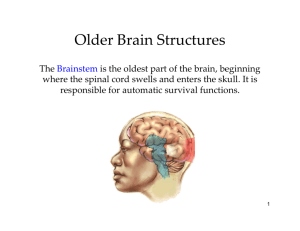
The Brain - Back - Henderson State University
advertisement

___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ PSYCHOLOGY ___________________________________ (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers ___________________________________ PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Worth Publishers, © 2007 1 ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ The Brain ___________________________________ Module 5 ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 2 ___________________________________ The Brain ___________________________________ The Brain ___________________________________ The Tools of Discovery ___________________________________ Older Brain Structures ___________________________________ The Cerebral Cortex Our Divided Brain ___________________________________ Left Brain‐Right Brain ___________________________________ 3 Psychology 8 ed., David Myers Module 5 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 1 OBJECTIVE 5‐1| Describe several techniques The Brain for studying the brain. ___________________________________ Techniques to Study the Brain ___________________________________ Brain lesion experimentally destroys brain tissue to study animal behaviors after such destruction. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Hubel (1990) ___________________________________ 4 ___________________________________ Clinical Observation ___________________________________ Clinical observations have shed light on a number of brain disorders. Alterations in brain morphology due to neurological and psychiatric diseases are now being catalogued. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Tom Landers/ Boston Globe ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 5 ___________________________________ Electroencephalogram (EEG) ___________________________________ An amplified recording of the electrical waves sweeping across the brain’s surface, measured by electrodes placed on the scalp. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ AJ Photo/ Photo Researchers, Inc. Psychology 8 ed., David Myers ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 6 Module 5 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 2 ___________________________________ PET Scan ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Courtesy of National Brookhaven National Laboratories PET (positron emission tomography) Scan a visual display of brain activity that detects a radioactive form of glucose while the brain performs a given task. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 7 ___________________________________ MRI Scan MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer‐ generated images that distinguish among different types of brain tissue. Top images show ventricular enlargement in a schizophrenic patient. Bottom image shows brain regions when a participants lies. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Both photos from Daniel Weinberger, M.D., CBDB, NIMH ___________________________________ ___________________________________ James Salzano/ Salzano Photo Lucy Reading/ Lucy Illustrations 8 OBJECTIVE 5‐2| Describe the components of Older Brain Structures the brainstem and summarize the functions of the brainstem, thalamus and cerebellum. Brainstem the oldest part of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells and enters the skull. Responsible for automatic survival functions. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 9 Psychology 8 ed., David Myers Module 5 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 3 ___________________________________ Brain Stem ___________________________________ Medulla [muh‐DUL‐uh] base of the brainstem, controls heartbeat and breathing. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Reticular Formation a nerve network in the brainstem that plays an important role in controlling arousal. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 10 ___________________________________ Brain Stem ___________________________________ Thalamus [THAL‐uh‐ muss] the brain’s sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem. It directs messages to the sensory areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 11 ___________________________________ Cerebellum ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ The “little brain” attached to the rear of the brainstem. It helps coordinate voluntary movements and balance. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 12 Psychology 8 ed., David Myers Module 5 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 4 OBJECTIVE 5‐3| Describe the structures and The Limbic System functions of the limbic system, and explain how one of these structures controls the Limbic System a doughnut‐shaped system of neural structures at the border of the brainstem and cerebrum, associated with emotions such as fear, aggression and drives for food and sex. It includes the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus. pituitary gland. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 13 ___________________________________ Amygdala ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Amygdala [ah‐MIG‐ dah‐la] two almond‐ shaped neural clusters linked to emotion of fear and anger. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 14 ___________________________________ Hypothalamus ___________________________________ Hypothalamus lies below (hypo) the thalamus; directs several maintenance activities like eating, drinking body temperature, and emotions. Helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 15 Psychology 8 ed., David Myers Module 5 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 5 ___________________________________ Reward Center ___________________________________ Rats cross an electrified grid for self‐stimulation, when electrodes are placed in the reward (hypothalamus) center (top picture). When the limbic system is manipulated rat will navigate fields or climb up a tree (bottom picture). ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Sanjiv Talwar, SUNY Downstate ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 16 OBJECTIVE 5‐4| Define cerebral cortex and The Cerebral Cortex explain its importance for the human brain. ___________________________________ The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres. The body’s ultimate control and information processing center. