Affordable Community Swimming Pools Brochure
advertisement

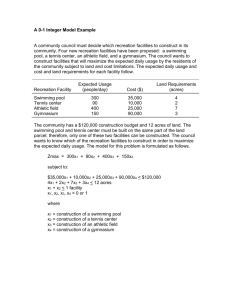
A summary of the contents e t i s b e w px s a e. nc a uid g _ st o c d_ an _ n sig e g/d n i n lan p s__ e i t ili ac f / g .or d n gla n e ort p w.s w ://w p t ht e ic w e N v d a n o o y la d a lo n w o d + le b a D A C s t u Affordable Community Swimming Pools Creating sporting opportunities in every community December 2011 There are many permutations for community swimming pools ranging from 4 lane to 8 lane pools which may also be combined with a secondary pool. In addition the pools may be enhanced by the installation of movable floors and booms. More water space and greater flexibility through the use of booms and movable floors is very desirable. However these come with a significant increase in both capital and running costs. It is therefore critical for the success of any pool project that the Strategic planning A seven step process is illustrated to create a brief for the ‘The Right Swimming Pool’. Further advice is being developed by Sport England and the Amateur Swimming Association. It aims to ensure that key issues such as supply and demand, site location, the levels of sporting activities and option appraisals are properly considered. 1 A range of indicative designs illustrate tightly planned, functionally efficient and economical building structures that can: • Comply with best practice standards • Be quickly constructed • Be tailored to individual sites to create architectural solutions that enhance the local environment • Create high levels of customer appeal • Operate at a surplus (or with reduced subsidies). B:B C:C DWC First aid 40 spectator viewing places FWC MWC A:A Office Reception Plant CPF D.Ch / WC V V Sh Sh A:A Pool hall Changing Sh Sh Sh BC Sh Sh Pool Store 25 temporary pool side seating places B:B C:C Sh Sh DWC F/D/G F/D/G F/D/G F/D/G Cl.St D:D D:D B:B Floor plan of 6 lane pool A:A SUPPLY AND DEMAND ISSUES Identify the issues of supply and demand that need to be addressed by any proposals for modernising or building new pools. (For example this will include the age and condition of existing pools as well as any plans for new pools, areas of housing growth or significant population change.) STRATEGIC CONSIDERATIONS 2 Identify if the site or sites are a priority for swimming provision or other complementary activity in local plans or strategies. 3 Identify the types of activities e.g. competition, training; the level of use such as community use, regional club use; and how much time and space will be needed. 4 Develop and review the different options that will meet the future aquatic needs of the area. (For example are there proposals for new sports halls, schools or health facilities?) TYPE, LEVEL AND AMOUNT OF ACTIVITY (It is important that the ASA are fully involved at this step to advise on the requirements for club and performance swimming and other aquatics disciplines.) DEVELOPING AND REVIEWING THE OPTIONS (For example this might include refurbishing existing pools, the number and location of pools, the role of other providers.) DEVELOPING THE PROJECT BRIEF 5 The project team will develop the selected option from high level requirements into a project brief that defines what is needed: the amount of water space, number of pools, use of movable floors and booms etc. 6 This step brings together all the information collected and the decisions made and determines whether there is a viable sport and business case. 7 At this step the decision is made either to proceed with an affordable and viable option or go back to an earlier step and review the requirements / identify an alternative solution. THE BUSINESS CASE / VALUE FOR MONEY APPRAISAL THE DECISION November Revision 002 5 Capital costs © Sport England 2011 An elemental cost breakdown is provided for alternative sizes of pools along with the indicative extra costs for additional elements that might be required for some locations (3rd Q – 2011). The base construction costs range from £2.1 m to £4.0 m. D:D DWC A clear understanding of what is required is crucial to the long term success of any pool project and it is important that the project is developed in a consistent and logical way. Sport England and the ASA are finalising a ‘Developing the Right Swimming Pool’ document that should be followed for every pool project. The recommended key steps are set out below: The 7 Step Process Design They include 25m pool size options from 4 to 8 lanes, and with a secondary pool. CAD drawings can be downloaded from the Sport England web site. project brief is based on clearly articulated needs and a strong evidence base. A:A Typical costs