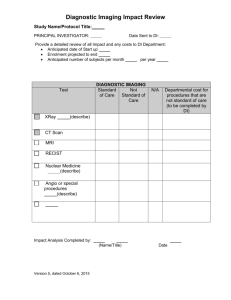
XDS-I
advertisement

ACC, HIMSS and RSNA Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise 5 IHE Radiology Technical Framework Supplement 2005-2006 10 Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging (XDS-I) 15 Trial Implementation Version Publication date: August 15, 2005 Copyright © 2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 20 Foreword 25 Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise (IHE) is an initiative designed to stimulate the integration of the information systems that support modern healthcare institutions. Its fundamental objective is to ensure that in the care of patients all required information for medical decisions is both correct and available to healthcare professionals. The IHE initiative is both a process and a forum for encouraging integration efforts. It defines a technical framework for the implementation of established messaging standards to achieve specific clinical goals. It includes a rigorous testing process for the implementation of this framework. And it organizes educational sessions and exhibits at major meetings of medical professionals to demonstrate the benefits of this framework and encourage its adoption by industry and users. 30 35 40 45 50 55 The approach employed in the IHE initiative is not to define new integration standards, but rather to support the use of existing standards, HL7, DICOM, IETF, and others, as appropriate in their respective domains in an integrated manner, defining configuration choices when necessary. IHE maintain formal relationships with several standards bodies including HL7, DICOM and refers recommendations to them when clarifications or extensions to existing standards are necessary. This initiative has numerous sponsors and supporting organizations in different medical specialty domains and geographical regions. In North America the primary sponsors are the American College of Cardiology (ACC), the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) and the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). IHE Canada has also been formed. IHE Europe (IHE-EUR) is supported by a large coalition of organizations including the European Association of Radiology (EAR) and European Congress of Radiologists (ECR), the Coordination Committee of the Radiological and Electromedical Industries (COCIR), Deutsche Röntgengesellschaft (DRG), the EuroPACS Association, Groupement pour la Modernisation du Système d'Information Hospitalier (GMSIH), Société Francaise de Radiologie (SFR), Società Italiana di Radiologia Medica (SIRM), the European Institute for health Records (EuroRec), and the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). In Japan IHE-J is sponsored by the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI); the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare; and MEDISDC; cooperating organizations include the Japan Industries Association of Radiological Systems (JIRA), the Japan Association of Healthcare Information Systems Industry (JAHIS), Japan Radiological Society (JRS), Japan Society of Radiological Technology (JSRT), and the Japan Association of Medical Informatics (JAMI). Other organizations representing healthcare professionals are invited to join in the expansion of the IHE process across disciplinary and geographic boundaries. The IHE Technical Frameworks for the various domains (IT Infrastructure, Cardiology, Laboratory, Radiology, etc.) defines specific implementations of established standards to achieve integration goals that promote appropriate sharing of medical information to support optimal patient care. It is expanded annually, after a period of public review, and maintained regularly __________________________________________________________________________ 1 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ through the identification and correction of errata. The current version for these Technical Frameworks may be found at www.ihe.net or http://www.himss.org/IHE. 60 65 The IHE Technical Framework identifies a subset of the functional components of the healthcare enterprise, called IHE Actors, and specifies their interactions in terms of a set of coordinated, standards-based transactions. It describes this body of transactions in progressively greater depth. The volume I provides a high-level view of IHE functionality, showing the transactions organized into functional units called Integration Profiles that highlight their capacity to address specific clinical needs. The subsequent volumes provide detailed technical descriptions of each IHE transaction. This supplement to the Radiology Technical Framework is issued for Trial Implementation through March 2006, per the schedule announced in February 2005. 70 Comments and change proposals arising from Trial Implementation may be submitted to: http://forums.rsna.org under the “IHE” forum Select the Radiology Supplements for Public Review sub-forum. 