natural magnets - Magnetite c. Radioactive – Give off radiation –Uraninite d. React to Acid – Calcite fizzes and gives off carbon dioxide. e. Electrical properties- Quartz gives off electrical charges when under pressure.