VSEPR (1/8) - Liberty Union High School District
advertisement

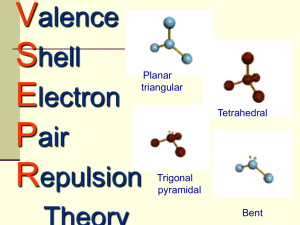
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=keHSCASZfc&feature=related Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR Theory): Looking at molecules in 3D!!! Friday, January 8th, 2016 Molecular Shape VSEPR theory assumes that the shape of a molecule is determined by the repulsion of electron pairs. VSEPR Theory • Based on Electron Dot (Lewis structures) • VSEPR Theory predicts shapes of compounds • VSEPR (pronounced “vesper”) stands for Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion • VSEPR predicts shapes based on electron pairs repelling (in bonds or by themselves) • Electrons around central nucleus repel each other. So, structures have atoms maximally spread out VSEPR overview • Each shape has a name (you should know these 5) • Names of Shapes: • tetrahedral • trigonal pyramidal • Bent • Linear • trigonal planar Tetrahedral Triangular Planar Trigonal pyramidal Bent Linear Example 1: Methane (CH4) Example 2: Ammonia (NH3) Example 3: Water(H2O) methane, CH4 Tetrahedral 109.5° Bonds are all evenly spaced electrons .. .. .. .. ammonia NH3 Trigonal Pyramidal Less repulsion between the bonding pairs of electrons .. .. .. water, H2O 109.5° (109.5°) 109.5° (107°) 109.5° (104.5°) .. .. .. Bent or V 2 unshared pairs of e’s at top of O repel bonds and force them to bend Steps to Success 1. Draw the Lewis Structure for each atom - Count up the valence electrons, determine central atom, bond terminal atoms, recount, add lone electron pairs, check & shift to share if necessary 2. Determine VSEPR Structure -- # atoms bound -- # unpaired electrons on central atom 3. Redraw as VSEPR Structure Example 4: Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Example 4: Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Molecule Kit Lab Activity • With your partner, you will draw the lewis dot structures for several compounds. • You will construct the compounds from the kits provided and sketch your models. • Identify the molecular geometry (shape) of your compound from the central atom and label the bond angles. • Lastly, determine if you compound is polar or nonpolar (horse & cart)