75 The IHE Radiology Technical Committee will address these comments resulting from implementation, connect-a-thon testing, and demonstrations. Final text is expected to be published in May 2006. __________________________________________________________________________ 2 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 80 These ”boxed” instructions for the author to indicate to the Volume Editor how to integrate the relevant section(s) into the overall Technical Framework 1 Introduction Background Documents and data representing a patient’s medical record are generated and archived on a variety of systems over the course of diagnosis and treatment. 85 90 95 Many imaging and clinical activities would benefit from a coordinated method for “sharing”, locating and accessing relevant imaging related documents. Images, diagnostics reports, and evidence documents derived from the processing of images represent important components of a patient’s medical record. However, they are managed and archived on a variety of imaging information systems such as RIS and PACS over the course of diagnosis and treatment. For the same patient some of this imaging information is produced in departments associated with one or more in-patient facilities (where the patient may have been hospitalized), as well as independent imaging centers. A number of healthcare delivery professionals (e.g., referring physicians, radiologists, surgeons, oncologists, etc.) would benefit from a coordinated method for locating and accessing relevant imaging information. The creation and subsequent usage of these documents may span several care delivery organizations and may be performed separately over different time periods. IHE IT Infrastructure has released the Cross-Enterprise Document Sharing (XDS) profile. It provides an integration solution to the problem of general-purpose document sharing in a broad healthcare environment. 100 105 This profile specifies sharing of imaging “documents” such as radiology images and reports; it presents a solution for sharing imaging documents based on XDS. XDS-I extends XDS by sharing, locating and accessing DICOM instances from its original local sources, e.g. for radiologists or oncologists. Even though this profile may be useful for sharing cardiology documents, cardiology specific use cases have not been addressed as the cardiology technical committee intends to address this topic in the near future. Since the XDS for Imaging Profile relies so heavily on the IT Infrastructure XDS Profile including the use of terms defined in XDS (e.g., affinity domain, submission set, etc.) the reader of XDS-I is expected to have read and understand the XDS Profile (See ITI TF-1: 10). Proposed Solution 110 The Cross-Enterprise Document Sharing (XDS) Profile in the IHE IT Infrastructure Domain is used and adapted to meet the imaging information sharing use cases. New XDS document types and actor capabilities are defined based on the standard artifacts of Radiology. The XDS design __________________________________________________________________________ 3 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 115 principle that one single registry is a single query/ access point and holds the indexing data about all documents that are available from multiple repositories in the Affinity Domain, is the key point here. The information to be shared includes one or more of the following: 120 1. Imaging studies that include images acquired on a broad range of different modalities, as well as evidence documents (e.g. post-processing measurements/analysis outcome), and presentation states. 2. Diagnostic reports resulting from the interpretation of one or more related imaging studies provided in a ready-for-display form. 3. A selection of diagnostically significant images associated with the report content. Scope of Supplement 125 130 This profile considers “imaging information sharing” in the sense of making imaging work products available to be shared by other authorized members of an affinity domain. This is intended to exclude (for now) the handshaking, notifications and immediate availability of intermediate work products necessary to co-ordinate workflows between the imaging departments of different enterprises (e.g. federated PACS/RIS where the acquisition and reading is distributed among independent enterprises, regional archiving serving multiple PACS, home on-call tele-radiology, etc.). IHE Radiology may address such workflows in the future. Connecting the sharing of imaging information across enterprises with intra-enterprise workflows seems to be an important issue, but one that is related more to the intra-enterprise IHE Integration Profiles (e.g. Scheduled Workflow, Reporting Workflow) than to the data transfer necessary for sharing information across enterprises. 