Print › Branches of Government | Quizlet | Quizlet
advertisement

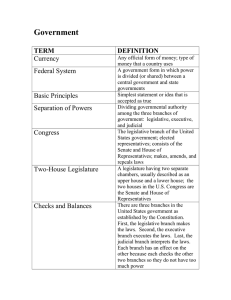
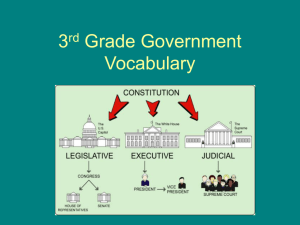
Constitution A document establishing the structure, functions, and limitations of a government. Legislative Branch Branch of government that makes the laws; Congress: made up of the Senate and House of Representatives Executive Branch Branch of government that enforces the laws; President, Vice President; Cabinet members Judicial Branch Branch of government that interprets laws, punishes criminals, and settles disputes between states; Supreme Court Congress made up of two houses: the House of Representatives and the Senate. House of Representatives 435 Members, based on population of the state Senate 100 members (two from each state) President Chief Executive of the United States, Head of State and Commander and Chief of the US Armed Forces; elected every 4 Vice-President Presiding officer in the Senate; he is the first in line to take the place of the president Supreme Court Highest court in the country. checks and balances A system that allows each branch of government to limit the powers of the other branches in order to prevent abuse of power citizen A person with certain rights and responsibilities in his or her country or community alien A resident of another country who is not yet a citizen of the country where he/she lives delegate A person appointed or elected to represent others constituent A person represented by an elected official. Separation of Powers The division of power among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government veto Power of the President to reject a bill passed by Congress. Republicanism A government where the power is in the hands of the people, and they have the right to elect their representatives. Federalism A system in which power is divided between the national and state governments civil rights Personal, human rights recognized and guaranteed by the U.S. Constitution