MEDIA Effects - WordPress.com
advertisement

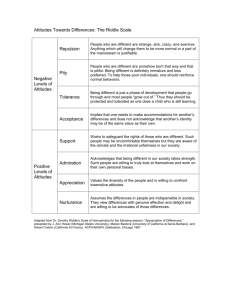
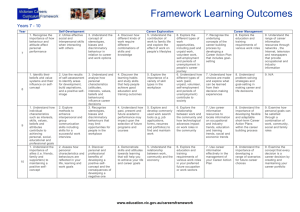
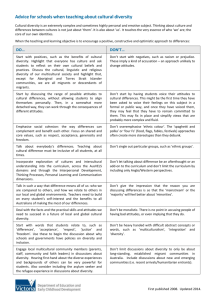
1-1 MDST 1010 CHAPTER 15 MEDIA EFFEC TS 15-2 MEDIA HISTORY In 1938, in New York City, Orson Welles broadcast a radio dramatization of “War of the Worlds” by H.G. Wells 15% of listeners ignored the repeated pointer that the broadcast was actually fiction, and took action, preparing to flee, etc. The 60-minute show portrayed a Mars blastoff, military conflict, and destruction of New York City Although it is not possible that all of this could take place in less than one hour, more than 1 million people believed it to be real 15-3 “MEDIA Effects” Theories Media theorists have studied the effects of consuming media on people to determine how media content will influence people Attitudes and behaviours are studied in response to consumption of specific media Laswell Model of Communication 15-4 MAGIC BULLET THEORY People internalize media messages without thinking about them critically Also known as the ‘Hypodermic Needle’ theory Has been challenged or nuanced in subsequent theories 1-5 ATTITUDES PRODUCED BY MEDIA EFFECTS Influencing Opinion Media effects on opinion are generally seen to be gradual rather than instantaneous Media sometimes play an agenda-setting role, emphasizing which issues are the important issues of the day Attitudes influenced by media can play a role in changing public opinion, but sometimes the public can reject media messages wholesale 15-6 AGENDA SETTING ROLE OF MEDIA The media tell us what to think about rather than what to think 1-7 CASE STUDY: KEYSTONE PIPLINE Saturday's Globe and Mail coverage 1-8 MINIMALIST EFFECTS THEORY The media have some effect on the audience, but interpersonal communications play a stronger role in how people interpret the news Opinion leaders in a social group will provide a critical framework for their peer or social group, which influences how people understand and interpret media messages 1-9 CUMULATIVE EFFECTS THEORY Media messages are strengthened with repetition Media effects are therefore gradual and cumulative 1-10 EFFECTS ON CULTURAL VALUES Values Innovations diffuse quickly through the media The rate of diffusion of new ideas depends on audience awareness, interest, and evaluation Cultural Imperialism A globally dominant culture may influence diverse local cultures to adopt their (foreign) cultural values e.g. norms of dress, behaviours, etc. The risk is a cultural homogenization that does not necessarily make sense in relation to local cultural traditions and values 1511 VIOLENCE EFFECTS Dr. George Gerbner The Killing Screens 1-12 NEXT WEEK • Media and Governance - Chapter 17 • More Digital Media Studies Project Presentations! 1-13