Print › Unit 3 - How our government works | Quizlet
advertisement
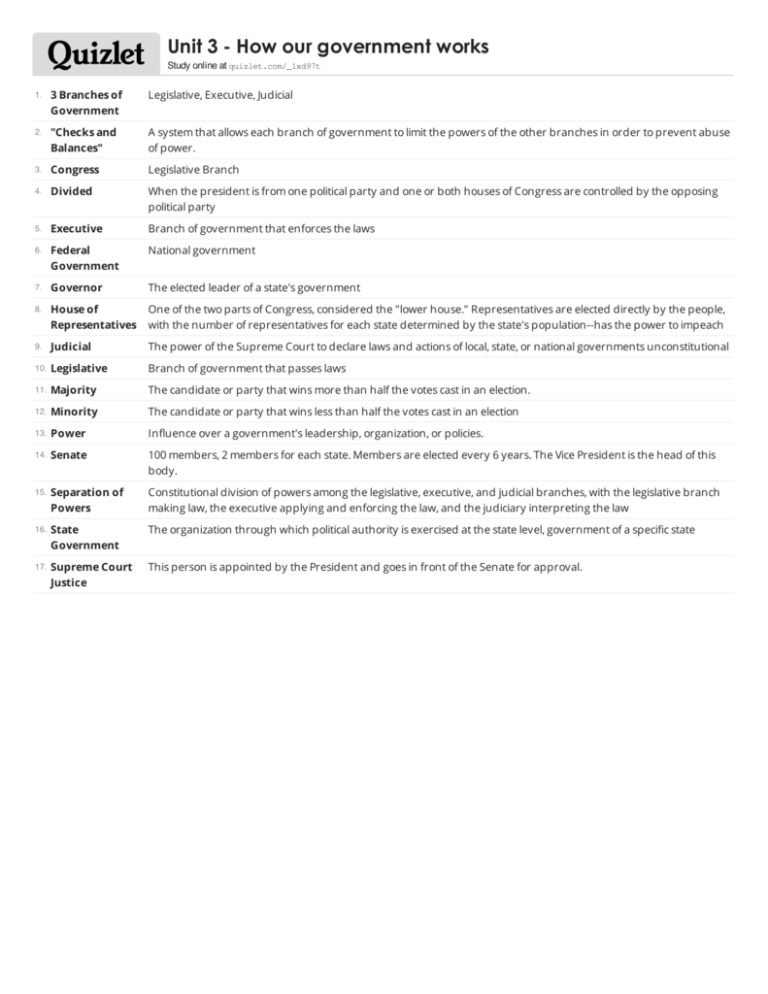
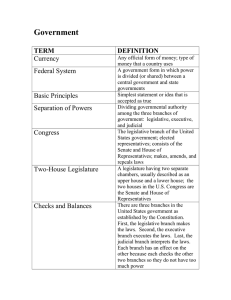
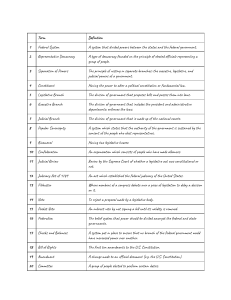
Unit 3 - How our government works Study online at quizlet.com/_1xd97t 1. 3 Branches of Government Legislative, Executive, Judicial 2. "Checks and Balances" A system that allows each branch of government to limit the powers of the other branches in order to prevent abuse of power. 3. Congress Legislative Branch 4. Divided When the president is from one political party and one or both houses of Congress are controlled by the opposing political party 5. Executive Branch of government that enforces the laws 6. Federal Government National government 7. Governor The elected leader of a state's government 8. House of Representatives One of the two parts of Congress, considered the "lower house." Representatives are elected directly by the people, with the number of representatives for each state determined by the state's population--has the power to impeach 9. Judicial The power of the Supreme Court to declare laws and actions of local, state, or national governments unconstitutional 10. Legislative Branch of government that passes laws 11. Majority The candidate or party that wins more than half the votes cast in an election. 12. Minority The candidate or party that wins less than half the votes cast in an election 13. Power Influence over a government's leadership, organization, or policies. 14. Senate 100 members, 2 members for each state. Members are elected every 6 years. The Vice President is the head of this body. 15. Separation of Powers Constitutional division of powers among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, with the legislative branch making law, the executive applying and enforcing the law, and the judiciary interpreting the law 16. State Government The organization through which political authority is exercised at the state level, government of a specific state 17. Supreme Court Justice This person is appointed by the President and goes in front of the Senate for approval.