Density Lab Worksheet: Regular & Irregular Solids
advertisement

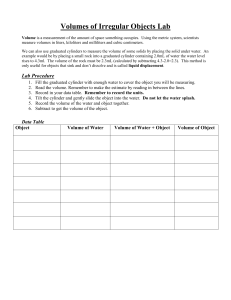
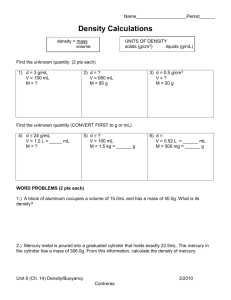
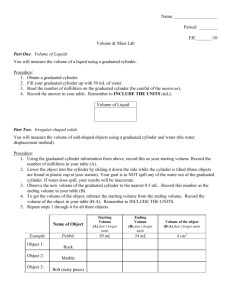
Blocks Density Lab Name ___________________________________________________ Period _____ Date _________________ Part 1 - Density of Regular-Shaped Solids 1. Use the balance to find the mass of the block. Include the correct units. 2. Use a ruler to find the length, width and height of the block. Remember to include the units. 3. Multiply the 3 ruler measurements together to find volume. Remember to include the units. 4. Divide mass by the volume to find the density. Round to the nearest hundredth. Are you remembering to include the units? Mass Length Width Height Volume Density block 1: block 2: block 3: block 4: Part 2 - Density of Irregular-Shaped Solids 1. Use the balance to find the mass of the mineral. Include the correct units. 2. Find the volume of just the water. This is the starting volume. Remember to include the units. 3. Carefully place the mineral in the beaker. Find the volume of the water plus the mineral. This is the ending volume. Remember to include the units. 4. Subtract the starting volume from the ending volume. This is the volume of the mineral. Remember to include the units. 5. Divide mass by the volume to find the density. REMEMBER UNITS. Mass of the block block 1: block 2: block 3: block 4: Starting water volume Ending water volume Volume of the block Density of the block Conclusion/Analysis: 1. What is density? Describe what density is in your own words. 2. What is the formula for density? 3. Density of water is 1 g/ml. If a piece of wood with a density of 5 g/ml is placed in a tub of water, will it sink or float? Explain. 4. Mercury has a density of 13.5 g/ml. What would an object’s density have to be in order for it to sink in mercury? 5. If block 1 were broken in two equal pieces, what would be the density of each piece? Why? 6. A student was conducting an experiment to find the volume of a spherical metal object. He placed it in the graduated cylinder and found the volume to be 5 g/ml. Upon taking it out, he accidently dropped and stepped on the sphere, changing it to an egg-shape. If he put the object back in the graduated cylinder, would it affect the volume? Why or why not?