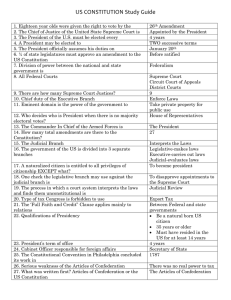
U.S. Constitution Reading Guide: Branches & Principles
advertisement
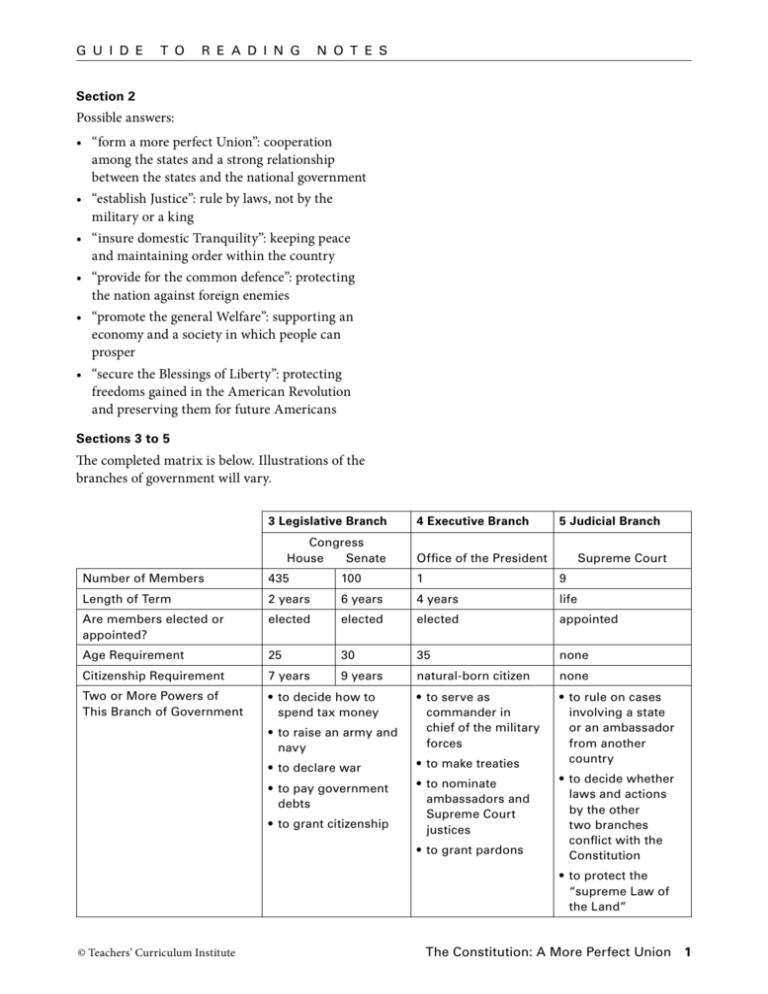
G u i d e t o R e a d i n g N o t e s Section 2 Possible answers: • “form a more perfect Union”: cooperation among the states and a strong relationship between the states and the national government • “establish Justice”: rule by laws, not by the military or a king • “insure domestic Tranquility”: keeping peace and maintaining order within the country • “provide for the common defence”: protecting the nation against foreign enemies • “promote the general Welfare”: supporting an economy and a society in which people can prosper • “secure the Blessings of Liberty”: protecting freedoms gained in the American Revolution and preserving them for future Americans Sections 3 to 5 The completed matrix is below. Illustrations of the branches of government will vary. 3 Legislative Branch Congress House Senate 4 Executive Branch 5 Judicial Branch Office of the President Supreme Court Number of Members 435 100 1 9 Length of Term 2 years 6 years 4 years life Are members elected or appointed? elected elected elected appointed Age Requirement 25 30 35 none Citizenship Requirement 7 years 9 years natural-born citizen none Two or More Powers of This Branch of Government • to decide how to spend tax money • to serve as commander in chief of the military forces • to rule on cases involving a state or an ambassador from another country • to raise an army and navy • to declare war • to pay government debts • to grant citizenship • to make treaties • to nominate ambassadors and Supreme Court justices • to grant pardons • to decide whether laws and actions by the other two branches conflict with the Constitution • to protect the “supreme Law of the Land” © Teachers’ Curriculum Institute The Constitution: A More Perfect Union 1 G u i d e t o R e a d i n g N o t e s Section 6 s. to n ca ve ls al e id nt c ss. s e e Pr sid gre • e n Pr o • of C nt ll bi l ia ec sp s on si s se l. na e tio ar tu cl sti de on a n nc s. tc u ge ur ns ud e o Co ti lj e ac ra em de pr em ve fe Su pr uti s Su e c nt e s • ex oi a t pp in t a om . en n es id nt tic e s de s Pr esi rt ju Pr u • Co 2. See diagram at right. Executive Branch • 1. The framers developed a system of checks and balances because they wanted to limit the government’s power to ensure that one branch did not dominate the others. e th s. h oe ac et e v p im de n rri ca ve o ss re nt. an ng ide ss c o s e C e r • pr ng Co • • Supreme Court rejects laws. Judicial Branch Legislative Branch • Congress can impeach federal judges. • Congress approves Supreme Court judges. Section 8 Section 7 1. The framers made sure the Constitution could be amended so that it could be responsive to changing times. They made the amendment process difficult, however, so that changes would not be made hastily and without the consent of a large majority of citizens. 2. Flowcharts will vary. An amendment can be proposed by a two-thirds vote of each house of Congress or by a national convention called by Congress at the request of two-thirds of the state legislatures. An amendment can be ratified by at least three-fourths of the state legislatures or by special conventions in at least three-fourths of the states. 1. The framers wanted a strong national government. At the same time, they wanted the states to have significant powers. 2. The commerce clause gives the national government the power to regulate interstate commerce. 3. With a common market, goods and resources could flow more easily across the country, and large businesses could cross state lines. The common market also helped to create a single national economy. Section 9 1. The principle of majority rule is based on the idea that government actions reflect the popular will. Laws are passed in Congress by majority vote and elections are decided by a majority of voters. 2. Illustrations will vary. Possible answers: People can join political parties or interest groups, vote, and express their interests and concerns to their elected officials. © Teachers’ Curriculum Institute The Constitution: A More Perfect Union 2