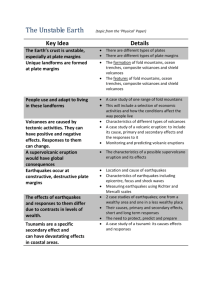
1 Restless Earth - Stratford School Academy
advertisement
Stratford School Academy Schemes of Work GEOG: RESTLESS EARTH Year 10 – Restless Earth Geography: YEAR 10 – Restless Earth The Earth and its layers Plate Margins Landforms at Plate Margins Fold Mountains Uses of Fold Mountains – Case Study: The Andes Super volcanoes Impacts and Effects of Eruptions – Case Study: Montserrat Causes of Earthquakes Effects and Impacts of Earthquakes – Case Study: Chile and Haiti Causes, Impacts and Effects of Tsunamis – Case Study: The Boxing Day Tsunami Assessment points and Written feedback points tasks Mid Unit – Week 4 Lesson 9 and Lesson 13, in line with Exam questions modelled on assessment points past GSCE papers Week 4 and week 8, books should be End of Unit Test – marked. Week 7 Exam questions modelled on past GSCE exam papers Exam question practise and feedback incorporated into every lesson Assumed prior learning (tested at the beginning of the unit) KS3 knowledge of unit on tectonic plates and movements. Learning Outcomes (tested at the end and related to subject competences) Drawing maps, graphs and diagrams. 8 Content of the unit Case studies Number of weeks I can add labels to sketches I can draw diagrams to explain a sequence I can plot data on to maps. I can add detailed annotations to sketches I can complete a graph using data given to me. I choose appropriate labels, keys and titles for my maps and graphs I can draw graphs accurately with data provided I can select which data to present on a map or chart I can choose appropriate types of graph / map to display my data I can identify and explain anomolous results I can evaluate data collection and presentation methods. I can suggest improvements to the data collection / presentation methods used. I can identify and give facts about an event or place I can identify and describe an issue facing a place I can apply a case study to describe causes, impacts and responses I can apply a case study to explain causes, impacts and responses I can explain how management can reduce the impacts of a problem / challenge. I can explain different opinions towards an event or process. I can explain the justification for a particular management strategy. I can evaluate different opinions towards an event or process. I can evaluate the impacts of a process or event for different stakeholders. I can evaluate the sustainability of management choices and provide further suggestions. Page 1 of 13 Stratford School Academy Schemes of Work GEOG: RESTLESS EARTH Lesson 1 Clear learning intentions Clear success criteria Hook Presentation of content Guided practice Independent practice (homework) Closure What is the Inside of the Earth Like? E/F - Identify and describe key features of the earth’s structure. Teacher explains structure of the course – how many units, how they will be assessed, which topics will be studied, when etc PowerPoint Diagram of Earth’s layers Keyword bank YouTube clip Oxford Textbook Close passage worksheet Video clip outlining the layers of the Earth. Students to complete diagram and labels. Differentiated questioning. Feedback to class Exam Practise – Explain how the tectonic plates move (4 marks) Close passage: ‘What do we mean by ‘plate tectonics’?’ Less able – includes a word bank. D/C - Label and describe the inside of the earth. B+ - Explain the link between plates, earthquakes and volcanoes. Picture of erupting volcano, geographical questioning. Recap of previous knowledge about the layers of the Earth and any other knowledge of tectonic processes. Keyword match up. Students to write in their keyword glossary Define the two types of crust. Create a table comparing the continental and oceanic crust (page 9) Draw and label a diagram showing how convection currents work (page 9). Write a definition for convection currents in own words. Feedback to class. Page 2 of 13 Stratford School Academy Schemes of Work GEOG: RESTLESS EARTH 2 Where are the edges of the Earth’s crust located and what happens there? E/F - Define tectonic plate, name some tectonic plates and label them on a map. Four pictures and differentiated questions – Variations on ‘how are these four objects related?’ PowerPoint Keyword match up exercise Blank world map YouTube clip D/C - Describe the location of the tectonic plate boundaries and the direction the plates are moving in. Keyword and definition match up. Self-marking. Stretch Activity – Draw a diagram to show all the ways tectonic plates could move in relation to one another Diagram displaying Pangea. Class discussion – How has the Earth’s crust changed over time? Watch clip showing the last 300 billion years and how tectonic plates have moved. B+ - Link the movement of tectonic plates to the distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes. On a blank world map, draw in the lines of the 8 major tectonic plates. Label with name of plate and direction plate is moving. Volcanoes of the World – Class discussion – do students notice anything about the location of volcanoes around the world? (If they don’t make