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 17 OBJECTIVE 5‐5| Identify the four lobes of the Structure of the Cortex cerebral cortex. ___________________________________ Each brain hemisphere is divided into four lobes, separated by prominent fissures. They are frontal lobes (forehead), parietal lobes (top to rear head), occipital lobes (back head) and temporal lobes (side of head). ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 18 Psychology 8 ed., David Myers Module 5 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 6 OBJECTIVE 5‐6| Summarize some of the Functions of the Cortex findings on the functions of the motor cortex and the sensory cortex, and discuss the Motor Cortex area at the rear of the frontal lobes controls voluntary movements. Sensory Cortex (parietal cortex) receives information from skin surface and sense organs. importance of the association areas. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 19 ___________________________________ Visual Function ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Courtesy of V.P. Clark, K. Keill, J. Ma. Maisog, S. Courtney, L.G. Ungerleider, and J.V. Haxby, National Institute of Mental Health Functional MRI scan shows the visual cortex activates as the subject looks at faces. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 20 ___________________________________ Auditory Function ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Functional MRI scan shows the auditory cortex is activate in patients who hallucinate. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 21 Psychology 8 ed., David Myers Module 5 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 7 ___________________________________ Association Areas ___________________________________ More intelligent animals have increased “uncommitted” or association areas of the cortex. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 22 OBJECTIVE 5‐7| Describe the five brain areas Language that would be involved if you read this Aphasia is an impairment of language, usually caused by left hemisphere damage either to Broca’s area (impaired speaking) or to Wernicke’s area (impaired understanding). sentence aloud. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 23 ___________________________________ Specialization & Integration ___________________________________ Brain activity when hearing, seeing, and speaking words ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 24 Psychology 8 ed., David Myers Module 5 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 8 OBJECTIVE 5‐8| Discuss brain’s plasticity The Brain’s Plasticity following injury or illness. ___________________________________ Brain is sculpted by our genes but also by our experiences. ___________________________________ Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to modify itself after some type of injury or illness. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 25 OBJECTIVE 5‐9| Describe split‐brain research, Our Divided Brain and explain how it helps us to understand the functions of our left and right hemispheres. Our brain is divided into two hemispheres. Left hemisphere processes reading, writing, speaking, mathematical, comprehension skills, and thus termed as the dominant brain in the 1960s. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 26 ___________________________________ Splitting the Brain ___________________________________ A procedure in which the two hemispheres of the brain are isolated by cutting the connecting fibers (mainly those of the corpus callosum) between them. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Psychology 8 ed., David Myers ___________________________________ Martin M. Rother Courtesy of Terence Williams, University of Iowa Corpus Callosum ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 27 Module 5 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 9 ___________________________________ Split Brain Patients ___________________________________ With the corpus callosum severed, objects (apple) presented in the right visual field can be named. Objects (pencil) in the left visual field cannot. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 28 ___________________________________ Divided Consciousness ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 29 ___________________________________ Try This! ___________________________________ Try drawing two shapes with both of you hands simultaneously. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ BBC Psychology 8 ed., David Myers 30 Module 5 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 10 ___________________________________ Non‐Split Brains ___________________________________ People with intact brains also show left‐right hemispheric differences in mental abilities. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ A number of brain scan studies have shown normal individuals engage their right brain when they engage in a perceptual task, and left brain when carrying out a linguistic task. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 31 OBJECTIVE 5‐10| Discuss the relationship Brain Organization & Handedness among brain organization, handedness, and mortality. Is handedness inherited? Yes. Archival and historic studies to modern medical studies point that right hand is preferred. This suggests, genes and/or prenatal factors influence handedness. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 32 ___________________________________ Is it All Right to be Left Handed? ___________________________________ Being a left hander is difficult in a right‐handed world. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 33 Psychology 8 ed., David Myers Module 5 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 11 ___________________________________ Is it All Right to be Left Handed? ___________________________________ The percentage of left‐handers decreases sharply in samples of older people (Coren, 1993). ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 34 Psychology 8 ed., David Myers Module 5 PowerPoint Slides, Aneeq Ahmad 12