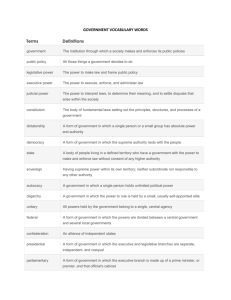
Term Definition 1 Federal System A system that divided powers between the states and the federal government. 2 Representative Democracy A type of democracy founded on the principle of elected officials representing a group of people. 3 Separation of Powers The principle of vesting in separate branches: the executive, legislative, and judicial powers of a government. 4 Constituent Having the power to alter a political constitution or fundamental law. 5 Legislative Branch The division of government that proposes bills and passes them into laws. 6 Executive Branch The division of government that includes the president and administrative departments; enforces the laws. 7 Judicial Branch The division of government that is made up of the national courts. 8 Popular Sovereignty A system which states that the authority of the government is sustained by the consent of the people who elect representatives. 9 Bicameral Having two legislative houses. 10 Confederation An organization which consists of people who have made alliances. 11 Judicial Review Review by the Supreme Court of whether a legislative act was constitutional or not. 12 Judiciary Act of 1789 An act which established the federal judiciary of the United States. 13 Filibuster Where members of a congress debate over a piece of legislation to delay a decision on it. 14 Veto To reject a proposal made by a legislative body. 15 Pocket Veto An indirect veto by not signing a bill until its validity is removed. 16 Federalism The belief system that power should be divided amongst the federal and state governments. 17 Checks and Balances A system put in place to ensure that no branch of the federal government would have increased power over another. 18 Bill of Rights The first ten amendments to the U.S. Constitution. 19 Amendment A change made to an official document (e.g. the U.S. Constitution). 20 Committee A group of people elected to perform certain duties.