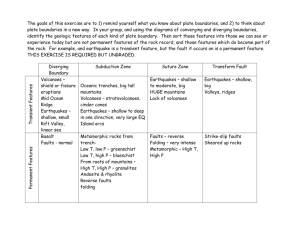
The Unstable Earth outline
advertisement
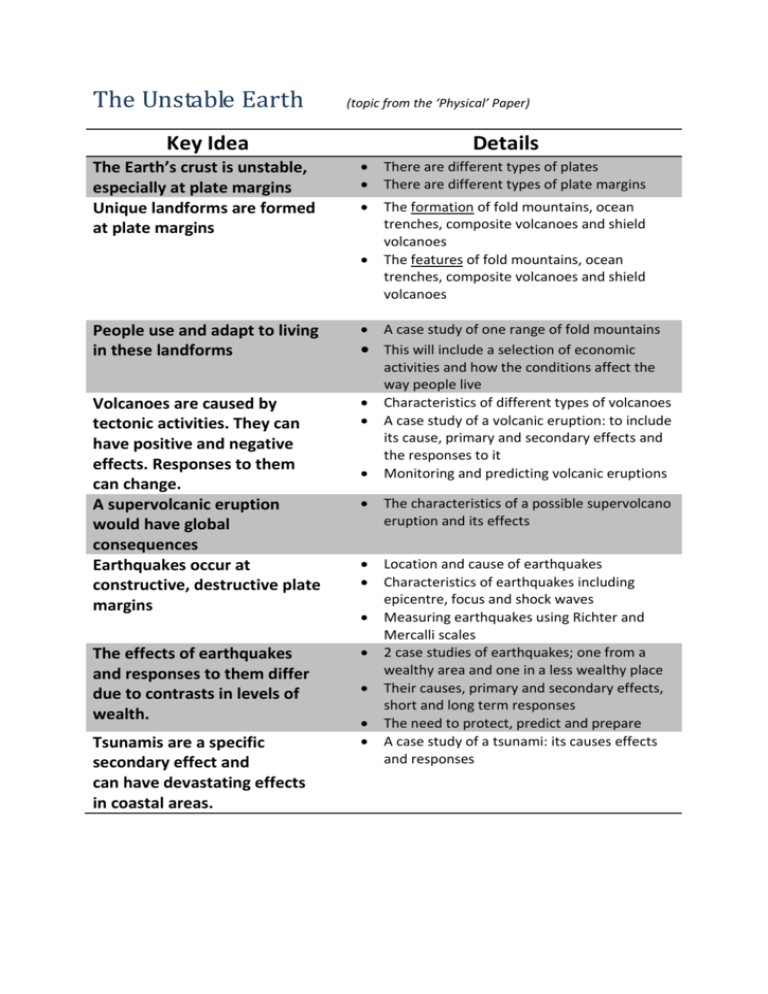
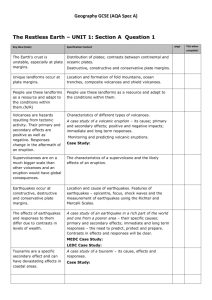
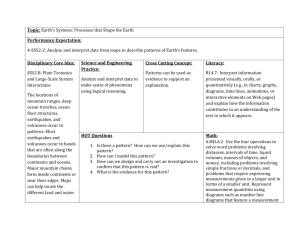
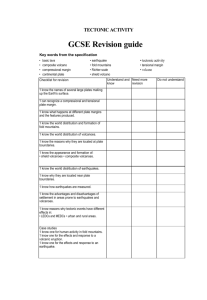
The Unstable Earth (topic from the ‘Physical’ Paper) Key Idea The Earth’s crust is unstable, especially at plate margins Unique landforms are formed at plate margins Details There are different types of plates There are different types of plate margins The formation of fold mountains, ocean trenches, composite volcanoes and shield volcanoes The features of fold mountains, ocean trenches, composite volcanoes and shield volcanoes People use and adapt to living in these landforms Volcanoes are caused by tectonic activities. They can have positive and negative effects. Responses to them can change. A supervolcanic eruption would have global consequences Earthquakes occur at constructive, destructive plate margins The effects of earthquakes and responses to them differ due to contrasts in levels of wealth. Tsunamis are a specific secondary effect and can have devastating effects in coastal areas. A case study of one range of fold mountains This will include a selection of economic activities and how the conditions affect the way people live Characteristics of different types of volcanoes A case study of a volcanic eruption: to include its cause, primary and secondary effects and the responses to it Monitoring and predicting volcanic eruptions The characteristics of a possible supervolcano eruption and its effects Location and cause of earthquakes Characteristics of earthquakes including epicentre, focus and shock waves Measuring earthquakes using Richter and Mercalli scales 2 case studies of earthquakes; one from a wealthy area and one in a less wealthy place Their causes, primary and secondary effects, short and long term responses The need to protect, predict and prepare A case study of a tsunami: its causes effects and responses