The cell cycle
advertisement

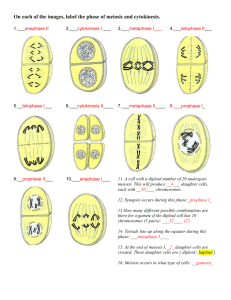
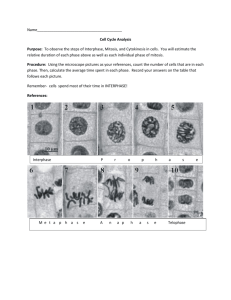
The cell cycle Chapter 6 Ask your neighbor. . . • Why do cells divide? What does this mean? • What do ALL cells have (that non-living things do not)? Cell division: The big picture The eukaryotic cell cycle The cell cycle in words. . . • Interphase – G1 –S – G2 • Mitotic phase – prophase – metaphase – anaphase – telophase & cytokinesis Interphase Mitotic phase • • • • prophase metaphase anaphase telophase & cytokinesis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase & cytokinesis Cytokinesis in animal cells Cytokinesis in plant cells • • • • • Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase & cytokinesis • How are the daughter cells produced after cell division genetically related to each other? Homologous chromosomes So, how many chromosomes are there in a cell? It depends. . . Let’s review so far. . . • How many parent cells? • How many daughter cells? • How many times did the DNA replicate before division? • How many mitotic divisions are there in each cycle? • How many chromosomes in daughter cells? • How are the daughter cells related to each other? Why? • How are the daughter cells related to the parent cell? Why is this important? • What is a sister chromatid? How are they related? • What are homologous chromosomes? Where do they come from? • What does diploid mean? What cells in humans are diploid? • What does haploid mean? What cells in humans are haploid? Quick mitosis summary • Purpose • Process • Products Reproduction by mitosis (asexually) • Advantages • Disadvantages Influences on cell division • Chemical factors • Physical factors Chemical factors • Growth factors Cell cycle control system Physical factors • Density-dependent inhibition • Anchorage dependence What happens when the cell cycle malfunctions? Cancer cells are not normal Programmed cell death • Called apoptosis Then what happens?