Unit 5 organizer
advertisement
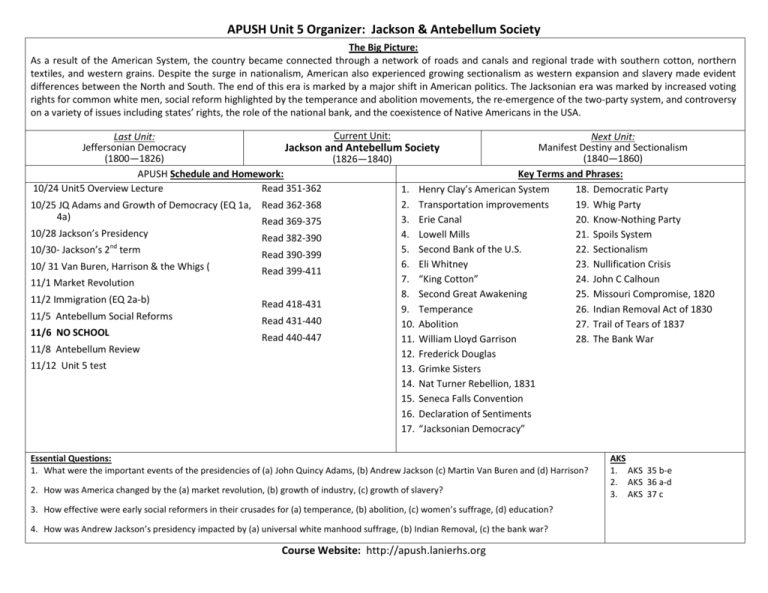
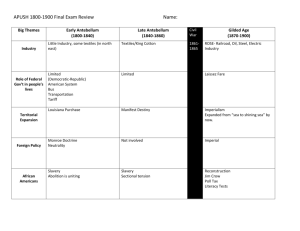
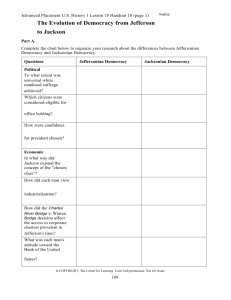
APUSH Unit 5 Organizer: Jackson & Antebellum Society The Big Picture: As a result of the American System, the country became connected through a network of roads and canals and regional trade with southern cotton, northern textiles, and western grains. Despite the surge in nationalism, American also experienced growing sectionalism as western expansion and slavery made evident differences between the North and South. The end of this era is marked by a major shift in American politics. The Jacksonian era was marked by increased voting rights for common white men, social reform highlighted by the temperance and abolition movements, the re-emergence of the two-party system, and controversy on a variety of issues including states’ rights, the role of the national bank, and the coexistence of Native Americans in the USA. Current Unit: Last Unit: Next Unit: Jeffersonian Democracy Manifest Destiny and Sectionalism Jackson and Antebellum Society (1800—1826) (1840—1860) (1826—1840) APUSH Schedule and Homework: Key Terms and Phrases: 10/24 Unit5 Overview Lecture Read 351-362 1. Henry Clay’s American System 18. Democratic Party 2. Transportation improvements 19. Whig Party 10/25 JQ Adams and Growth of Democracy (EQ 1a, Read 362-368 4a) 3. Erie Canal 20. Know-Nothing Party Read 369-375 10/28 Jackson’s Presidency 4. Lowell Mills 21. Spoils System Read 382-390 nd 5. Second Bank of the U.S. 22. Sectionalism 10/30- Jackson’s 2 term Read 390-399 6. Eli Whitney 23. Nullification Crisis 10/ 31 Van Buren, Harrison & the Whigs ( Read 399-411 7. “King Cotton” 24. John C Calhoun 11/1 Market Revolution 8. Second Great Awakening 25. Missouri Compromise, 1820 11/2 Immigration (EQ 2a-b) Read 418-431 9. Temperance 26. Indian Removal Act of 1830 11/5 Antebellum Social Reforms Read 431-440 10. Abolition 27. Trail of Tears of 1837 11/6 NO SCHOOL Read 440-447 11. William Lloyd Garrison 28. The Bank War 11/8 Antebellum Review 12. Frederick Douglas 11/12 Unit 5 test 13. Grimke Sisters 14. Nat Turner Rebellion, 1831 15. Seneca Falls Convention 16. Declaration of Sentiments 17. “Jacksonian Democracy” Essential Questions: 1. What were the important events of the presidencies of (a) John Quincy Adams, (b) Andrew Jackson (c) Martin Van Buren and (d) Harrison? 2. How was America changed by the (a) market revolution, (b) growth of industry, (c) growth of slavery? 3. How effective were early social reformers in their crusades for (a) temperance, (b) abolition, (c) women’s suffrage, (d) education? 4. How was Andrew Jackson’s presidency impacted by (a) universal white manhood suffrage, (b) Indian Removal, (c) the bank war? Course Website: http://apush.lanierhs.org AKS 1. AKS 35 b-e 2. AKS 36 a-d 3. AKS 37 c CP US History AKS for Unit 4—The Early Antebellum Era (1800-1840) D - Revolution and the Formation of a New Nation analyze the development of American Constitutional government, explaining relationship to Enlightenment, and describe how the early national leaders implemented the new government 34g - describe the