Processes & Stages of Birth
advertisement

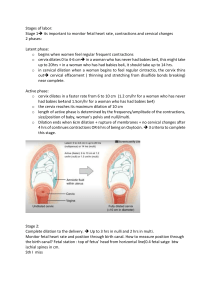
PROCESSES AND STAGES OF BIRTH N160 Nursing of Women and Newborns Key Factors of Labor Passenger (the fetus) Passageway (the pelvis) Powers (contractions and bearing down efforts) Psychosocial (personal history, beliefs, culture, SES, PASSAGEWAY Size of pelvis Type of pelvis Ability of cervix to dilate PASSENGER Fetal head Lie Attitude Position Station POWERS Uterine contractions Intra-abdominal pressure (pushing) Position for labor Musculature changes in the pelvic floor PSYCHOSOCIAL FACTORS Education Cultural beliefs Fatigue level Pain tolerance Previous experience Anxiety level Availability of coping techniques CAUSES OF LABOR Oxytocin stimulation Progesterone withdrawl Estrogen stimulation Fetal cortisol Uterine distension Prostoglandins PREMONITORY SIGNS OF LABOR Lightening Burst of energy Braxton-Hicks contractions Cervical softening and effacement Bloody show Rupture of membranes TRUE VS. FALSE LABOR TRUE regular UC UC: stronger, longer, closer over time UC’s increase with walking Cervix thins and opens FALSE/PRACTICE irregular UC UC don’t change or lessen over time UC’s don’t change with activity Cervix doesn’t change STAGES OF LABOR FIRST Latent Active Transition SECOND THIRD FOURTH FIRST STAGE- latent Labor onset to 3 cm longest phase of labor woman may remain at home woman feels able to cope with contractions woman my be excited, anxious, talkative, reflective, smiling SECOND STAGE-active Cervix dilates 4- 8 cm fetal descent is progressive cervical dilation is usually 1.2 cm/hr in primips and 1.5 cm/hr in multips woman is having to concentrate on contractions and breathing patterns FIRST STAGE-transition Cervical dilation from 8-10 cm rate of descent increases usually 3 hrs for primips and 1 hr for multips Woman may be increasingly anxious & uncomfortable, feel out of control, change positions frequently, be very inner-directed and withdrawn “I can’t do this anymore” SECOND STAGE OF LABOR Complete dilation/ ready to push to delivery 1 hr for primip, 15 min. for multip Woman uses the forces of ctxs and intra-abdominal pressure to deliver fetus Woman feels more in control and able to DO something THIRD STAGE OF LABOR Birth of baby to delivery of placenta placental separation happens in 5-30 minutes Signs: gush of blood, lengthening of cord, return of maternal contractions Shultz (shiny)/ Duncan (dirty)- appearance of placenta indicates mechanism of separation FOURTH STAGE OF LABOR Recovery fundus at umbilicus moderate amt of rubra lochia mother may be thirsty and hungry shaking is common mother is excited, happy, tired, bonding, breastfeeding, proud, euphoric CARDINAL MOVEMENTS OF DELIVERY Descent Flexion Internal Rotation Extension Restitution External rotation Expulsion MATERNAL SYSTEMIC RESPONSE TO LABOR Cardiovascular system Cardiac output increases between Ucs as labor progresses Increase in BP during UC Increase in BP r/t anxiety, pain, meds Slow progressive rise in pulse MATERNAL SYSTEMIS RESPONSE TO LABOR Gastrointestinal Gastric motility decreases Decreased emptying Absorption of fluid not effective OK to eat during labor MATERNAL SYSTEMIC RESPONSE TO LABOR Respiratory Oxygen consumption increases Hyperventilation secondary to anxiety is common (numbness and tingling of face, fingers, arms) MATERNAL SYSTEMIC RESPONSE TO LABOR Hemoatopoietic WBCs increase from 5-10K to 25K/mm3 Increased plasma fibinogen Decreased clotting time MATERNAL SYSTEMIC RESPONSE TO LABOR Renal and Urologic Decreased sensory perceptions may impair ability to feel full bladder Pressure of presenting part may cause bladder neck edema Trace protein is normal r/t muscle breakdown MATERNAL SYSTEMIC RESPONSE TO LABOR Fluid and Electrolyte Fluid loss r/t diaphoresis, increased respiratory rate and emesis