Aspirin Synthesis Lab: Procedure & Calculations
advertisement

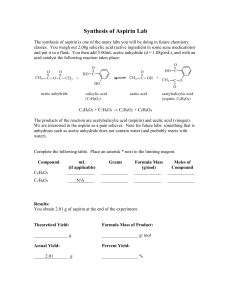
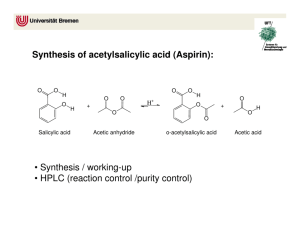
Synthesis of Aspirin CLAB 104 – Lab 9 Experiment IX: Synthesis of Aspirin In today’s laboratory we will carry out the following synthesis reaction: Sulfuric Acetic Aspirin Salicylic Acetic Acid Acid + Anhydride Catalyst + Acid (C2H4O2) (C9H8O4) (C7H6O3) (C4H6O3) + + This is a stoichiometrically-balanced equations:1 mole of each reactant will produce 1 mole of each product. Laboratory Procedure 1. In a weigh boat, accurately weigh out and record the mass of around 5 g of salicylic acid. Add this plus 10.0 mL of acetic anhydride, and 25 drops of concentrated sulfuric acid into the same beaker. (Suppose for sample calculations that you added 2.113 g of salicylic acid and 6.00 mL of acetic anhydride) Sulfuric Acid Salicylic Acid Acetic Anhydride EVERYTHING NECESSARY TO CALCULATE THE THEORETICAL YIELD OF ASPIRIN HAS NOW BEEN MEASURED. Finding the Theoretical Yield of Aspirin a. The molar mass of salicylic acid is 138.1 g/mole. Use this to find the moles of salicylic acid used: 1mole From sample 2.113 g 0.01530 mole data: 138.1 g b. Using the density of acetic anhydride of 1.081 g/mL, calculate the mass of acetic acid added. 1.081 g From sample 6.00 mL 6.49 g data: mL c. The molar mass of acetic anhydride is 102.1 g/mole. Use this to find the moles of acetic anhydride used: From sample data: 1mole 6.49 g 0.0636 mole 102.1 g Laboratory Procedure d. From the 1:1 stoichiometry of reactants, determine which is the limiting reagent: 0.01530 moles salicylic acid added Limiting Reagent 0.0636 moles acetic anhydride added e. From the 1:1 stoichiometry of products to reactants, calculate the number of moles of product theoretically formed: 1mole aspirin 0.01530 mole salicylic acid 1 mole salicylic acid 0.01530 mole aspirin Laboratory Procedure f. The molar mass of aspirin is 180.1 g/mole. Use this to find the theoretical yield of aspirin in grams: 180.1 g 0.01530 mole 2.756 g mole Follow the procedure on page 97 to complete your synthesis of aspirin. 50 mL ice water 2. Swirl beaker to break up any large chunks. Allow reaction to proceed for 20 minutes. After that time, add 50 mL of ice water. Place the beaker into a container with ice in it to further cool your sample. Aspirin should crystallize in the beaker. Laboratory Procedure Rinse crystals and beaker several times Place filter paper in funnel Attach hose to faucet 3. Filter the crystals using a Buchner funnel. Wash the filter paper several times with distilled water. side-arm After filtration is complete, carefully remove your filter paper from the funnel. Place it in a weigh boat with your names on it so that it can dry and be weighed during next week’s lab period. 4. Place a small chunk of your wet aspirin in a test tube. Add about 10 mL of water to the test tube and dissolve the chunk. Laboratory Procedure 5. Add 3 drops of yellow FeCl3 solution. Record your observations. (A change of color to purple is a qualitative test that shows the presence of salicylic acid. If your test tube turns purple, has all your reactant been consumed?) 6. The following week, weigh and report the mass of your dried sample of aspirin Calculate the %yield of aspirin in your experiment: (Suppose your experimental yield is 1.884 g from our practice problem where we determined a theoretical yield of 2.756 g of aspirin) experiment al yield 1.884 g % yield 100 100 68.36% theoretical yield 2.756 g