significance of Marbury v. Madison analyze the impact of territorial expansion and population growth and its impact in the early decades of the new nation 35b - describe Jefferson's diplomacy of obtaining the Louisiana Purchase from France and the territory's exploration and Lewis and Clark searching for water route westward 35c - explain reasons for War of 1812 and its significance on the development of nationalism and sectionalism 35d - describe the construction of the Erie Canal (include economic impact), the rise of New York City, and the development of the nation's infrastructure 35e - describe the reasons for and importance of the Monroe Doctrine explain the process of economic growth in the first half of the 19th century, its regional and national impact, and the different responses to it 36a - explain the impact of the Industrial Revolution as seen in Eli Whitney's invention of the cotton gin and his development of interchangeable parts for muskets 36b - describe reform movements, specifically temperance, abolitionism, and public schools 36c - explain women's efforts to gain suffrage, including Elizabeth Cady Stanton and the Seneca Falls Convention 36d - explain Jacksonian Democracy (spoils system, Trail of Tears), expanding suffrage, the rise of popular political culture, and the development of American nationalism (Know Nothing Party) E - Growth, Change, Crisis, Compromise, and Conflict explain the relationship between westward expansion and the rise of sectionalism 37a - explain how slavery became a significant issue in American politics, including the slave Nat Turner, and the rise of abolitionism (William Lloyd Garrison, Frederick Douglass, and the Grimke sisters) 37b - explain the Missouri Compromise and the issue of slavery in western states and territories 37c - describe the Nullification Crisis and the emergence of states' rights ideology, including the role of John C. Calhoun, and rise of sectionalism AP US History Outline for Unit 4—The Early Antebellum Era (1800-1840) 7. The Transformation of Politics in Antebellum America Emergence of the second party system Jacksonian democracy and its successes and limitations Federal authority and its opponents: judicial federalism, the Bank War, tariff controversy, and states’ rights debates Expansion into the trans-Appalachian West; American Indian resistance, forced removal of American Indians to the trans-Mississippi West 8. Religion, Reform, and Renaissance in Antebellum America Second Great Awakening, evangelical Protestant revivalism Social reforms Ideals of domesticity Transcendentalism and utopian communities American Renaissance: literary and artistic expressions Check out http://www.ucopenaccess.org (link to US History or AP US History) for video, short chapter readings, documents, vocab lists, extension activities Lesson #23 – A Growing National Economy Lesson #24 – The Transportation Revolution Lesson #25 – King Cotton Lesson #26 – Democracy and the “Common Man” Lesson #27 – Nullification Crisis Lesson #28 – The Bank of the United States Lesson #29 – Indian Removal Lesson #30 – Transcendentalism, Religion, and Utopian Movements Lesson #31 – Reform Crusades