the link themselves, ask them to compare their map they have drawn the tectonic plate lines on with the map of the location of volcanoes. Can also direct them to page 13 of the textbook) Differentiated questions for students to answer. Class feedback. Exam question – Discuss with students how to answer the question. Show the answers and ask students what mark they would award it. Need to justify why based on the mark scheme. Page 3 of 13 Exam Practise – Explain the location of the world’s volcanoes (4 marks) Post It Notes - Two things you have learned today. One thing you would still like to know. Stratford School Academy Schemes of Work GEOG: RESTLESS EARTH 3 How are the different types of volcanoes formed? F/E - Know the difference between destructive and constructive plate boundaries. D/C - Describe how a constructive volcano and a destructive volcano are formed, using a diagram. Constructive Destructive What do these two words make you think of? What is happening to the Earth’s crust at each boundary? PowerPoint Oxford Textbook Differentiated worksheets Homework sheet Discuss homework question. Students to peer mark and give WWW and EBI. Draw diagram of constructive plate boundary and label. Remind students that all diagrams in Geography need titles and labels. Students to self-mark and correct work if needed. Write paragraph explaining how constructive margins are formed. Differentiation – SEN: print close passage, give word bank G&T: Put into own words. Self-mark and correct if needed. Further questioning – How is new crust made? How is crust destroyed? How is rock turned into mantle? B+ - Explain how different types of volcanoes are formed using process vocabulary and geographical key words. Draw destructive plate boundary diagram and label. Self-mark and correct if needed. Write paragraph explaining how destructive plate boundaries are formed. Self-mark and correct if needed. Differentiation – SEN: print close passage, give word bank G&T: Put into own words. Self-mark and correct if needed. Read page 10 and 11. Create a table summarising each plate boundary and landforms that occur there. Page 4 of 13 Homework sheet – Past exam question – Write one sentence to explain what is happened in each diagram. (3 marks) True or False – Use red and green sheets in back of student planners Stratford School Academy Schemes of Work GEOG: RESTLESS EARTH 4 What are the different types of crust and how does this affect the landforms created? F/E - Know the 2 types of crust and 4 differences between the 2 types. D/C - Know the names of 3 types of plate boundary and say what type of crust is involved at each and which direction it is moving. Picture of gas and ash clouds coming out of the sea – geographical questioning Different crust types sheet Direction of plate movement sheet PowerPoint Oxford Textbook Recap differences in continental and oceanic crusts, plate boundaries and direction they move Exam question and scaffolded response. Students complete close passage to get a 4 mark answer. Can use textbook. Differentiation – Word bank for SEN Students self-mark and correct if needed. B/A - Describe the characteristics of landforms created at plate boundaries. View fold mountain, shield and composite volcanoes. What do they have in common? At what plate boundaries do they occur? A* - Explain how the type of plate boundary affects the characteristics of the landforms there. Read page 12-13 and summarise information into a table that shows characteristics and landforms at each type of plate boundary. Stretch Activity for G&T Look at completed table. Questioning – Which boundary causes the most damage? Which boundary is the safest? Exam question practise. Look at exemplar answers once students have written their own. Choose 2-3 students to read their answer and others to critique. What mark? Why? What could they add to improve their work? No hands classroom. Page 5 of 13 Homework sheet – several past exam questions Can you? Get a show of hands for who can answer each question, starting at red. Choose one student at random to answer, keep going until the question is answered completely and perfectly. Stratford School Academy Schemes of Work GEOG: RESTLESS EARTH 5 What are fold mountains and how are they formed? F/E - Identify where fold mountains are located. D/C - Describe how fold mountains are formed and complete a labelled diagram. Exam Question – Where are fold mountains located? Share 2 answers, choose a student to give a mark, WWW and an EBI verbally PowerPoint Oxford textbook Table worksheet B+ - Explain how fold mountains are formed using process vocabulary and key geographical words. Watch video clip explaining how fold mountains form. Complete past exam question, writing one sentence to explain what is happening in the diagram. Choose students to read out answers, put on slide so students can correct and mark their work. Stretch Activity Case Study – Himalayas Students to use textbook to build a case study for uses of fold mountains. Activity is colour coded to show students what they need to do to achieve each grade. Fill out table. Exam