You should be able to list the hierarchy of biological organization
advertisement

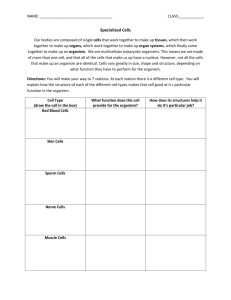
7-4 The Diversity of Cellular Life (Biosphere) You should be able to list the hierarchy of biological organization from biosphere to molecule (or visa versa). Practice! specific) specific) 7-4 The Diversity of Cellular Life Levels of Organization Levels of Organization in Multicellular Organisms Muscle cell Level & Definition Cellular: A collection of mollecules and organelles that function together to carry out the metabolic processes necessary for life. Smooth muscle tissue Stomach Level & Definition Tissue: A collection of cells specialized to function together in performing a specific function within an organ. Types Level & Definition Organ: A collection of tissues specialized to function together in performing a specific function within an organism.. 1. Epithelial (coverings & linings) 2. Nervous (regulation) 3. Muscle (contractile) 4. Connective (bone, tendons, ligaments) Digestive system Level & Definition Organ System: A collection of organs specialized to function together in performing a specific function within an organism.. 7-4 The Diversity of Cellular Life 7-4 The Diversity of Cellular Life The differences among living things arise from the ways in which cells are specialized to perform certain tasks and the ways in which cells associate with one another to form multicellular organisms. Unicellular organisms are made up of only one cell. Unicellular organisms dominate life on Earth. A spirilla bacterium. 7-4 The Diversity of Cellular Life Multicellular Organisms Organisms that are made up of many cells are called Multicellular Organisms. There is great variety among multicellular organisms. A 2-cell Embryo (Multicellular organisms start out unicellular.) A tree of multicellular life. (A unucellular common ancestor.) 7-4 The Diversity of Cellular Life Multicellular Organisms Cell Specialization: Cells throughout an organism can develop in different ways to perform different tasks. Specialized Animal Cells Red blood cells transport oxygen. Muscle cells allow movement. Cells in the pancreas produce proteins (digestive enzymes and insulin) 7-4 The Diversity of Cellular Life Multicellular Organisms Specialized Plant Cells Plants exchange carbon dioxide, oxygen, water vapor, and other gases through tiny openings called stomata on the undersides of leaves. Highly specialized cells, known as guard cells, regulate this exchange. Guard cells forming a stomate in the epidermis of a leaf. (opening for gas exchange) 7-4 The Diversity of Cellular Life 7-4 Cell specialization is characteristic of a. bacteria. b. all unicellular organisms. c. yeasts. d. multicellular organisms. 7-4 The Diversity of Cellular Life 7-4 Which of the following cells is specialized for contraction? ● muscle cell ● red blood cell ● pancreatic cell ● nerve cell 7-4 The Diversity of Cellular Life 7-4 The stomach is an example of a(an) a. tissue. b. organ. c. organ system. d. organism. 7-4 The Diversity of Cellular Life 7-4 Which of the following shows the levels of organization in an organism from the simplest to the most complex? ● organ system, organ, cell, tissue ● tissue, cell, organ, organ system ● cell, tissue, organ, organ system ● cell, organ, tissue, organ system 7-4 The Diversity of Cellular Life 7-4 Which of the following would probably contain the greatest variety of specialized cells? a. an organ system b. a tissue c. an organ d. a multicellular organism