Chapters 1-4 SmartSkills Assignment Theme in Biology Explanation
advertisement

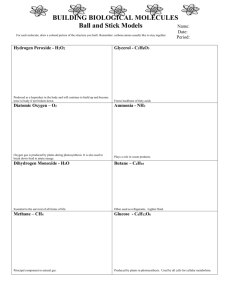
Name: _____________________________________ Chapters 1‐4 SmartSkills Assignment SmartCards (front of card is the vocabulary word, back of card is the definition) Chapter 1: Introduction: Evolution and the Foundations of Biology Chapter 1 SmartCards DNA Genes Controlled Experiment Chapter 1 Questions: 1. Fill in the following chart using information from chapter 1. Theme in Biology Explanation Example 2. List the ten (10) levels of Biological Organization and give an example of each. 1. __________________________________________________________________________________ 2. __________________________________________________________________________________ 3. __________________________________________________________________________________ 4. __________________________________________________________________________________ 5. __________________________________________________________________________________ 6. __________________________________________________________________________________ 7. __________________________________________________________________________________ 8. __________________________________________________________________________________ 9. __________________________________________________________________________________ 10. _________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Explain three examples of form fits function in the picture above. ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What are three differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells 5. What is the shape of a DNA molecule? _____________________________________ 6. For what type of molecule does DNA carry the instructions to make? _________________________ 7. Label the diagram above. 8. How does energy enter an ecosystem? _____________________________________ 9. How does energy leave an ecosystem? _____________________________________ 10. What factor is recycled in the diagram? ____________________________________ 11. Identify the theme or themes exemplified by each of the following: * the sharp spines of a porcupine ____________________________________________________________________________________ * the cloning of a plant from a single cell: ____________________________________________________________________________________ * a hummingbird using sugar to power its flight: ____________________________________________________________________________________ 12. What are the three domains of life? __________________________ _____________________________ ___________________ 13. What were the two main points in Darwin’s book, On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 14. Label the diagrams above. 15. Do individuals evolve or do populations evolve? ______________________________ 16. Label the diagram above. 17. What does each branch point represent? ________________________________________________________ 18. Explain why “editing” is an appropriate metaphor for how natural selection acts on a population’s heritable variation. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Scientific Skills Exercise, page 15. Read and analyze the data from the experiment. 1. What are the independent variables? ___________________________________________________________ 2. What is the dependent variable? _______________________________________ 3. How many dark brown mice were caught in the light‐colored soil enclosure on a moonlit night? ____________ 4. How many dark brown mice were caught in the dark‐colored soil enclosure on a moonlit night? ________________ 5. On a moonlit night, would a dark brown mouse be more likely to escape predation by owls on dark‐ or light‐colored soil? Explain your answer. ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. Is a dark brown mouse on dark‐colored soil more likely to escape predation under a full moon or with no moon? _________________________________ 7. Is a light brown mouse on light‐colored soil more likely to escape predation under a full moon or with no moon? _________________________________ 8. Under which conditions would a dark brown mouse be most likely to escape predation at night? __________________________________________________ 9. Under which conditions would a light brown mouse be most likely to escape predation at night? __________________________________________________ 10. What combination of independent variables led to the highest predation level in enclosures with light‐colored soil? _____________________________________________ 11. What combination of independent variables led to the highest predation level in enclosures with dark‐colored soil? _____________________________________________ 12. What relationship, if any, do you see in your answers to 10 and 11? ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 13. What conditions are most deadly for both colors of mice? _________________________________________ 14. Combining the data shown in both graphs, estimate the total number of mice caught in moonlight versus no‐ moonlight conditions. Which condition is optimal for predation by the owl on mice? Explain your answer. ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life SmartCards: Hydrogen bond Isotope Van der Waals interactions Single bond Polar molecule Double bond Cohesion Valence Adhesion Electronegativity Surface tension Nonpolar covalent bond Thermal energy Polar covalent bond Specific heat Ion Chapter 2 Questions 1. Give two examples of how radioactive isotopes are used in biology. _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Heat of vaporization Evaporative cooling Aqueous solution Hydration shell Hydrophilic Hydrophobic Buffer 2. Label the diagram above. 3. What happens to an electron when it absorbs energy? _________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What happens to an electron when it releases energy? _________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. When energy is released from an electron, in what form is the energy from an electron usually released as? _______________________ 6. What element has the highest electronegativity? __________________________ 7. Draw a diagram of several water molecules. Show the polar bond between hydrogen and oxygen and show how the polar bond causes interactions between water molecules. 8. What would be the effect on the properties of the water molecule if oxygen and hydrogen had equal electronegativity? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. Label the diagram above. 10. Explain the process of how water can be pulled upward through a tree. ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 11. What property of water allows the water strider to stay on top of the water? _____________________________ 12. What property can water’s high specific heat be attributed to? ___________________________________ 13. How does evaporative cooling help you on a hot day? _________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 14. How does the frozen surface on body of water protect the ecosystem below? _______________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 15. Is ice more or less dense than liquid water? _______________________________________ 16. If ice were more dense, how would your answer to #14 be different? ______________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 17. If water did not form hydrogen bonds, what would happen to the shrimp’s environment? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 18. How can freezing of water crack boulders? ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 19. What type of molecules are hydrophobic. Describe the bonding structure. _______________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ Scientific Skills Exercise, page 37: 1. What is the independent variable? ________________________________________ 2. What is the dependent variable? __________________________________________ 3. Describe the relationship between carbonate ion concentration and calcification. ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. If the seawater carbonate ion concentration is 270 μmol/kg, what is the approximate rate of calcification, and approximately how many days would it take 1 square meter of reef to accumulate 30 mmol of calcium carbonate (CaCO3)? _____________________________________ __________________________ 5. If the seawater carbonate ion concentration is 250 μmol/kg, what is the approximate rate of calcification, and approximately how many days would it take 1 square meter of reef to accumulate 30 mmol of calcium carbonate (CaCO3)? _____________________________________ __________________________ 6. If carbonate ion concentration decreases, how does the calcification rate change, and how does that affect the time it takes coral to grow? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Do the results of this experiment support the hypothesis that increased atmospheric CO2 will slow the growth of coral reefs? Why or why not? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ Chapter 3: Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life SmartCards: Functional Group Structural Isomers Tetravalence Adenosine triphosphate Geometric Isomers Hydrocarbons Enantiomers Isomers Polymer Fatty acid Monomer Secondary Structure Triglyceride (triacylglycerol) Condensation reaction Tertiary structure Saturated fatty acid Dehydration reaction Quaternary Structure Unsaturated fatty acid Enzymes Denaturation Phospholipids Hydrolysis Chaperonins Steroids Monosaccharides Gene Cholesterol Disaccharide Nucleic acid Catalysis Glycosidic linkage Pyrimidine Polypeptides Polysaccharides Purine Protein Glycogen Double helix Amino acid Cellulose Antiparallel Peptide bond Chitin Lipids Primary Structure 1. How many valence electrons are in each of the above elements? a. H _____ b. O _____ c. N _____ d. C _____ 2. What are the four main skeletal variations of hydrocarbons? ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 3. What is the structural difference between the above molecules? ______________________________________ 4. Label the above diagram. 5. What is the importance of the above molecule? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Label the diagram above. What process is occurring in the diagram above? ________________________________ Is water being added or taken out? ___________________________ Are molecules combining or being broken apart? _____________________________ Give an example of where or when this happens. _____________________________________________________________________________ 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Label the diagram above. What process is occurring in the diagram above? ________________________________ Is water being added or taken out? ___________________________ Are molecules combining or being broken apart? _____________________________ Give an example of where or when this happens . ________________________________________________________________________ 16. To what category of biomolecules do the above molecules belong? _______________________ 17. What is the name of the molecule above? _________________________ 18. What do the numbers around the hexagon represent? _____________________________ 19. What process combines the monosaccharides above? _________________________________ 20. What are the names of the two disaccharides? ____________________________________ 21. What is the name of the bond that holds the disaccharide together? _______________________ 22. Label the names of the above molecules AND where they are found. 23. Can the same enzyme break down starch and cellulose? __________ 24. What advantages does a diet high in cellulose provide for humans? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 25. Label the parts of the above fat. 26. Which part of the above molecule makes fat hydrophobic? ____________________________ 27. How many water molecules are removed from the fatty acid/glycerol to make the above molecule? __________________________________ 28. What is the name of the type of bond that is outlined with dotted lines (in the dotted line boxes)? ___________________________________________________ 29. What is the difference between the two molecules above? ____________________________________________________________________________ 30. Why doesn’t the unsaturated fat solidify at room temperature? _____________________________________________________________________________ 31. Explain the difference between the two ends of a phospholipid. _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 32. What cell structure is composed of phospholipids? _________________________________ 33. Label the diagram above. 34. To what group of macromolecules does the above molecule belong? _____________________ 35. Draw a diagram and label the parts of the general structure of an amino acid. SPECIAL NOTE: You will NOT have to memorize the names of the 20 amino acids or their categories!!!! 36. What type of bond holds the molecule in the bottom part of the above diagram together? __________________________ 37. What two elements that are part of the polypeptide (most of them) are not found in carbohydrates and lipids? ______________________ 38. Label the four level of protein structure above (they are not in the correct order). 