2.3 Carbs and Lipids Notes 14-15
advertisement

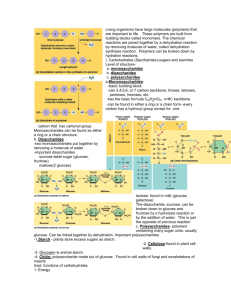
2.3 Carbohydrates and Lipid Notes IB Biology HL 1 Mrs. Peters Fall 2014 U1. Monosaccharides • Monosaccharides: simplest carbohydrates simple sugars General formula (CH2O)n Major nutrients for cells U1. Monosaccharides • Monosaccharides: Linked using condensation reaction to disaccharides and polysaccharides Ex: glucose, fructose, galactose C6H12O6 U1. Monosaccharides • Glucose: energy source carried by the blood to cells • Galactose: used to make milk U1. Monosaccharides • Fructose: used to make fruit sweet tasting and attractive to animals U1. Disaccharides • Disaccharides: • two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic linkage (covalent bond between monosaccharides using condensation) Ex: sucrose; maltose; lactose U1. Disaccharides • Sucrose: glucose + fructose; carried by phloem to transport energy to cells in plants U1. Disaccharides • Maltose: 2 glucose; used in creating starch • Lactose: glucose + galactose; the sugar in milk; source of energy U1. Polysacchrides • Polysaccharides: storage and structural macromolecules made from a 40- over 1000 monosaccharides using the condensation reaction Ex: starch, glycogen, cellulose U1.Polysaccharides Storage Polysaccharides Starch: found in plants, polymer made of long chains glucose molecules that coil into a helical shape, used for energy, compact shape and insoluble U1. Polysaccharides Storage Polysaccharides **Glycogen: found in animals, a highly branched polymer of glucose (short term energy storage in liver and muscle cells), insoluble U1. Polysaccharides Structural Polysaccharides Cellulose: used to make strong fibers; major components on plant cell walls, long straight chains of glucose Bioweb.wku.edu U2. Fatty Acids Fatty Acid: a long hydrocarbon “tail” with a carboxyl group at the head end U2. Fatty Acids Fatty Acid Types: Saturated: have no double bonds in the carbon chains Unsaturated: have double bonds in carbon chains U2. Fatty Acids Fatty Acid Types: Monounsaturated: have one double bond in carbon chains Polyunsaturated: have more than one double bond in carbon chains U3. Unsaturated Fatty Acids Types of Unsaturated Fatty Acid Structures: • cis-fatty acids: the hydrogen atoms bonded to the two carbons of the double bond are on the same side U3. Unsaturated Fatty Acids Types of Unsaturated Fatty Acid Structures: •cis-fatty acids: Have a bend in the carbon chain Usually liquid at room temp – oils Have a lower melting point U3. Unsaturated Fatty Acids Types of Unsaturated Fatty Acid Structures: • trans-fatty acids: the hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbons in the double bond are on the opposite sides. U3. Unsaturated Fatty Acids Types of Unsaturated Fatty Acid Structures: •trans-fatty acids: Do not have a bend in the carbon chain Solid at room temperature – usually artificially produced – margarine and partially hydrogenated U4. Triglycerides Triglyceride: Examples: fat in adipose tissue, oil in sunflower seeds U4. Triglycerides • Triglyceride: Consists of three fatty acids linked to glycerol by condensation reactions • Used as energy stores, used during aerobic cell respiration • Examples: fat in adipose tissue, oil in sunflower seeds Types of Lipids Phospholipids: major components of cell membranes Hydrophilic head Two fatty acid tails (hydrophobic) Draw and label a phospholipid Carbohydrates vs. Lipids Carbohydrates • Easily digested, energy is released more rapidly • Soluble in water, easy to transport • Short term energy storage • Stored as glycogen in animals and starch in plants Lipids • Twice as much energy per gram than carbs, but harder to break down (slow process) • Non-polar, insoluble • Long term energy storage • Lipid storage is lighter for same amount of carbs; • stored as fat in animals • Used for insulation and buoyancy in animals Time to Build!! • Practice condensation and hydrolysis reactions by building different types of carbohydrates. Time to build!! • Practice condensation and hydrolysis reactions by building different types of lipids. Role of Condensation and Hydrolysis • Describe how condensation