Plantae
advertisement

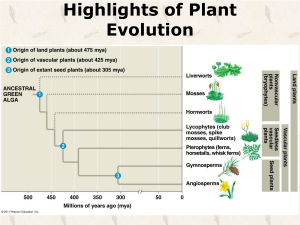
Plantae Seed Plants Vascular Plants • Formation of vascular tissue – Xylem (water) – Phloem (food) – True leaves, roots, and stems • Lignin Sporophyte • ____________ generation dominate Alternation of Generation Alternation of Generation • Sporophyte dependent on gametophyte – mosses • Large sporophyte and small independent gametophyte – ferns • Gametophyte dependent on sporophyte – seed plants Why be Sporophyte Dominant? • Reduced mutations – UV light harmful to DNA – Diploid (2n) form copes better with mutations • two alleles Why Retain Gametophyte Generation? • Ability to screen alleles – doesn’t require a large amount of energy • Sporophyte embryos rely on some gametophyte tissue Seeds • A seed is a sporophyte in a package – spores are only single cells – packaged with food • All seed plants are Heterosporous _____________ (more than one kind of spore) – megasporangia – microsporangia From Ovule to Seed Develops from megaspore Whole structure Embryo, food supply, protective coat Overview of Seed Plants • Produce Seeds – Can remain dormant for years – Pollination replaces swimming sperm • Gametophyte generation reduced – Gymnosperms lack antheridium – Angiosperms lack both archegonium and antheridium Phylogeny Gymnosperms (Naked Seed) • Division: • Division: • Division: • Division: Cycadophyta Ginkgophyta Gnetophyta Coniferophyta Ginkgophyta • Ginkgo or Maidenhair Tree • Characteristic leaves • Only one species Males • Only ______ are planted Cycadophyta • Cycads • Palm-like plants – Sago Palms • Leaves in cluster at top of trunks Secondary • True __________ Growth Gnetophyta • 3 Genera • Ephedra • Mormon Tea Ephedrine – ____________ • raises heart rate • raises blood pressure Coniferophyta Coniferophyta • Pine tree is the sporophyte generation • Contains both male and female cones – Pollen (___________) Staminate cones (low in tree) • produces pollen – Ovulate cones (high in tree) with scales • produces seeds Pine Life Cycle • No Antheridium (microsporangia) produce pollen grain (4 cells) – 2 prothallial cells – 1 generative cell » produces 2 sperm – 1 tube cell Wings – __________ for dispersal Pine Life Cycle • Ovule in a ovulate cone – integument (seed coat) (2n) – megasporangia or nucellus (nutrition) (2n) Megaspores – 4 _______________ from female gametophyte (3 die) • develops into female gametophyte – archegonium with eggs (n) Angiosperms Angiosperm Flower • Sepals • Petals • Receptacle (part of the stem) • Stamen – Anther – Filament • Carpel – Stigma – Style – Ovary with ovule Angiosperm Life Cycle Angiosperm Life Cycle • No Antheridium (microsporangia diploid) • produce pollen grain generative cell – 1 ___________ » produces 2 sperm – 1 tube cell Angiosperm Life Cycle • Ovule in Ovary – megasporangia – produces 4 megaspores (3 die) • remaining one develops into female Embryo sac gametophyte called the _____________ Angiosperm Life Cycle • Embryo sac (Female Gametophyte) consists of: – 7 cells (eight nuclei) due to 3 mitotic divisions • 3 • 2 • 2 • 1 Antipodals ___________ polar nuclei (one cell) Synergids __________ egg Angiosperm Life Cycle • Double fertilization – one sperm unites with egg – one sperm unites with polar nuclei • develops into endosperm (3n) • Fruit and Seed development – ovule = seed – ovary = fruit Angiosperm Life Cycle Cross Pollination • Most flowers do not self-pollinate – stamen and carpal may develop at different times – stamen and carpal may be arranged in flower to avoid contact Angiosperm Radiation • Begins the Cenozoic era (65 mya) • Most closely related to the Gnetophyta Coevolution • __________ – the mutual influence of two species on each other – plants and animals (insects, birds, bats)