Classification of Organisms Picture Vocabulary
advertisement

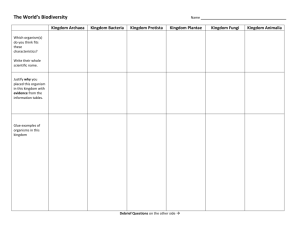
Classification of Organisms Picture Vocabulary Organisms and Environments Taxonomy The branch of science that formally names and classifies organisms by their structure, function, and relationships. Structure The arrangement of parts that form a living thing. Eukaryotic Cell A cell containing a membrane-enclosed nucleus and organelles. Prokaryotic Cell A cell lacking a nucleus or any other membrane-enclosed organelle. Unicellular Organism An organism made up of one cell. Multicellular Organism An organism made up of more than one cell, and often made up of different types of cells. Function The special activity of a part. Autotrophic Organism An organism that is able to make its own food. Heterotrophic Organism An organism that cannot make its own food. Reproduction Hydra budding The process of an organism producing more of its own kind. Sexual Reproduction A method of reproduction that requires both a male and a female parent. Asexual Reproduction A method of reproduction that requires only one parent. Domains The primary or highest-ranking classification of organisms, which includes three groups: Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. Domain Bacteria One of the three taxonomic domains; includes prokaryotic, single-celled organisms that lack a membrane-enclosed nucleus and that can be classified by shape. Domain Archaea One of the three taxonomic domains; includes unicellular organisms that are prokaryotic like bacteria, but also share characteristics with eukaryotes. Domain Eukarya One of the three taxonomic domains of organisms; cells contain a membrane-enclosed nucleus. Kingdoms A taxonomic rank below domain that is composed of smaller groups: Archaea, Bacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom of prokaryotic, single-celled organisms that lack a membrane-enclosed nucleus and can be classified by shape. Kingdom Archaea Kingdom of unicellular organisms that are prokaryotic like bacteria, but also share characteristics with eukaryotes. Kingdom Protista Kingdom of single-celled and simple multiplecelled eukaryotic organisms. Kingdom Fungi Kingdom of heterotrophic eukaryotes that reproduce through asexual spores and have chitin in their cell walls. Kingdom Plantae Kingdom of autotrophic eukaryotes that includes all plants. Kingdom Animalia Kingdom of heterotrophic eukaryotes that includes all animals.