Chimica di base: Acidi, Sali e Reazioni
advertisement
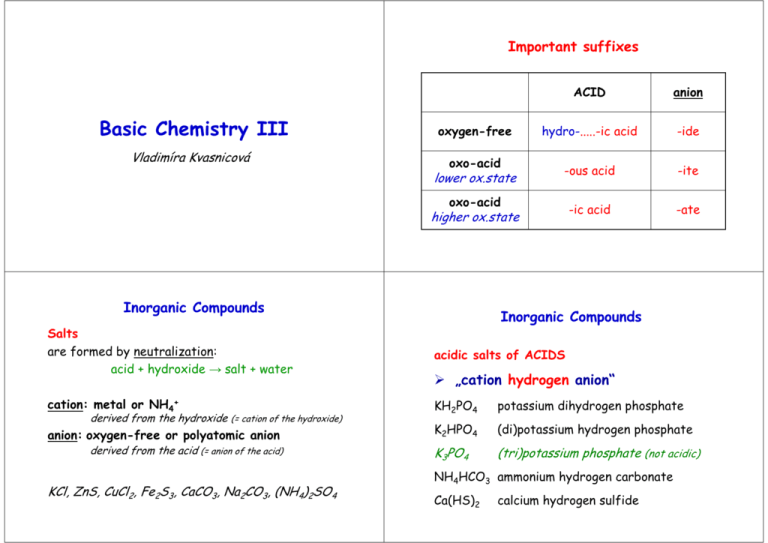
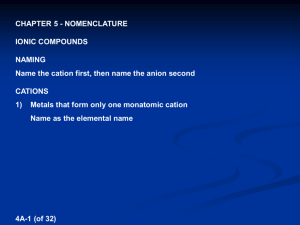
Important suffixes Basic Chemistry III Vladimíra Kvasnicová ACID anion oxygen-free hydro-.....-ic acid -ide oxo-acid lower ox.state -ous acid -ite oxo-acid higher ox.state -ic acid -ate Inorganic Compounds Inorganic Compounds Salts are formed by neutralization: acid + hydroxide → salt + water acidic salts of ACIDS cation: metal or NH4+ KH2PO4 potassium dihydrogen phosphate K2HPO4 (di)potassium hydrogen phosphate K3PO4 (tri)potassium phosphate (not acidic) derived from the hydroxide (= cation of the hydroxide) anion: oxygen-free or polyatomic anion derived from the acid (= anion of the acid) „cation hydrogen anion“ NH4HCO3 ammonium hydrogen carbonate KCl, ZnS, CuCl2, Fe2S3, CaCO3, Na2CO3, (NH4)2SO4 Ca(HS)2 calcium hydrogen sulfide Other types of compounds Other types of compounds basic salts of ACIDS double salts of ACIDS „cation hydroxy anion“ a) „cation1 cation2 anion“ Mg(OH)Cl magnesium hydroxychloride KMgF3 potassium magnesium fluoride KLiSO4 potassium lithium sulfate Sb(OH)2(NO3) antimony(III) dihydroxynitrate Total charge of molecule is ZERO Total charge of molecule is ZERO Other types of compounds Other types of compounds double salts of ACIDS HYDRATES OF SALTS b) „cation anion1 anion2“ „cation anion multiple prefix hydrate“ CaCl(ClO) calcium chloride hypochlorite Cu3(CO3)2F2 copper(II) carbonate fluoride MgCl2 . 6H2O magnesium chloride hexahydrate CaHPO4 . 2H2O calcium hydrogen phosphate Total charge of molecule is ZERO dihydrate Other types of compounds Other types of compounds THIOACIDS AND THIOSALTS POLYACIDS AND SALTS „thio.... acid“ „multiple prefix.... acid“ H2S2O3 thiosulfuric acid (H2SO4 = sulfuric acid) H2B4O7 tetraboric acid HSCN thiocyanic acid (HOCN = cyanic acid) H2Cr2O7 dichromic acid „cation thio....anion“ „cation multiple prefix....anion“ K2S2O3 potassium thiosulfate Na2B4O7 sodium tetraborate KSCN potassium thiocyanate K2Cr2O7 potassium dichromate Problems – add formulas • • • • • • • • • • • sodium sulfite potassium phosphate ammonium hydrogen phosphate lithium dihydrogen phosphate calcium hydrogen carbonate silver sulfide zinc sulfate potassium permanganate sodium hypobromite barium nitrate hydrargyric chloride Problems – add formulas • • • • • • • • • • • sodium tetraborate decahydrate potassium aluminium sulfate sodium aluminium sulfate dodecahydrate ammonium carbonate calcium sulfate hemihydrate (hemi = ½) zinc sulfate heptahydrate potassium dichromate potassium magnesium fluoride ammonium magnesium phosphate led(II) chloride fluoride cupric biscarbonate difluoride (bis = twice) Chemical reactions Chemical reactions = chemical changes stoichiometry = the reactants combine in simple wholenumber ratios (see stoichiometric coefficients: a, b, c, d) aA+bB→cC+dD equilibrium constant (K) describes the ratio of concentrations of products and reactants in the equilibrium aA+bB↔cC+dD • the single arrow (→) is used for an irreversible reaction • double arrows (↔) are used for reversible reactions chemical equilibrium = a state of a reversible chemical reaction in which the concentrations of reactatnts and products are not changing with time ie K = [C]c [D]d / [A]a [B]b • K is constant for given reaction and fixed temperature • the definition of K is called Guldberg-Waage´s law (= law of chemical equilibrium) the rates of both the forward and back reactions are equal Chemical reactions • a chemical reaction is described by a chemical equation • the equation is balanced if substance amount of each element is the same on both sides of a chemical equation ⇒ each element must be balanced in the order: metal – nonmetal – hydrogen - oxygen Conservation law (Law of conservation of mass / energy) = the total magnitude of mass (or energy or charge) remain unchanged even though there may be exchanges of that property between components of the system (the sum of masses of reactants equals to the sum of masses of products) Chemical reactions • NEUTRALIZATION = acid-base reactions H2SO4 + 2 NaOH → Na2SO4 + 2 H2O acid + base → salt + water • PRECIPITATION NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl (s) + NaNO3 → insoluble product = precipitate is formed • REDOX reactions = oxidative-reduction reactions → oxidation states of elements are changed !!!