Bacteria to Plants 5-1 The Characteristics of Seed
advertisement

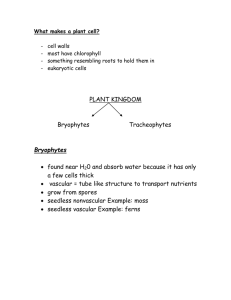
Bacteria to Plants Chapter 5 Seed Plants Section 1 The Characteristics of Seed Plants Key Concepts: 1. What characteristics do seed plants share? 2. How do seeds become new plants? 3. What are the main functions of roots, stems, and leaves? Key Terms: • Phloem • Xylem • Pollen • Seed • Embryo • Cotyledon • Germination • Root Cap • Cambium • Stomata • Transpiration Characteristics of Seed Plants 1.Vascular Tissue Most live on land Have thick cell walls Phloem- Where food moves Xylem- Where water and minerals move Characteristics of Seed Plants 2. Pollen and Seeds Pollen- Tiny structures that contain cells that will later become sperm cells Delivery system of sperm cells to egg cells Seeds- Form from fertilized egg cells A structure that contains a young plant inside a protective covering Seed Plants to New Plants 1. Seed Structure Embryo- Young plant that develops from the zygote or fertilized egg Has the beginnings of: Roots Stems Leaves Cotyledons- One or more embryo leaves that can store food Seat Coat Skins/wraps on some seeds Seed Plants to New Plants 2. Seed Dispersal Scattering of seeds Some organisms take the seeds to other places Eat and “Dispose” of seeds later Barbed seeds get stuck on them then fall off Water Wind Light weight seeds Some have structures to catch the wind Some explode out seeds to throw them Seed Plants to New Plants 3. Germination Germination- Occurs when the embryo begins to grow and pushes out of the seed Does not happen right away Seed needs to absorb water from its environment first First roots grow down Then stem and leaves grow up The further the seed is away from parent the better chance of survival No competition for the same resources Seed Plants: Roots Purposes of Roots 1. Anchor plants in the ground 2. Absorb water from the soil 3. Absorb minerals from the soil 4. Stores extra food Seed Plants: Roots 1.Types Fibrous root system Many similarly sized roots that form a dense tangled mess Take a lot of soil when you pull them out of the ground Lawn Grass, Onion s Taproot One long, thick main root Hard to pull out of the ground Carrots, Cacti Seed Plants: Roots 2. Structure Root Cap- Protects the root from injury from rocks as the root grows through the soil Cells that multiple are right behind the root cap Root hairs Tiny hairs Reach into space between soil particles Absorb water and minerals Grow out of root’s surface Help anchor the plant in the soil Seed Plants: Stems 1.Two (2) Main Functions 1. Carry substances between the plants roots and leaves 2. Provide support for the plant and holds the leaves so they are exposed to the sun. (Hermes) Seed Plants: Stems 2. Structure Herbaceous No wood- Often Soft Woody Hard and Rigid Several layers of tissue Bark= Outer Most layer Outer protective layer Inner layer of phloem Cambium- Divides to produce new phloem and xylem Xylem Most of what we refer to as “wood” Seed Plants: Stems 3. Annual Rings Each ring is made of xylem Quick Spring Growth Large Thin walls Wide, light brown rings Slow Summer Growth Small Thick Walls Thin, dark rings Together (each pair) counts as one (1) year Rainy seasons More xylem produced Wide rings Dry seasons Less xylem produced Narrow rings Seed Plants: Leaves Many shapes and sizes All capture the sun’s energy and carry out the food making process of photosynthesis 1.Structure Protective top and bottom layers Between layers are veins containing phloem and xylem Surface layers contain Stomata- Small openings or pores Act like tiny mouths Open and close to control gases enter/leaving Carbon Dioxide enters Oxygen and water vapor exit. Seed Plants: Leaves 2. Photosynthesis Contains the most chloroplasts at the leaf’s upper surface Chlorophyll traps the sun’s energy Water is brought to leaves through the xylem Sugar and oxygen are produced from the carbon dioxide and water Sugar travels through phloem to feed plant Oxygen exists the leaf via the stomata Seed Plants: Leaves 3. Water Loss TranspirationProcess of water evaporating out of a plant’s leaves Stomata close to keep water in the leaf Chapter 5 Seed Plants Section 1 The Characteristics of Seed Plants 1. What characteristics do seed plants share? 2. How do seeds become new plants? 3. What are the main functions of roots, stems, and leaves? Section Review on p. 145