Question practise – How would you answer this question? What information is needed? What is the command word asking you for? Look at answer. What mark would they award? Justify. How can it be improved? Page 6 of 13 For next lesson – Research one super volcano eruption. How was the earth affected? True or false? Series of questions, use red and green planner pages Stratford School Academy Schemes of Work GEOG: RESTLESS EARTH 6 What is a super volcano? F/E - Know what a super volcano is and describe its characteristics and location Investigative skills using key geographical terminology – asking and answering questions about a specific picture PowerPoint Oxford Textbook Differentiated worksheet for Sen students D/C - Describe the potential impact of a super volcano eruption. Watch clip showing the characteristics of the Yellowstone caldera. Students to write a definition of a super volcano. Exam practise – Look at a picture showing the worlds known locations of super volcanoes. Where are super volcanoes located in the world? Stretch Activity – Compare to plate boundaries B+ - Compare and contrast the impact of super volcanoes compared to ordinary volcanoes Use textbook to add more words to the keyword mat. Check understanding of each. Can students explain using their own words? Keep asking until it is perfect. Draw and label diagram showing the characteristics of the Yellowstone caldera. Check they understand what is meant by ‘characteristics’. Write a paragraph explaining how the caldera was formed as well as specific data about it. Differentiation – print to give to SEN students a s a gap fill G&T students to write in their own words. Can use textbook for reference if needed. Page 7 of 13 Homework – A look at Yellowstone national Park. Diagram and questions. 3, 2, 1 – 3 effects of a super volcano eruption, 2 facts about Yellowstone, 1 thing they found interesting Stratford School Academy Schemes of Work GEOG: RESTLESS EARTH How are super volcanoes different to other volcanoes? Create side by side lists. Students can use textbooks for reference. Diagram of the effects and impacts of a super volcano eruption. Shows two different eruptions millions of years apart. If Yellowstone was to erupt now, how would the world be affected? 7 What were the effects of the Montserrat eruption? F/E - Identify effects of a volcanic eruption. D/C - Categorise effects (primary, secondary, social, economic, environmental) Exam Questions – What is pyroclastic flow? What is a primary and secondary effect of a volcanic eruption? PowerPoint Oxford Textbook Video clip Keyword mat Linking statements worksheet B+ - Describe effects in detail using a case study. Add the lessons keywords to their keyword mat. Questioning to ensure understanding of each word. Clip showing the eruption and impacts of it. Students to create a case study file of the eruption and effects of the Montserrat eruption. Write effects they can see in the clip. Need to categorise these effects into primary and secondary. Add these definitions to keyword mat. They also need to classify each as either social, economic or environmental. Go over what each means, choose student to provide an example for each. Add specific detail and data using page 16-17 of the textbook. Include a table to show the immediate and long term responses to the disaster. Page 8 of 13 Revise for mid unit test Look at sample answer. Students to mark, need to be able to justify. Look back over their own answer and attempt to improve. Stratford School Academy Schemes of Work GEOG: RESTLESS EARTH Model linked statements and explain how important it is to do this to move from level 1 or 2 answer to a level 3. Activity sheet where students need to match the effect with its explanation Exam Question Practise Choose one volcanic eruption you have studied. Explain the effects of the volcanic eruption. (8 marks). Discuss how to answer the question. Students to answer question in their book. Differentiation – keyword bank to include in answer for SEN 8 What Do I Need To Know For My Mid-Unit Test? 9 Mid Unit Test F/E - List information in Create flashcards to revise exam answers keywords, processes and D/C - Explain information structure of the Earth in some detail in response to exam questions B+ - Understand what the question is asking me and use in depth case studies and examples to explain the answer. Flash cards Revision Guides Oxford Textbook Discuss and complete a series of past exam questions in order to revise for the mid unit test. Test paper Students to complete test paper in half an hour to model GCSE paper Page 9 of 13 Revise for the test Discussion of how the test would be set out and remind student to complete past papers online. Stratford School Academy Schemes of Work GEOG: RESTLESS EARTH 10 How are earthquakes formed? F/E - Describe where earthquakes occur and define ‘Conservative margin.’ Know what the Richter and Mercalli Scales are. Picture of the where earthquakes occur around the world. Exam question: How are earthquakes distributed around the world? (4 marks) Oxford textbook Video clip Powerpoint Keyword mat Differentiated worksheet D/C - Outline how earthquakes are formed using process vocabulary. Describe the differences between the Richter and Mercalli Scales. Go over how plates move at constructive and deconstructive margins. How else can the plates move in relation to one another? Draw a diagram of how plates move at a conservative margin. Watch the video clip and answer the questions, Two stretch questions. Can also use the textbook for this. Use page 20 of the textbook to draw a diagram of an earthquake within the crust. Add definitions of the keywords to the keyword mat. Stretch questions. B+ - Use key words (focus, epicentre, seismic waves) in my answer. A* - Evaluate the utility of the Richter and Mercalli scales, and the way they measure earthquakes Exam Question practise – Discuss how to answer the question. What will get marks? What is unnecessary? Students to answer question. Differentiation – SEN can have close passage, more able students to have word bank or not. Copy definitions into keyword mat for Richter Scale and Mercalli Scale/ Answer questions. Stretch questions. Page 10 of 13 Research the world’s strongest earthquake and create a factfile on it. What have I learnt? What progress have I made? What else do I want to know? Stratford School Academy Schemes of Work GEOG: RESTLESS EARTH 11 How Do Different Countries Cope After Earthquakes? F/E - Identify the effects of earthquakes Create an acrostic poem using geographical terminology ‘Earthquakes’ PowerPoint Oxford Textbook D/C - Categorise effects and give some detail B - Explain further consequences of earthquakes A-A* - Use detailed case study facts in my answer Using the information in the PowerPoint, create fact files comparing an earthquake in Chile (MEDC) and in Haiti (LEDC). Need to be able to compare both effects and responses and be able to say how being a MEDC or LEDC affects these things. Exam question practise - How does the depth of the earthquake’s focus, and the location of its epicentre, help to explain some of the effects seen in Chile and Haiti? (4 marks) Using case studies of earthquakes you have studied in MEDC’s and LEDC’s, compare and describe the responses to these earthquakes (6 marks) Using examples of earthquakes, explain why some cause more destruction and death than others (6 marks) Can use the textbook if needed Students to peer mark using the mark scheme provided Page 11 of 13 Explain the effects of an earthquake or volcano you have studied. Use a case study in your answer. (8 marks) Post it notes – Something I’ve learned, something I don’t understand Stratford School Academy Schemes of Work GEOG: RESTLESS EARTH 12 What is a Tsunami? F/E - Know what a Tsunami is. D/C - Describe the effects of a Tsunami Mark homework question: Explain the effects of an earthquake or volcano you have studied. Use a case study in your answer. PowerPoint Oxford textbook SEN differentiation – scaffold for report, diagrams of tsunami forming B+ - Explain the cause of a Tsunami Watch clips showing the tsunami devastation. Students should make notes about the effects of tsunami that they can see. Feedback after the clip to ensure that all students have covered all the effects. Ask them to label either as immediate or secondary effects. Two diagrams showing how a tsunami is formed and how the wave changes as it approaches land. Students should darw both into their books. Make sure they include the title and labels. Differentiation – Give students diagram and get them to copy the labels onto it. Write a paragraph explaining in their own words how a tsunami is formed. Differentiation – SEN: Give students a close passage or can read a paragraph and try to put it in their own words. Can use the textbook if needed. Using the textbook and what they have seen in the clip, students produce a seismologists report about the tsunami that hit on Boxing Day. Differentiation – Provide SEN with scaffold to answer the questions Give students the answer to a question – what question do they think it is answering? Page 12 of 13 Exam Practise Outline how a tsunami happens (4 marks) Describe the effects of one Tsunami you have studied. (8 Marks) Give one fact for Immediate effects Tsunami features/ Plate tectonics Secondary effects Explain how people Immediate response could reduce the effects of tsunamis in the future. Long term response (8 marks) Stratford School Academy Schemes of Work GEOG: RESTLESS EARTH 13 14 15 End of Unit Assessment Prep End of Unit Assessment End of Unit Assessment run through BTEOTL I will: Know how to answer those questions I find hardest. Smith proformas…prioritise your skills and subject knowledge. Dependent on group BTEOTL I will: PLC up on the board. Model answers Know my weaknesses for Pupils to note down future revision strengths and weaknesses. Page 13 of 13 Groups to select resources to help with skill/knowledge revision. Run through model answers with class. Class to annotate papers. Revise for end of unit assessment Tell me something you know now that you didn’t know before. Prep for your “therapy” Sharing…what are our biggest weaknesses?