39. Summarize primary structure in one or two sentences. _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 40. Summarize secondary structure in one or two sentences. _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 41. Summarize tertiary structure in one or two sentences. _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 42. Summarize quaternary structure in one or two sentences. _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 43. What is happening to the above protein? _________________________________________ 44. List three factors which may cause this to happen to proteins. _____________________________________________________________________ 45. Label the diagram above. 46. What is the sequence (flow) of genetic information? ___________________________________ 47. Which bases are purines? _______________________________ 48. Which bases are pyrimidines? _________________________________ 49. What are the monomers of nucleotides? _____________________________________ 50. What are the three parts to this monomer? ___________________________________ 51. What is the shape of a DNA molecule? ___________________________________ Scientific Skills Exercise, page 63. Read the description on page 63 and then answer the following questions. 1. Scan along the monkey and gibbon sequences, letter by letter, circling any amino acids that do not match the human sequence. 2. How many amino acids differ between the monkey and the human sequences? _________ 3. How many amino acids differ between the gibbon and human? ___________ 4. For each nonhuman species, what percent of its amino acids are identical to the human sequence of β‐globin? __________________ 5. Based on these data alone, state a hypothesis for which of these species is more closely related to humans. What is your reasoning? ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. What other evidence could you use to support your hypothesis? _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ Chapter 4: A Tour of the Cell SmartCards Cytosol Eukaryotic Cell Prokaryotic Cell Nucleoid Plasma Membrane Nuclear Envelope Chromatin Nucleolus Ribosomes Endomembrane System Vesicles Endoplasmic Reticulum Figure Questions: Smooth ER Rough ER Glycoproteins Transport vesicles Golgi apparatus Lysosome Phagocytosis Food vacuole Contractile vacuole Mitochondria Chloroplasts Endosymbiont theory 1. What type of cells are shown? _______________________________ Cristae Mitochondrial matrix Plastids Thylakoids peroxisome cytoskeleton Cilia Cell wall Extracellular matrix plasmodesmata 2. What two structures are these type of cells lacking? ________________________________________________ 3. Do they have a cell wall? ________________________ 4. Label the diagram above. 5. Describe the components of a phospholipid that allow it to function as the major element in the plasma membrane. ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. Fill in the chart above. 7. What type of cell exchanges materials most efficiently? One with a high surface to volume ratio or a low surface to volume ratio? _______________________________________ 8. Imagine an elongated cell (such as a nerve cell) that measures 125 x 1 x 1 arbitrary units. Predict how its surface‐to‐ volume ratio would compare to those in the above diagram. Calculate the ratio and check your prediction. Prediction:_________________________________________________________________________ Calculation: _______________________________ 9. Label the diagram above (function of each part does NOT have to be labeled). 10. What are components that are found in animal cells but not in plant cells. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ 11. Label the diagram above (function of each part does NOT have to be labeled). 12. What are components that are found in plant cells but not in animal cells. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Scientific Skills Exercise, page 74. Read the description and Interpreting the data carefully!!!! 1. Calculate the volume of each cell using the formula for the volume of a sphere (on page 74). Large cell ________________ Small budding cell: ___________ 2. How much new cytoplasm will the new cell have to synthesize as it matures? ________________ 3. Calculate the surface area of each cell. Large cell: ____________ Small budding cell: __________ 4. How much area of new plasma membrane will the new cell have to synthesize as it matures? _____________ 13. Label the diagrams above. 14. What does the nucleolus do? ___________________________ 15. How are chromosomes and chromatin related? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 16. What structure is shown in this diagram? ____________________________ 17. What is its function? ___________________________________________________ 18. Where is it found in the cell? ___________________________________________________________________ 19. What structure is shown above? __________________________________________ 20. What structures are included in the endomembrane system? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 21. What is the difference between rough ER and smooth ER? _________________________________________ 22. Fill in the following chart with the functions of Rough ER and Smooth ER. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 23. What is the structure above? _______________________________________ 24. What is its function? __________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 25. Where do vesicles arrive FROM? _____________________________________ 26. Where do vesicles go TO? __________________________________________ 27. What do vesicles carry? _________________________________________________ 28. What organelle is shown above? _________________________________ 29. What is inside of it? ____________________________________________ 30. What does it do? ________________________________________________________________________ 31. What organelle is shown above? ____________________________ 32. What are three different types of this structure? ___________________________________________________ 33. Based on the organelle, is this a plant or animal cell shown? ____________________________ 34. Label the diagram above for the summary of the relationship among the endomembrane system. 35. Label the diagram above. 36. What are three pieces of evidence that support the endosymbiont theory. ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 37. How is the structure of the mitochondria related to its function? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 38. Label the diagram above. 39. What does a peroxisome do? __________________________________________________________________ 40. Label the diagram above. 41. What are the two main kinds of membrane proteins? __________________________ ______________________________ 42. What type of molecules are glycolipids and glycoproteins? _______________________ 43. What is the function of glycolipids and glycoproteins? __________________________________________________________________