Introduction to Sensation and Perception
advertisement

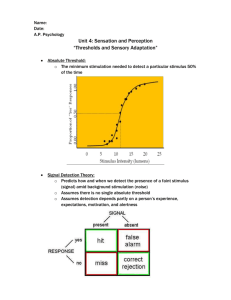
___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ PSYCHOLOGY ___________________________________ (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers ___________________________________ PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Worth Publishers, © 2007 1 ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Introduction to Sensation and Perception ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Module 12 2 ___________________________________ Sensation ___________________________________ Sensing the World: Some Basic Principles ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Threshold Sensory Adaptation ___________________________________ Selective Attention ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 3 Psychology 8 ed., David Myers Module 12 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 1 OBJECTIVE 12‐1| Contrast sensation and Sensation & Perception perception, and explain the difference between bottom‐up and top‐down processing. How do we construct our representations of the external world? ___________________________________ ___________________________________ To represent the world, we must detect physical energy (stimulus) from the environment and convert it into neural signals, a process called sensation. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ When we select, organize, and interpret our sensations, the process is called perception. ___________________________________ 4 ___________________________________ Bottom‐up Processing ___________________________________ Analysis of the stimulus begins with the sense receptors and works up to the level of the brain and mind. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Letter “A” is sensed as a black blotch decomposed into features by the brain and perceived as an “A” by our mind . ___________________________________ 5 ___________________________________ Top‐Down Processing ___________________________________ Information processing guided by higher‐level mental processes as we construct perceptions drawing on our experience and expectations. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ THE CHT ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 6 Psychology 8 ed., David Myers Module 12 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 2 ___________________________________ Making Sense of Complexity ___________________________________ Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complex images. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 7 “The Forest Has Eyes,” Bev Doolittle ___________________________________ Sensing the World ___________________________________ Senses are nature’s gift that suit the organism’s needs. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ A frog feeds on flying insects; A male silkworm moth is sensitive to female sex‐attractant odor; and we as human beings are sensitive to sound frequencies that represent the range of human voice. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 8 ___________________________________ Exploring the Senses ___________________________________ 1. What stimuli cross our threshold for conscious awareness? ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 2. Could we be influenced by stimuli too weak (subliminal) to be perceived? ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 3. Why are we unaware of unchanging stimuli, like a band‐aid on our skin? ___________________________________ 9 Psychology 8 ed., David Myers Module 12 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 3 ___________________________________ Psychophysics ___________________________________ A study of the relationship between physical characteristics of stimuli and our psychological experience of them. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Physical World Psychological World Light Brightness Sound Volume ___________________________________ Pressure Weight ___________________________________ Sugar Sweet ___________________________________ 10 ___________________________________ 22nd October 1850 Relative increase in mental intensity, [Fechner] realized, might be measured in terms of the relative increase in physical energy required to bring it about (Wozniak, 1999). ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Gustav Fechner (1801‐1887) 11 ___________________________________ Detection ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Absolute Threshold ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Intensity No No No Yes ___________________________________ Yes Observer’s Response ___________________________________ Detected Tell when you (observer) detect the light. Psychology 8 ed., David Myers 12 Module 12 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 4 OBJECTIVE 12‐2| Distinguish between Thresholds absolute and difference thresholds, and Proportion of “Yes” Responses 0.00 0.50 1.00 Absolute Threshold: Minimum stimulation needed to detect a particular stimulus 50% of the time. discuss whether we can sense stimuli below our absolute thresholds and be influenced by them. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 0 5 10 15 20 Stimulus Intensity (lumens) 25 13 ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Subliminal Threshold ___________________________________ When stimuli are below one’s absolute threshold for conscious awareness. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Kurt Scholz/ Superstock ___________________________________ 14 ___________________________________ Difference Threshold ___________________________________ Difference Threshold: Minimum difference between two stimuli required for detection 50% of the time, also called just noticeable difference (JND). Difference Threshold ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ No No Yes ___________________________________ Observer’s Response Tell when you (observer) detect a difference in the light. Psychology 8 ed., David Myers 15 Module 12 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 5 ___________________________________ Weber’s Law ___________________________________ Two stimuli must differ by a constant minimum percentage (rather than a constant amount), to be perceived as different. Weber fraction: k = δI/I. Stimulus Constant (k) Light 8% Weight 2% Tone 3% ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 16 ___________________________________ Signal Detection Theory (SDT) ___________________________________ Predicts how and when we detect the presence of a faint stimulus (signal) amid background noise (other stimulation). Assumes that there is no single absolute threshold and detection depends on: ___________________________________ Person’s experience Expectations Motivation Level of fatigue ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Carol Lee/ Tony Stone Images ___________________________________ 17 ___________________________________ SDT Matrix ___________________________________ The observer decides, whether she hears the tone or not, based on the signal being present or not. This translates into four outcomes. Decision ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Yes No Present Hit Miss Absent False Alarm Correct Rejection Signal ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 18 Psychology 8 ed., David Myers Module 12 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 6 OBJECTIVE 12‐3| Describe sensory Sensory Adaptation adaptation, and explain how we benefit from being unaware of changing stimuli. Diminished sensitivity as a consequence of constant stimulation. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Put a band aid on your arm and after a while you don’t sense it. ___________________________________ 19 ___________________________________ Now you see, now you don’t ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 20 OBJECTIVE 12‐4| Describe the interplay Selective Attention between attention and perception. Perceptions about objects change from moment to moment. Different forms of Necker cube become available to our perception, however, one can pay attention only to one aspect of the object. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Necker Cube Psychology 8 ed., David Myers 21 Module 12 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 7 ___________________________________ Inattentional Blindness ___________________________________ Daniel Simons, University of Illinois Inattentional blindness refers to inability to see a an object or a person amidst an engrossing scene. Simmons & Chabris (1999) showed that half of the observers failed to see the gorilla‐suited assistant in a ball passing game. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 22 ___________________________________ Change Blindness ___________________________________ Change blindness is a form of inattentional blindness, where two‐thirds of direction giving individuals failed to notice a change in the individual who was asking for directions. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ © 1998 Psychonomic Society Inc. Image provided courtesy of Daniel J. Simmons. 23 Psychology 8 ed., David Myers Module 12 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 8