135 140 145 A number of conventions, such as the use of coded concepts in the XDS Registry, can be established as policies by an Affinity Domain or by Regional IHE Extensions. XDS sharing concepts such as Submission Sets and folders should be used as basic tools for organization. Both the XDS and XDS for Imaging Integration Profiles are not intended to address all crossenterprise EHR communication needs. Some scenarios may require the use of other IHE Integration profiles, such as Patient Identifier Cross-Referencing (PIX), Audit Trail and Node Authentication (ATNA), Enterprise User Authentication (EUA), Cross-enterprise User Authentication (XUA) and Retrieve Information for Display (RID). Other scenarios may be only partially supported, while still others may require future IHE Integration profiles, which will be defined by IHE as soon as the necessary base standards are available. Specifically: 1. The operation of any XDS-I Clinical Affinity Domain will require that a proper security model be put in place. It is expected that a range of security models should be possible. Although the XDS-I Integration Profile is not intended to include nor require any specific security model, it is expected that XDS-I implementers will group XDS-I Actors with actors from the IHE Audit Trail and Node Authentication and will need an __________________________________________________________________________ 4 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 150 Access Control capability that operates in such a cross-enterprise environment. New IHE Integration Profiles have been identified as candidates (e.g. Public Key Infrastructure, Access Control, etc.). There is a discussion of XDS-I security considerations in RAD TF-1: Appendix X2. 2. The establishment of independent but consistently XDS-based Affinity Domains will call for their federation, as patients expect their records to follow them as they move from region to region, or country to country. IHE foresees a need for transferring information from one Clinical Affinity Domain to another, or to allow access from one Affinity Domain to documents managed in other Affinity Domains. XDS/ XDS-I has been designed with this extension in mind. An XDS/ XDS-I Domains Federation Integration Profile that complements XDS may be anticipated in the future. 3. XDS and XDS-I do not address transactions for the management or configuration of a clinical affinity domain. For example, the configuration of network addresses or the definition of what type of clinical information is to be shared is specifically left up to the policies established by the clinical affinity domain. 4. XDS and XDS-I do not specifically address the patient information reconciliation process necessary between the Clinical Affinity Domain and any other local patient identity domains that Document Sources and Document Consumers may be members of. For a discussion of some of these issues see RAD TF-1: Appendix X1. 155 160 165 Profile Abstract 170 This Supplement introduces a new IHE Integration Profile known as the Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging (XDS-I) Profile that facilitates the sharing of Imaging Information across health enterprises. Imaging Information includes sets of DICOM instances, diagnostic reports provided in a ready-for-display form and a selection of diagnostically significant images associated with the report content. 175 In this context, sharing means making imaging information available in accessible repositories and registering them in a central registry. A registry query provides consumers with the details necessary to retrieve relevant data. 180 This Integration Profile provides specifications for managing the sharing of imaging information that healthcare enterprises (anywhere from a private physician to a clinic to an acute care inpatient facility) have decided to share in an Affinity Domain. This defines the imaging component of a shared longitudinal Electronic Health Record. Since the XDS for Imaging Profile relies so heavily on the IT Infrastructure XDS Profile including the use of terms defined in XDS (e.g., affinity domain, submission set, etc.) the reader of XDS-I is expected to have read and understand the XDS Profile (See ITI TF-1: 10). __________________________________________________________________________ 5 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Volume I – Integration Profiles 185 Changes to Sections 1 – 1.X 1.7 History of Annual Changes Add the following item to the bullet list in volume 1, section 1.7 • Added the Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging (XDS-I) Profile that specifies actors and transactions allowing users to share across enterprises sets of DICOM instances, imaging reports in a “ready-for-display” format, as well as significant images in non-DICOM format. 190 Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Integration Profile Dependencies 195 Add the following row to the Profile Dependency table in volume 1, section 2.x Table 2-1 defines the required dependencies between the Integration Profiles in a tabular form. Table 2-1 Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Integration Profiles Dependencies 200 Integration Profile … XDS for Imaging Depends on Dependency type Comments … … … IT Infrastructure XDS Document Consumer, Document Registry, Document Repository actors are required to support XDS Document content types and metadata are specialized. __________________________________________________________________________ 6 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Integration Profiles Overview Add the following to 2.1 Integration Profiles overview 2.1.X Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging (XDS-I) 205 210 The Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging (XDS-I) Integration Profile specifies actors and transactions that allow users to share imaging information across enterprises. This profile depends on the IHE IT-Infrastructure Cross-Enterprise Document Sharing (XDS) profile. XDS for