Practice test Chapters 8 & 9.
advertisement

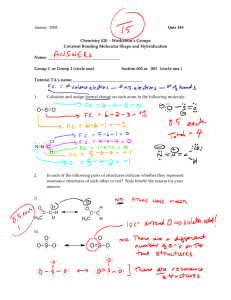
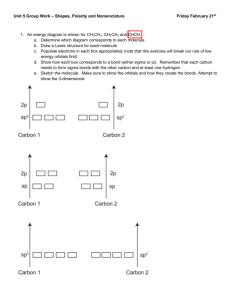
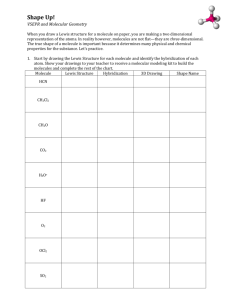
AP Chemistry – Practice Test for Chapters 8 & 9 Bonding, VSEPR, Molecular Shapes, Hybridization Multiple Choice: 1. All of these molecular shapes can be explained by dsp3 hybridization of electrons on the central atom EXCEPT a) linear b) T-shape c) see-saw d) octahedral e) trigonal bipyramid 2. The Lewis dot structure of which of the following molecules shows only one unshared pair of valence electrons? a) Cl2 b) N2 c) NH3 d) CCl4 e) H2O2 3. As indicated by Lewis structures, which of the following would probably not exist as a stable molecule? a) CH3OH b) CH2O c) CH3O d) CH4 e) C3H4 4. Which of the following molecules is predicted to have the greatest dipole moment? a) CO2 b) HBr c) HCl d) HI e) O2 5. All species below have Lewis dot diagrams that illustrate the octet rule EXCEPT a) NO3¯ b) NH3 c) NH4+ d) N2 e) NO2 6. The shape of the IO3¯ ion is best described as a) see-saw b) T-shaped c) tetrahedral d) trigonal planar e) trigonal pyramidal 7. Consider a molecule of 1-chloro-2-butyne, represented below: H H | | H ⎯ C ⎯ C ≡ C ⎯ C ⎯ Cl | | H H Which gives the correct specification of sigma and pi bonds in this molecule? a) 6 sigma, 5 pi b) 8 sigma, 1 pi c) 8 sigma, 3 pi d) 9 sigma, 2 pi e) 10 sigma, 1 pi 8. In the molecule C2H4 the valence orbitals of the carbon atoms are: a) not hybridized b) sp hybridized c) sp2 hybridized d) sp3 hybridized e) dsp3 hybridized 9. For which of the following molecules are resonance structures necessary to describe the bonding satisfactorily? a) H2S b) CO2 c) PF3 d) SO2 e) OF2 10. The SbCl5 molecule has a trigonal bipyramid structure. Therefore, the hybridization of Sb orbitals should be: a) sp2 b) sp3 c) dsp2 d) dsp3 e) d2sp3 Free Response: 1. Draw Lewis electron-dot structures for each of the following species, give the arrangement of electrons, name the molecular shape of each species, state whether the molecule is polar or non-polar, state whether resonance is required to describe the molecule, and identify the type of hybridization on the central atom. a) carbon dioxide b) hydrosulfuric acid c) sulfur trioxide d) thiocyanate ion e) chlorite ion f) ozone ( O3) g) chlorine trifluoride h) phosphorus pentachloride i) selenium dichloride j) ammonia 2. Draw the Lewis dot structure for the C2H4 molecule and name the type of hybridization of the carbon atoms. 3. Draw the Lewis dot structure for the SF6 molecule and name the type of hybridization of the sulfur atom. 4. Two distinct molecules of difluorodiazine (N2F2) exist. a) Draw the Lewis dot structures for both molecules. (Hint: FNNF) b) What are the N-N-F bond angles in each molecule? c) What is the polarity of each molecule? 5. a) Atom A has electronegativity 2.8 on the Pauling scale. If the electronegativities of atoms X, Y and Z are 2.3, 3.0 and 4.0, respectively, what is the order of the diatomic species AX, AY, AZ and AA (A2) in terms of the magnitude of their dipole moment, from smallest (left) to largest (right)? b) The electronegativities of carbon, hydrogen, fluorine and bromine are 2.5, 2.1, 4.0 and 2.8, respectively. Which of the following molecules has the largest dipole moment? CH4 , CBr4 , CF4 , CH3Br. Give a brief explanation. 6. Use simple structure and bonding models to account for each of the following. a) The bond length between the two carbon atoms is shorter in C2H4 than in C2H6. b) The H-N-H bond angle is 107.5° in NH3. c) The bond lengths in SO3 are all identical and are shorter than a sulfur-oxygen single bond. d) The I3- ion is linear.