De-Escalation Techniques: Calming the Storms Presentation
advertisement

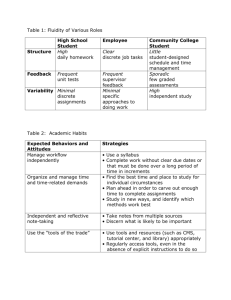
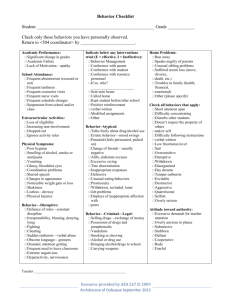
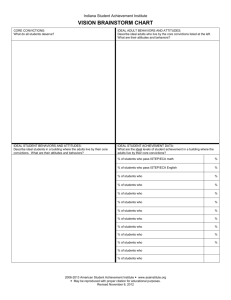
De-Escalation: Calming the Storms Presenter: Mike Paget mpaget@ed.sc.gov Recognizing emotional and behavioral escalation This presentation is based on material from the Crisis Prevention Institute CPI provides training on topics of crisis prevention and crisis management, including physical intervention The priorities of CPI are to ensure safety, and to prevent escalation, including physical restraint Think about a situation you have been in where things were getting tense and out-of-control What clued you in that things were escalating? What were your thoughts? What were your feelings? How did you respond? How did things turn out? Did the experience have any aftereffects? CPI Crisis Development Model Integrated Experience Behaviors and attitudes of adults impact on the behaviors and attitudes of children and youth Crisis Development/Behavior Levels 1. 2. Anxiety notable change or increase in someone’s normal behavior Adult Attitudes/Approaches 1. non-judgmental and empathic 2. Defensive (overt behaviors) beginning to lose rationality/challenge authority 3. Acting out person 3. total loss of rationality and control 4. Tension reduction • decrease in energy level both physical & emotionally • beginning to regain control Be supportive 4. Be directive • give control by setting limits; • give options and choices to allow child/youth to regain rational control through appropriate self-directed behavior Non violent Physical Crisis Intervention (NVPCI) non harmful control techniques used to help individual regain control Therapeutic rapport begin to reestablish communication and regain trust Experiment: Let’s play the mime game 2 volunteers Without words, show “anger” “happiness” “fear” Nonverbal Behavior 7% Verbal 38% Paraverbal 55% Non verbal Proxemics Definition: The area where you feel comfortable Factors influencing: size gender location age experience frame of mind sense of control culture history personal hygiene Note: Personal property functions like an extension of personal space Kinesics Examples eye contact avoiding staring crossed arms eye rolling clenching fists huffing pacing Signs of Anxiety shrugging shoulders punching the air clenched teeth eyebrows perspiring Paraverbal Communication: Definition: Vocal part of speech excluding words. How we say what we say. Elements: Volume- appropriate for situation Cadence: rate /rhythm at which we speak) Tone of voice (where is the inflection) Arguing Have you ever gotten into an argument that became a real power struggle? What makes these arguments worse? What helps you avoid or back out of these arguments? Verbal Escalation Continuum 3. Release: loss of verbal control 4. Intimidation (threats) Take it seriously, document, report, reflect, get help Allow venting, isolate, focus on safety, listen 2. Refusal- overt noncompliance Set limits 1. Questioning 5. Tension Reduction Therapeutic rapport Information seeking-answer Challenging Ignore, redirect, set limits Talking Tips and Techniques Do: Do not: Listen Talk less Speak softly Respect privacy Remain calm Embarrass Call out in front of others Criticize Over-react Use sarcasm Fake attention Rational Detachment Definition: The ability to stay in control of one’s own behavior and not take acting-out personally. before •Good health •Meditation •Prayer •Training •Planning during •Calm •Breath •Team work •Humor •Follow plan after •Debrief •Vent •Evaluate •Modify plan •Leave work at work Rational Detachment Don’t •Lose cool Do •Use calm voice •Embarrass •Maintain respect for child/youth •Use sarcasm •Listen •Bring up the past •Talk less •Fake attention •Use privacy •Touch •Allow time •Become a precipitating factor •Praise when appropriate How the adult reacts makes matters better or worse The behaviors and attitudes of adults impact on the behaviors and attitudes of children and youth, and vice versa Anxiety ----- Support Defensive ----- Directive AOP ----- NVPCI Tension reduction Therapeutic rapport Adult Fear and Anxiety Fear: of the unknown – “What is happening?” Anxiety: fear of the known – “Can I handle this?” Productive 1. Heightened senses 2. Shortened reaction time 3. Increase in speed and strength Unproductive Minimize 1. freezing 2. Overreaction 3. responding inappropriately Maximize: 1. understand your fears 2. learn techniques to protect yourself 3. get support: teamwork 4. learn physical intervention skills After the storm Learning, processing, closure, moving forward CO- Control Orient Listen to the AOP or adult PING- Patterns Investigate and Improvement Negotiate Give Are you interested in more training? The Crisis Prevention Institute has a number of trainings primarily intended for adults who work with children and youth CPI also has useful training material for parents and home care-givers