Imaging (XDS-I) defines the information to be shared such as sets of DICOM instances (including images, evidence documents, and presentation states), diagnostic imaging reports provided in a ready-for-display. Since the XDS for Imaging Profile relies so heavily on the IT Infrastructure XDS Profile including the use of terms defined in XDS (e.g., affinity domain, submission set, etc.) the reader of XDS-I is expected to have read and understand the XDS Profile (See ITI TF-1: 10). Add the following to 2.2 Actor Descriptions 215 220 225 230 2.2 Actor Descriptions Imaging Document Source - The Imaging Document Source actor is the producer and publisher of imaging documents. It is responsible for providing imaging documents and meta-data to the Document Repository actor, which subsequently registers the imaging documents with the Document Registry actor. It also supports the retrieval services for DICOM SOP Instances referenced in a published imaging manifest document. Document Consumer - The Document Consumer actor queries a Document Registry actor for documents meeting certain criteria, and retrieves selected documents from one or more Document Repository actors. Imaging Document Consumer - The Imaging Document Consumer actor parses an imaging manifest document that is retrieved by the Document Consumer actor from the Document Repository actor, and retrieves DICOM SOP Instances referenced within that manifest from the Imaging Document Source actor. Document Registry - The Document Registry actor maintains meta-data about each registered document in a document entry. This includes a link to the Document Repository where the actual document is stored. The Document Registry responds to queries from Document Consumer actors about documents meeting specific criteria. It also enforces some healthcare specific technical policies at the time of document registration. __________________________________________________________________________ 7 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 235 Document Repository - The Document Repository actor persistently stores documents. It assigns and maintains a unique identifier for each document, to allow Document Consumers to retrieve them. Patient Identity Source - The Patient Identity Source actor assigns a unique identifier to each instance of a patient as well as maintains a collection of identity traits. 240 Update the Integration Profile Actors table2.2-1 as follows Table 2.2-1. Integration Profile Actors Integration Profile Actor Acq. Modality ADT Patient Reg. Audit Record Rep Charge Processor DSS/OF Enterprise Rep. Repository Evidence Creator Ext. Rep. Access Image Archive Image Display Image Manager Order Placer PostProcessing Manager SWF PIR PWF RWF CHG X X X X X X CPI PGP KIN ED X X X SINR PDI ARI SEC X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X __________________________________________________________________________ 8 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA XDSI IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Integration Profile Actor PPS Manager Print Composer Print Server Report Creator Report Manager Report Reader Report Repository Removable Media Creator Removable Media Importer Secure Node Time Server Imaging Document Source Document Consumer Imaging Document Consumer Document Repository Document Registry SWF PIR X X PWF RWF CHG X X CPI PGP KIN ED SINR PDI ARI X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X __________________________________________________________________________ 9 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 XDSI X X X SEC Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Integration Profile Actor SWF PIR PWF RWF CHG CPI PGP KIN ED SINR PDI ARI SEC Patient Identity Source X 2.3 Transaction Descriptions Add the following to 2.3Transaction description 245 250 255 260 54. Provide and Register Imaging Document Set - An Imaging Document Source actor initiates the Provide and Register Imaging Document Set transaction. For each document in the Submission Set, the Imaging Document Source actor provides both the documents as an opaque octet stream and the corresponding meta-data to the Document Repository. The Document Repository is responsible to persistently store these documents, and to register them in the Document Registry using the Register Documents transaction by forwarding the document meta-data received from the Imaging Document Source Actor. [RAD-54, derived from ITI-15]. ITI-14. Register Document Set - A Document Repository Actor initiates the Register Document Set transaction. This transaction allows a Document Repository Actor to register one or more documents with a Document Registry, by supplying meta-data about each document to be registered. This document meta-data will be used to create an XDS Document Entry in the registry. The Document Registry actor ensures that document meta-data is valid before allowing documents to be accessed through a query. If one or more documents fail the meta-data validation, the Register Document Set transaction fails as a whole. To support composite documents, an XDS Document may be a multipart document. The Document Repository must handle multi-part data sets as an “opaque entity”. The Document Repository does not need to analyze or process its multi-part structure nor the content of any parts in the context of the XDS Integration Profile [ITI-14]. 