Intro ws complete - SCH4U1-CCVI
advertisement

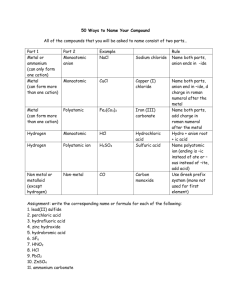
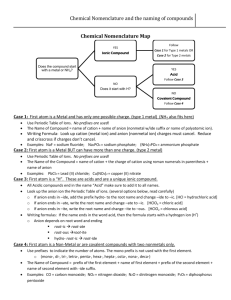
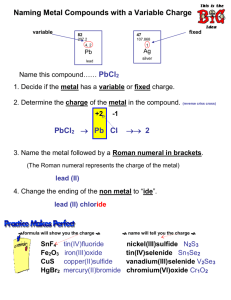
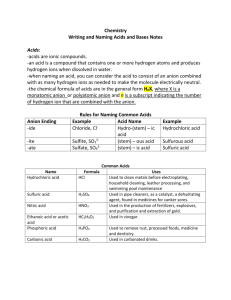
COMPOUND BINARY COVALENT two nonmetals only - the most electropositive element first - the most electronegative element second - use prefixes in the name to show the #s of each atom in the compound - the prefix mono isdropped from the first element - doesn’t apply to H compounds - attach the suffix “ide” to the 2nd element eg. P2O5 diphosphorus pentoxide SO3 sulphur trioxide IONIC at least one metallic and one nonmetallic element present BINARY two elements only UNIVALENT METAL MULTIVALENT METAL ie. Group 1 & 2 metals and Al3+, Zn2+ and Ag1+ ie. All other metals - metal 1st with no name change - non-metal 2nd and with the suffix changed to “-ide” eg. CaCl2 calcium chloride POLYATOMIC more than two elements UNIVALENT METAL OR POSITIVE ION WITH KEY ANION WITH ANION DERIVED FROM KEY HYDRATE salts containing bound water WITH ACID ANION ie. Group 1 & 2 metals and Al3+, Zn2+ and Ag1+ AND +1 H1+ and NH 4 - metal 1st - Roman numeral in brackets to show charge on the metal ion - non-metal 2nd with the suffix “-ide” eg. FeCl3 – iron (III) chloride - same as with Binary elements eg. Ca2+ - Calcium MULTIVALENT METAL - same as with Binary elements eg. Sn2+ - tin(II) - name the ionic salt then by the prefix for the # of H2O molecules and then the word hydrate eg. CaCl2·2H2O calcium chloride dihydrate - name the - name the derived memorized anion based upon key anion the key anions list (see using the following over) rules; eg.. SO -2 , 4 −2 CrO 4 , etc. 1 more O: per___ate 1 less O : ___ite 2 less O : hypo___ite eg. Ca(ClO2)2 calcium chlorite Sn(ClO)2 tin(II) hypochlorite - name the acid anion by using prefixes to denote the # of H’s combined with the anion then followed by the anion name eg. SnHPO4 tin (II) hydrogen phosphate Sn(H2PO3)2 tin (II) dihydrogen phosphite Page 9 of 15 POLYATOMIC IONS AND THEIR NAMES -2 SO4 sulphate -3 PO4 phosphate -2 CO3 carbonate -1 NO3 nitrate -1 ClO3 chlorate -1 BrO3 bromate -1 IO3 iodate -2 CrO4 chromate -2 Cr2O7 dichromate -1 CH3CO2 acetate -1 C2H3O2 acetate C2O −4 2 -1 MnO4 S2O −2 3 -1 OH CN-1 OCN-1 SCN-1 +1 NH4 oxalate permanganate thiosulphate ARCHAIC ION NAMES AND THEIR CHARGES GREEK PREFIXES Cu+1 Cu+2 cuprous cupric 1/2 hemi 1 mon Fe+2 Fe+3 ferrous ferric 2 di 3 tri 4 tetra 5 penta 6 Hg+1 Hg+2 mercurous mercuric Sn+2 Sn+4 stannous stannic Pb+2 Pb+4 plumbous plumbic Au+1 Au2+ aurous auric Co+2 Co+3 cobaltous cobaltic Sb+3 Sb+5 stibnous stibnic ACID NOMENCLATURE RULES NB - use these rules when naming the water solutions of hydrogen compounds I hydrogen _____ide : hydro_____ic acid II hydrogen _____ate : _____ic acid III hydrogen _____ite : _____ous acid eg. H2S(aq) hydrosulphuric acid hexa HClO4 (aq) perchloric acid 7 hepta H3PO3 (aq) phosphorous acid 8 octa 9 nona 10 deca hydroxide cyanide cyanate thiocyanate ammonium Page 10 of 15