Kingdom: Plantae
advertisement

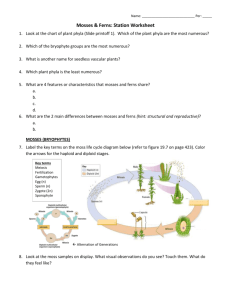
Kingdom: Plantae Characteristics of Plants • • • • • • Eukaryotic Multicellular Carry out photosynthesis Cells have a cell wall made of cellulose Mostly land dwelling Develop from embryos that are protected by tissues of parent plant Life cycles • • • • Plants go through alternation of generations One generation is haploid called gametophyte One generation is diploid called sporophyte Haploid spores produce plants which eventually produce gametes which fuse to produce diploid zygote that grows into a sporophyte plant • These generations can look quite different from one another Five Major Groups of Plants Green Algae • Green algae has recently been reclassified as belonging to the Kindom Plantae • Green algae has cell walls and photosynthetic pigments that are identical to plants • Other algae remain in the Kingdom Protista Five Major Groups of Plants Seedless Non-Vascular Plants Mosses and Relatives • • • • These plants are known as Bryophytes Grow close to the ground in damp locations Do not have seeds or stems Do not have any rigid support structures such as lignin-reinforced cell walls • Do not have any vascular tissue to transport water through the plant Seedless Non-Vascular Plants Mosses and Relatives • Bryophytes comprise nearly 10% of all plant species • The gametophyte generation is the dominant generation • Male and female gametes are produced in separate reproductive structures • Sperm are flagellated and must swim through water to the eggs Five Major Groups of Plants Seedless Vascular Plants: Ferns and Relatives • Contain conducting tissues called xylem and phloem which transport materials throughout the plant • This development allowed the ferns to become tall and successful on dry land • The dominant generation is sporophyte Reproduction in Ferns • Ferns produce gametes in structures on the underside of the gametophyte • Ferns need water to complete their life cycle because sperm have to swim through a film of water to fertilize the eggs • The brown “dots” on the underside of the mature (sporophyte) fronds are spore capsules containing many haploid spores that will produce gametophytes Five Major Groups of Plants Seed-producing Vascular plants Gymnosperms • Conifers such as pine, fir, spruce, redwood and cedar trees – cone bearing plants • Plants that bear “naked” seeds – seeds not enclosed in an ovary (fruit) • Seeds are plant embryos covered in a protective coat along with food • The gametophyte is smaller than in ferns and mosses Gymnosperm Reproduction in Gymnosperms Five Major Groups of Plants Flowering Plants Angiosperms • The reproductive structures are the flowers • Angiosperm means “enclosed seed” • The gametophytes develop within the flowers of angiosperms • Flowers have many adaptations that attract organisms to help transfer pollen • Once pollination occurs, the ovary develops into a fruit Angiosperm fruit Life cycle of an Angiosperm Parts of a Flower Stigma Stamen (male) Anther Filament Style Ovary petals ovule sepal Carpel/ Pistil (female) Five Major Groups of Plants