Crisis Prevention Institute's
advertisement

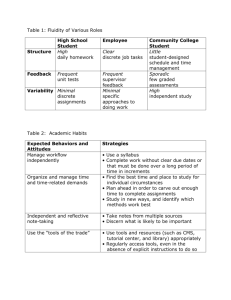
Using CPI Strategies (COPING) to Prevent/Respond to Challenging Behavior Lance L. Hawkins, M.Ed. Harford County Public Schools Adapted from CPI Nonviolent Intervention Crisis Training - 2012 What is the philosophy of the Nonviolent Crisis Intervention Program (CPI)? To provide the best care, welfare, safety, and security to both students and staff in crisis situations. What Is CPI? CPI Is…. • A behavioral management approach that provides for the Care, Welfare, Safety, and Security of all those who are involved in a crisis situation CPI Is Not… • A program to teach you how to physically restrain students/clients • A punitive approach to handling crisis • A means to dominate or retaliate in any crisis situation Who Can Use CPI? • • • • Administrators Teachers Counselors Staff Part I. The CPI Development Model The CPI Crisis Development Model Integrated Experience Crisis Development/Behavior Levels 1. Anxiety Examples: • pacing • fidgeting • hyper-verbal • withdrawn Staff Attitudes/Approaches 1. Supportive Examples: • listen • acknowledge • validate • assist The CPI Crisis Development Model Integrated Experience Crisis Development/Behavior Levels Staff Attitudes/Approaches 1. Anxiety 1. Supportive 2. Defensive 2. Directive Examples: • cursing • yelling • non-compliance Examples: • give options (includes both positive and negative) • set limits Unit 1: The CPI Crisis Development Model Integrated Experience Crisis Development/Behavior Levels Staff Attitudes/Approaches 1. Anxiety 1. Supportive 2. Defensive 2. Directive 3. Acting-Out Person Examples: • throwing • biting • hitting • kicking 3. Non-violent Physical Crisis Intervention Examples: • transport procedures • child’s control position • team control position Unit 1: The CPI Crisis Development Model Integrated Experience Crisis Development/Behavior Levels Staff Attitudes/Approaches 1. Anxiety 1. Supportive 2. Defensive 2. Directive 3. Acting-Out Person 4. Tension Reduction Examples: • tired • crying • embarrassed/ashamed 3. Non-violent Physical Crisis Intervention 4. Therapeutic Rapport Examples: • empathic listening • process/debrief Non-Verbal Behavior • Refers to the actions/attitudes of the staff members • Non-verbal behavior can determine the outcome of the crisis Integrated Experience Crisis Development/Behavior Levels 1. Anxiety Staff Attitudes/Approaches 1. Supportive Proxemics: Typically (in the U.S.) 1 ½ - 3 ft. Factors to consider: familiarity, family member, situation, culture, past experiences, age, size, health Integrated Experience Crisis Development/Behavior Levels 1. Anxiety Staff Attitudes/Approaches 1. Supportive Proxemics: • Typically (in the U.S.) 1 ½ - 3 ft. • Factors to consider: familiarity, family member, situation, culture, past experiences, age, size, health Kinesics: (Also known as body language) • Four Components: • Facial Expression , Gestures, Posture, Movement Unit 2 Crisis Development/Behavior Levels 1. Anxiety Staff Attitudes/Approaches 1. Supportive Proxemics: Typically (in the U.S.) 1 ½ - 3 ft. Factors to consider: familiarity, family member, situation, culture, past experiences, age, size, health Kinesics: Four Components: Facial Expression , Gestures, Posture, Movement CPI Supportive Stance: Reasons for using: • Safety • Non – threatening • Shows respect for personal space Crisis Development/Behavior Levels 1. Anxiety Level 1 Staff Attitudes/Approaches 1. Supportive Proxemics: Typically (in the U.S.) 1 ½ - 3 ft. Factors to consider: familiarity, family member, situation, culture, past experiences, age, size, health Kinesics: Four Components: Facial Expression , Gestures, Posture, Movement CPI Supportive Stance: Reasons for using: • Safety • Non – threatening • Shows respect for personal space Paraverbal Communication: “how we say, what we say” Three Components: Tone, Volume, Cadence Verbal Intervention (Levels of verbal escalation) Crisis Development/Behavior Levels 2. Defensive 2. Directive 3. Release Emotional Outburst 4. Intimidation threats 2. Refusal Non-compliance 5. Tension Reduction Decrease in physical and emotional energy Level 2 Staff Attitudes/Approaches 1. Questioning Can be rational (info-seeking) or evasive (challenging) Crisis Development/Behavior Levels 2. Defensive 2. Directive 3. Release Emotional Outburst 4. Intimidation threats 2. Refusal Non-compliance 5. Tension Reduction Decrease in physical and emotional energy Level 2 Staff Attitudes/Approaches 1. Questioning Can be rational (info-seeking) or evasive (challenging) Interventions: 1. Questioning Info-seeking: answer the question challenging: redirect/set limits 2. Refusal Set limits 3. Release allow time to vent, may need to isolate individual or move class 4. Intimidation document; get 2nd staff member to assist (still hands-off) 5. Tension Reduction re-establish therapeutic rapport Verbal Intervention Keys to Setting Limits • Clear/Simple • Reasonable • Enforceable Empathic Listening • Be nonjudgemental • Give undivided Attention • Active Listening (focus on feelings, not just facts) • Allow quiet time/wait time for reflection • Repeat statements to clarify message Important Points to Consider… Important Points to Consider Integrated Experience – Behaviors and attitudes of staff will impact behaviors and attitudes of students (and vice versa) Important Points to Consider Integrated Experience – Behaviors and attitudes of staff will impact behaviors and attitudes of students (and vice versa) Precipitating Factors – internal and external causes of acting out behavior over which staff have little or no control. Important Points to Consider Integrated Experience – Behaviors and attitudes of staff will impact behaviors and attitudes of students (and vice versa) Precipitating Factors – internal and external causes of acting out behavior over which staff have little or no control. Rational Detachment – Ability to stay in control of our own behaviors and not take the acting-out behavior personally Fear and Anxiety (psychological and physiological responses) Harmful • Freeze • Overreacting • Inappropriate responses Verbally Physically Helpful • Increase in speed and strength • Sharpened sensors • React quicker to escalation Are there any questions? Thank You Feel free to contact me for further questions @ Lance.hawkins@hcps.org