Nomen- clature
advertisement

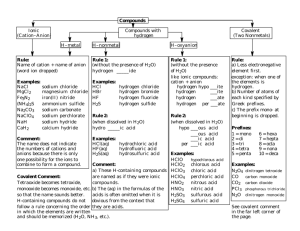
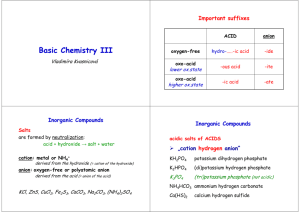
CHAPTER 5 - NOMENCLATURE IONIC COMPOUNDS NAMING Name the cation first, then name the anion second CATIONS 1) Metals that form only one monatomic cation Name as the elemental name 4A-1 (of 32) Al3+ Group 1 (1+) Group 2 (2+) Zn2+ Ag+ 4A-2 Ca2+ K+ Al3+ calcium potassium aluminum 4A-3 2) Metals that form more than one monatomic cation Name as the elemental name, followed by their charge as a roman numeral in parenthesis 4A-4 Mn2+ Mn3+ Sn4+ manganese (II) manganese (III) tin (IV) George Foreman George Foreman George Foreman George Foreman George Foreman 4A-5 3) Cations that are polyatomic NH4+ UO22+ Hg22+ ammonium uranyl mercury (I) 4A-6 ANIONS 1) Nonmetals that form a monatomic anion Name as the root of the elemental name, ending in -ide 4A-7 H (1-) Group 17 (1-) Group 16 (2-) Group 15 (3-) 4A-8 O2- Cl- N3- oxide chloride nitride S2- P3- H- 4A-9 2) Anions that are polyatomic Name polyatomic anions that contain oxygen as the root of the elemental name, ending in –ate or –ite CO32- NO3- NO2- carbonate nitrate nitrite PO43- SO42- SO32- phosphate sulfate sulfite 4A-10 Some elements can make 4 oxyions ClO4- perchlorate ClO3- chlorate ClO2- chlorite ClO- hypochlorite 4A-11 Name the following: CaCl2 Na2O calcium chloride sodium oxide 4A-12 MgS AuI3 PbBr2 3+ 111- 2+ 11- gold (III) iodide lead (II) bromide 4A-13 Cu2O Cr2S3 K2SO4 3+ 23+ 22chromium (III) sulfide 4A-14 potassium sulfate SnCO3 FORMULAS Base formulas on charge balance barium fluoride Ba2+ F- potassium oxide K+ O2- (2+) + (1-) + (1-) = 0 (1+) + (1+) + (2-) = 0 Need 2 to make total charge 0 Need 2 to make total charge 0 BaF2 K2O 4A-15 lithium nitride aluminum sulfide Al3+ S2- (3+) + (3+) + (2-) + (2-) + (2-) = 0 Makes 6+ Al2S3 4A-16 Makes 6- cobalt (III) chloride Co3+ Cl- (3+) + (1-) + (1-) + (1-) = 0 lithium nitrate Li+ (1+) + (1-) = 0 Need 3 to make total charge 0 CoCl3 4A-17 NO3- LiNO3 Sodium bicarbonate Na+ HCO3- (1+) + (1-) = 0 barium hydroxide Ba2+ OH- (2+) + (1-) + (1-) = 0 Need 2 to make total charge 0 NaHCO3 BaOH2 Ba(OH)2 4A-18 NO! iron (III) nitrate Fe3+ NO3- (3+) + (1-) + (1-) + (1-) = 0 Need 3 to make total charge 0 Fe(NO3)2 4A-19 zinc phosphate HYDRATES Compounds with water molecules trapped in their crystals Name ionic compound first, then a prefix for the number of waters, followed by -hydrate 1 2 3 4 5 4A-20 mono di tri tetra penta 6 7 8 9 10 hexa hepta octa nona deca CuCl2.6H2O iron (III) nitrate nonahydrate copper (II) chloride hexahydrate Fe(NO3)3.9H2O 4A-21 COVALENT COMPOUNDS NAMING BINARY COMPOUNDS Name the 1st nonmetal as element name, using prefix if more than 1 atom Name the 2nd nonmetal with –ide, always use a prefix CO2 CO N2O carbon dioxide carbon monoxide dinitrogen monoxide 4A-22 FORMULAS OF BINARY COMPOUNDS Base formulas on prefixes Phosphorus triiodide PI3 4A-23 diarsenic pentasulfide NAMING ACIDS ARRHENIUS ACID – A compound that loses hydrogen ions in solution ARRHENIUS BASE – A compound that loses hydroxide ions in solution Out of water – named as an ionic compound HCl (g) hydrogen chloride Dissolved in water – name based on name of the acid’s anion 4A-24 Anion in acid ends in –ide hydro–root–ic acid HBr Anion in acid ends in –ate root–ic acid bromide ion Anion in acid ends in –ite root–ous acid 4A-25 Br- hydrobromic acid Anion in acid ends in –ide hydro–root–ic acid H2S Anion in acid ends in –ate root–ic acid sulfide ion Anion in acid ends in –ite root–ous acid 4A-26 S2- hydrosulfuric acid Anion in acid ends in –ide hydro–root–ic acid HNO3 Anion in acid ends in –ate root–ic acid nitrate ion Anion in acid ends in –ite root–ous acid 4A-27 NO3nitric acid Anion in acid ends in –ide hydro–root–ic acid H2SO4 Anion in acid ends in –ate root–ic acid sulfate ion Anion in acid ends in –ite root–ous acid 4A-28 SO42sulfuric acid Anion in acid ends in –ide hydro–root–ic acid H3PO3 Anion in acid ends in –ate root–ic acid phosphite ion Anion in acid ends in –ite root–ous acid 4A-29 PO33phosphorous acid FORMULAS OF ACIDS Anion in acid ends in –ide hydro–root–ic acid hydrofluoric acid Anion in acid ends in –ate root–ic acid F- Anion in acid ends in –ite root–ous acid 4A-30 fluoride ion HF FORMULAS OF ACIDS Anion in acid ends in –ide hydro–root–ic acid carbonic acid Anion in acid ends in –ate root–ic acid CO32- Anion in acid ends in –ite root–ous acid 4A-31 carbonate ion H2CO3 FORMULAS OF ACIDS Anion in acid ends in –ide hydro–root–ic acid nitrous acid Anion in acid ends in –ate root–ic acid NO2- Anion in acid ends in –ite root–ous acid 4A-32 nitrite ion HNO2