Preamble and Articles of Constitution Amendments
advertisement

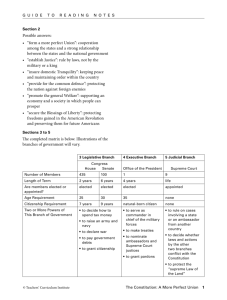
Introduction to the US Constitution – 1 sentence States where power comes from Lists the 6 goals of US government We the People of the United States, in order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defense, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America. We the People of the United States” The power of the US government is in the hands of the people “ “Form a more perfect union” Act as one country “Establish justice” The law must be reasonable, fair, and impartial “Insure domestic tranquility” Keep peace within the country; maintain order at home “Provide for the common defense” Protect US interests in the world “Promote the general welfare” Provide people with basic services “Secure the blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our posterity” Guarantee our freedoms today and for future generations The Legislative Branch (Article I) MAKES THE LAWS The House and Senate Senate originally chosen by state legislatures First Article because Congress seen as most important Elastic clause (Section 8, Clause 18) gives Congress wide freedom to pass laws “necessary and proper” to running the country. The Executive Branch (Article II) ENFORCES THE LAWS The President The Judicial Branch (Article III) INTERPRETS THE LAWS SCOTUS and the federal courts Most vague; left to the most interpretation Relations among the states: establishes uniformity among states Full Faith and Credit clause: states should accept legal proceedings from other states EX: birth certificate, driver’s licenses, ownership of a vehicle Privileges and immunities clause: citizens in each state have the same rights as citizens in other states Extradition clause: states must return criminals to states where they have been convicted or have to stand trial. Amending the constitution (Article V) National Supremacy and Other Random Stuff (Article VI) Assumes Confederacy’s debt and obligations Supremacy Clause: Constitution the supreme law of the land Ratification (Article VII) Sets conditions for accepting the Constitution Two-thirds of Congress, three-fourths of state legislatures most common method Two-thirds of Congress, three-fourths of state conventions used once to repeal Prohibition Two-thirds of states to call a ratifying convention than would have to be approved by three-fourths of state legislatures never used, and no one knows how it would work if they did Amendments 1-10 Part of the deal to ratify the constitution, although took some time to get passed because Congress had more pressing matters 1-8 deal with personal rights 9 answers Madison’s concerns by stating that a right doesn’t have to be here to exist 10 affirms federalism; the Supreme Court (1931) said it was redundant Amendments 13-15 Dealt with issues related to the Civil War, most notably African-Americans 13th Amendment: emancipated the slaves 14th Amendment: among other things established citizenship for all people living in the U.S. set specific legal provisions (more on this much later) dealt with matters related to Confederate officers and Confederate debt 15th Amendment: gave black men the right to vote Amendments 16-19 Dealt with specific areas of reform 16th amendment: national income tax to fund government programs 17th amendment: direct election of senators Senators originally chosen by state legislatures 18th amendment: prohibition (outlawing of alcohol) to deal with social problems stemming from alcoholism 19th amendment: women’s suffrage (women’s right to vote)