THE VSEPR MODEL
advertisement
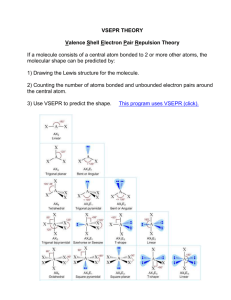
THE VSEPR MODEL (VALENCE SHELL ELECTRON PAIR REPULSION MODEL) 1. Introduction • • • • Modern Theory put‐forward by Ronald Gillespie and Ronald Nyholm. VSEPR theory helps in the prediction of the shape of the polyatomic molecules. This theory predicts the electron pairs, which are as Bonding pairs or Non‐bonding pairs, they adopt a shape of geometry to maximum distance itself to minimize the repulsions and thus results in a geometry with least possible energy. The VSEPR model holds the key in analysing the Electron‐Electron interactions. 2. RULES • • • Draw the lewis structure for the molecule. Count the total number of Regions (electron pairs as bonded and non‐bonded) around a central atom. Identify the most stable arrangement. Determine the positions of the atoms based on the types of electron pairs present. Identify the molecular structure based on the positions of the atoms not on the regions of high electron density Identify Ψ* ‐ polyhedra (geometry untder consideration of lonepairs): ‐ linear (no. of ligands + lonepairs = 2) ‐ trigonal planar (no. of ligands + lonepairs = 3) ‐ tetrahedral (no. of ligands + lonepairs = 4) ‐ trigonal bipyramidal (no. of ligands + lonepairs = 5) ‐ octahedral (no. of ligands + lonepairs = 6) for other rules e.g. multiple bonds see textbooks 3. EXAMPLES 1. ClF3 : Lewis structure : • • • • VSEPR MODELS (a,b,c) : → “ a ” is more favoured than “ b “ and “ c “ since in “a “ lone pair –lone pair interactions are less stable. (Ψ* polyhedron is a trigonal bipyramid) 2. XeF4 : Lewis structure : (Ψ* polyhedron is an octahedron). VSEPR MODEL : 4. TASKS : 1. What is the VSEPR theory? Illustrate its rules and determine the shapes of the following molecules! (a) PCl5 (b) SF6 (c) H3O+ 2. Why is the H‐O‐H bond angle in a water molecule (H2O) smaller than the H‐C‐H bond angles in methane (CH4) ?