of the base construction: 4 Lanes 5 Lanes 6 Lanes 6 Lanes + Secondary pool 8 Lanes 8 Lanes + Secondary pool = = = = = = £ 2.1 m £ 2.6 m £ 2.8 m £ 3.4 m £ 3.4 m £ 4.0 m Overview The new information is aimed at the early briefing and design stages of swimming pool projects and aims to give a better understanding of the interrelationships between the: • • • • • • Design Specifications and sustainability Capital funding Programmes of use Operating budgets Need for subsidies. Potential uses include: • • • • • • Developing feasibility studies and option appraisals Establishing a robust project brief Developing the business plan and operational budget Selecting a procurement route and project programme Validate key project details Forming a template for a future project. It is an essential reference for new community swimming projects or where the rationalisation of the existing swimming pool stock is being considered. The study has a particular focus on the ‘affordability’ and ‘future financial sustainability’ of swimming pools but at the same time it illustrates how new projects can meet a full range of community needs and comply with best practice standards. The use of a ‘one-stop-shop’ procurement route is also illustrated that can speed up and simplify the planning, design and construction processes. B:B The base construction costs range from £2.1 m to £4.0 m The operating budget can create a surplus of circa £24 k / year C:C D:D Pool hall Changing Plant A new swimming pool can be opened within 24 months of the decision to proceed. B:B C:C D:D Typical section A:A A:A Plant Pool Store Pool hall Plant A:A First Aid A:A Changing Reception T u e 1 2 3 4 5 6 W e d 1 2 3 4 5 6 T h u 1 2 3 4 5 6 21.30 22.00 20.30 21.00 19.30 20.00 18.30 19.00 17.30 18.00 16.30 17.00 15.30 16.00 14.30 15.00 13.30 14.00 12.30 13.00 11.30 12.00 11.00 9.30 10.00 9.00 8.00 7.00 6.00 Lane 1 2 3 4 5 6 10.30 The indicative specification details that are included in the costs are in line with current best practice. They cover building fabric, structural design, energy / sustainability and building services issues. M o n 8.30 Key factors for achieving a ‘break even’ operating budget are discussed along with the various aspects of creating a viable business plan for the catchment market. 7.30 Energy / sustainability / specification issues 6.30 Operational budget and programme of use Indicative operating budgets are shown for the various sizes of swimming pool and for a typical programme of use. The key assumptions such as pricing, user through put and staff structures are also indicated. The analysis suggests that swimming pools with 6 lanes (and more) are most likely to operate on a ‘break even’ basis, subject to market catchment and business planning considerations. S a t 1 2 3 4 5 6 S u n 1 2 3 Main 4 5 6 ‘Linear’ Options for reconfiguring the main elements to suit individual sites The reception and support spaces may be reduced if the Entrance building can be linked to suitable existing accommodation Indicative programme of use (6 lane pool) Activity Key Lane (fitness) swimming M o n Casual swimming Swimming Clubs / Squads T u e 1 2 3 4 5 6 W e d 1 2 3 4 5 6 T h u 1 2 3 4 5 6 F r i 1 2 3 4 5 6 S a t 1 2 3 4 5 6 Learn to Swim (beginner to adult) Schools Specialist sessions (women only / aquafit / canoeing etc) Private Hire / Galas Staff Training / Maintenance Closed S u n 21.30 22.00 20.30 21.00 19.30 20.00 19.00 18.30 18.00 17.30 17.00 16.30 16.00 15.30 14.30 15.00 14.00 13.30 13.00 12.30 12.00 11.30 11.00 10.30 10.00 9.30 9.00 8.30 8.00 7.30 7.00 Lane 1 2 3 4 5 6 Reception / Control Spectator viewing pool - term time (39 weeks) 6.30 Typical programme of use for a 6 lane pool 1 2 3 4 5 6 6.00 F r i Additional details are given on the internal areas of the range of buildings, the area ratios of main elements to the size of the pool water and calculations for the changing rooms against the programmes of use that are assumed in the operational budget. Pool Hall Plant / Store Changing Plant linked to deep end ‘Square’ Reception / Control Entrance Plant / Store Changing Viewing Alternative Spectator Viewing Pool Hall 1 2 3 4 5 6 Activity Key View of the entrance October Revision 001 Lane (fitness) swimming 21 © Sport England 2011 Entrance Casual swimming ‘L-shaped’ Swimming Clubs / Squads Learn to Swim (beginner to adult) Schools Plant / Store Reception / Control Viewing Specialist sessions (women only / aquafit / canoeing etc) Private Hire / Galas Staff Training / Maintenance Pool Hall Changing Closed No Spectator viewing Alternative external cladding materials can be used to suit the particular character and environmental requirements of each site.