265 270 XDSI ITI-16.Query Registry – The Query Registry transaction is issued by the Document Consumer Actor on behalf of a care provider (EHR-CR) to a Document Registry. The Document Registry Actor searches the registry to locate documents that meet the criteria specified in the query request. It will return a list of document entries that contain metadata found to meet the specified criteria including the locations and identifier of each corresponding document in one or more Document Repositories [ITI-16]. ITI-17. Retrieve Document – A Document Consumer Actor initiates the Retrieve Document transaction. The Document Repository will return the document that was specified by the Document Consumer. To support composite documents, an XDS Document may be a __________________________________________________________________________ 10 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 275 280 multipart document. In this case, the Document Consumer must take appropriate actions to make the multipart content accessible to the user [ITI-17]. ITI-8. Patient Identity Feed – This is IHE ITI Transaction 8, defined as part of the Patient Identifier Cross-referencing Integration Profile. It conveys the patient identifier and corroborating demographic data, captured when a patient’s identity is established, modified or merged or in cases where the key corroborating demographic data has been modified. Its purpose in the XDS Integration Profile is to populate the registry with patient identifiers that have been registered in the affinity domain [ITI-8]. 55. WADO Retrieve – A WADO Retrieve transaction is issued by an Imaging Document Consumer to an Imaging Document Source to retrieve DICOM objects over HTTP/HTTPS protocol [RAD-55]. 285 Update the following existing transactions descriptions. 290 295 300 16. Retrieve Images –An Image Display or an Imaging Document Consumer requests and retrieves a particular image or set of images from the Image Archive or an Imaging Document Source, respectively. 17. Retrieve Presentation States – An Image Display or an Imaging Document Consumer requests and retrieves the Grayscale Softcopy Presentation State (GSPS) information for a particular image or image set 27. Retrieve Reports – A Report Reader or an Imaging Document Consumer requests and retrieves a diagnostic report from the Report Repository or External Report Repository Access or an Imaging Document Source. 31. Retrieve Key Image Note – An Image Display or an Imaging Document Consumer requests and retrieves a Key Image Note from the Image Archive or an Imaging Document Source, respectively. 45. Retrieve Evidence Documents – A user of Evidence Documents (Image Display, Report Creator or Report Reader) or an Imaging Document Consumer requests and retrieves an Evidence Document from the Image Archive or an Imaging Document Source, respectively. Update the Integration Profile Transactions table as follows 305 Table 2.3-1. Integration Profile Transactions Integration Profile Transaction SWF Patient Registration [1] X PIR PWF RWF CHG CPI PGP KIN ED SINR PDI ARI X __________________________________________________________________________ 11 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA SEC XD S-I IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Integration Profile Transaction Placer Order [2] Filler Order [3] Procedure Scheduled [4] Query Modality Worklist [5] Modality Procedure Step In Progress [6] Modality Procedure Step Completed [7] Modality Images Stored [8] Modality Presentation State Stored [9] Storage Commitment [10] Images Availability Query [11] Patient Update [12] SWF PIR X X X X X X X X X X X KIN ED SINR PDI ARI X X X X X X X X X X X X X SEC XD S-I X X X X X X X X X X X Query Images [14] X X X Query Presentation States [15] Retrieve Images [16] X X Retrieve Presentation States [17] Creator Images Stored [18] Creator Presentation State Stored [19] Creator Procedure Step In Progress [20] Creator Procedure Step Complete [21] Print Request with Presentation LUT [23] Report Submission [24] Report Issuing [25] PGP X X Procedure Update [13] PWF RWF CHG CPI X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X __________________________________________________________________________ 12 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA X X IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Integration Profile Transaction SWF Query Reports [26] PIR PWF RWF CHG CPI KIN ED X X Retrieve Reports [27] SINR PDI X X X Structured Report Export [28] Key Image Note Stored [29] Query Key Image Notes [30] Retrieve Key Image Notes [31] Authenticate Node [32] Maintain Time [33] ARI SEC X X XD S-I X X X X X X X X X X Record Audit Event [34] Charge Posted [35] Account Management [36] Query PostProcessing Worklist [37] Workitem Claimed [38] Workitem Completed [39] Workitem PPS InProgress [40] Workitem PPS Completed [41] Performed Work Status Update [42] Evidence Documents Stored [43] Query Evidence Documents [44] Retrieve Evidence Documents [45] Query Reporting Worklist [46] Distribute Media [Y] PGP X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X __________________________________________________________________________ 13 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA X IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Integration Profile Transaction SWF PIR PWF RWF CHG CPI PGP KIN ED SINR PDI ARI SEC Provide and Register Imaging Document Set [RAD-54] Register Document Set [ITI-14] Query Registry [ITI16] Retrieve Document [ITI-17] Patient Identity Feed [ITI-8] WADO Retrieve [RAD-55] X X X X X X 2.4 Product Implementations Add the following grouping descriptions to the end of section 2.4 310 The Imaging Document Consumer shall be grouped with a Document Consumer. Add the following sections (18, 18.1,) at the end of volume 1, before Appendix A. 18. Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Integration Profile 315 The Cross-Enterprise Document Sharing (XDS) Profile in the IHE IT Infrastructure Domain provides a solution for sharing (publishing, finding and retrieving) documents across a group of affiliated enterprises. The XDS for Imaging (XDS-I) Profile, defined here, extends and specializes XDS to support imaging “documents”, specifically including the following: • Imaging studies that include images acquired on a broad range of different modalities, as well as evidence documents (e.g. post-processing measurements/analysis outcome), and presentation states. • Diagnostic reports resulting from the interpretation of one or more related imaging studies provided in a ready-for-display form • A selection of diagnostically significant images associated with the report content. 320 325 These document types along with the actor capabilities required to share them are defined by this profile. __________________________________________________________________________ 14 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 XD S-I Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ The XDS for Imaging Profile relies so heavily on the IT Infrastructure XDS Profile including the use of terms defined in XDS (e.g., affinity domain, submission set, etc.) the reader of XDS-I is expected to have read and understand the XDS Profile (See ITI TF-1: 10). 330 335 Both the XDS and XDS for Imaging Integration Profiles are not intended to address all crossenterprise EHR communication needs. Many scenarios may require the use of other IHE Integration profiles, such as Patient Identifier Cross-Referencing (PIX), Audit Trail and Node Authentication (ATNA), Enterprise User Authentication (EUA), Cross-enterprise User Authentication (XUA) and Retrieve Information for Display (RID). Other scenarios may be only partially supported, while still others may require future IHE Integration profiles, which will be defined by IHE as soon as the necessary base standards are available. Specifically: 1. The operation of any XDS-I Clinical Affinity Domain will require that a proper security model be put in place. It is expected that a range of security models should be possible. Although the XDS-I Integration Profile is not intended to include nor require any specific security model, it is expected that XDS-I implementers will group XDS-I Actors with actors from the IHE Audit Trail and Node Authentication and will need an Access Control capability that operates in such a cross-enterprise environment. New IHE Integration Profiles have been identified as candidates (e.g. Public Key Infrastructure, Access Control, etc.). There is a discussion of XDS-I security considerations in RAD TF-1: Appendix X2. 2. The establishment of independent but consistently XDS-based Affinity Domains will call for their federation, as patients expect their records to follow them as they move from region to region, or country to country. IHE foresees a need for transferring information from one Clinical Affinity Domain to another, or to allow access from one Affinity Domain to documents managed in other Affinity Domains. XDS/ XDS-I has been designed with this extension in mind. An XDS/ XDS-I Domains Federation Integration Profile that complements XDS may be anticipated in the future. 3. XDS and XDS-I do not address transactions for the management or configuration of a clinical affinity domain. For example, the configuration of network addresses or the definition of what type of clinical information is to be shared is specifically left up to the policies established by the clinical affinity domain. 4. XDS and XDS-I do not specifically address the patient information reconciliation process necessary between the Clinical Affinity Domain and any other local patient identity domains that Document Sources and Document Consumers may be members of. For a discussion of some of these issues see RAD TF-1: Appendix X1. 340 345 350 355 360 18.1 Actors/ Transactions Figure 18.1-1 shows the actors directly involved in this profile and the transactions between actors. __________________________________________________________________________ 15 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Patient Identity Source Patient Identity Feed [ITI-8] ↓ Query Registry [ITI-16] ← Document Registry Imaging Document Consumer ↑ Register Document Set[ITI-14] Provide & Register Imaging Document Set[RAD-54] → Imaging Document Source Document Consumer Retrieve Document [ITI-17] ← Document Repository WADO Retrieve [RAD-55] ← Retrieve Images [RAD-16] ← Retrieve Presentation States [RAD-17] ← Retrieve Reports [RAD-27] ← Retrieve Key Image Note [RAD-31] ← Retrieve Evidence Documents [RAD-45] ← Figure 18.1-1. Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Diagram 365 370 Table 18.1-1 lists the transactions for each actor directly involved in the Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile. In order to claim support of this Integration Profile, an implementation shall perform the required transactions (labeled “R”). Transactions labeled “O” are optional. A complete list of options defined by this Integration Profile is listed in RAD TF-1: 18.2. Note that a number of actors must be grouped with Imaging Document Source as described in RAD TF-1: 2.4. __________________________________________________________________________ 16 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Table 18.1-1 Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Integration Profile - Actors and Transactions Actors Document Consumer Imaging Document Consumer Transactions Optionality Query Registry [ITI-16] R ITI TF2:3.16 Retrieve Document [ITI-17] R ITI TF2:3.17 Retrieve Images [RAD-16] O (note2) 4.16 Retrieve Presentation States [RAD-17] O 4.17 Retrieve Reports [RAD-27] O (note2) 4.27 O 4.31 Retrieve Evidence Documents [RAD-45] O (note2) 4.45 WADO Retrieve [RAD-55] O (note2) 4.55 Provide and Register Imaging Document Set [RAD-54] R (note 3) 4.54 Retrieve Images [RAD-16] R 4.16 Retrieve Presentation States [RAD-17] R 4.17 Retrieve Reports [RAD-27] R 4.27 Retrieve Key Image Note [RAD-31], R 4.31 Retrieve Evidence Documents [RAD-45] R 4.45 WADO Retrieve [RAD-55] R 4.55 Provide and Register Imaging Document Set [RAD-54] R 4.54 Retrieve Key Image Note [RAD-31], Imaging Document Source Document Repository R (note1) ITI TF2:3.14 R ITI TF2:3.17 R (note1) ITI TF2:3.14 Query Registry [ITI-16] R ITI TF2:3.16 Patient Identity Feed [ITI-8] R ITI TF2:3.8 Patient Identity Feed [ITI-8] R ITI TF2:3.8 Register Document Set [ITI-14] Retrieve Document [ITI-17] Document Registry Patient Identity Source Note1: 375 Section in Vol. 2 Register Document Set [ITI-14] The Register Transaction is not required in implementations where the Document Registry Actor is grouped with the Document Repository Actor. However, it is strongly recommended that these transactions be supported to allow for future configuration with multiple Repositories. __________________________________________________________________________ 17 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Note 2: At least one of the optional retrieve transactions is required to be supported. Refer to section 18.4 for additional requirements on the Imaging Document Consumer. Note 3: Support of at least one of the four document types described by the options in section 18.2 is required.. 18.2 Integration Profile Options 380 Options that may be selected for this Integration Profile are listed in table 18.2-1 along with the Actors to which they apply. Dependencies between options when applicable are specified in notes. Table 18.2-1 Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging - Actors and Options Actor Vol & Section Options Set of DICOM Instances (Note 1) RAD TF-1: 18.2.1 PDF Report (Note 1) RAD TF-1: 18.2.2 Text Report (Note 1) RAD TF-1: 18.2.3 Multipart Text/PDF Report (Note 1) RAD TF-1: 18.2.4 Document Repository No options defined - Document Registry No options defined - Document Consumer No options defined - Imaging Document Consumer No options defined - Patient Identity Source No options defined - Imaging Document Source Note 1: At least one of these four options is required. 385 390 18.2.1 Set of DICOM Instances Option This option requires the Imaging Document Source to provide and register a DICOM manifest that references DICOM instances. These DICOM instances are made available to be retrieved from the Imaging Document Source, as specified in the manifest. The Imaging Document Source is required to ensure that the referenced images from within a published manifest are available to be retrieved. For details of the transaction affected by this option, refer to RAD TF-2: 4.54.4.1.2.2. 18.2.2 PDF Report Option 395 This option requires Imaging Document Source to provide and register an Imaging Report in a PDF format. The published report may contain embedded images or pre-computed links that reference images in a non-DICOM format. The Imaging Document Source is required to ensure that image references are valid links. For details of the transaction affected by this option, refer to RAD TF-2: 4.54.4.1.2.3 __________________________________________________________________________ 18 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 18.2.3 Text Report Option 400 This option requires Imaging Document Source to provide and register an Imaging Report in a Text format. For details of the transaction affected by this option, refer to RAD TF-2: 4.54.4.1.2.3. 18.2.4 Multipart Text/PDF Report Option 405 This option requires Imaging Document Source to provide and register an Imaging Report in Text and in PDF format as multipart of one document. For details of the transaction affected by this option, refer to RAD TF-2: 4.54.4.1.2.3. Text documents may serve as subsets or a specific summary of other document formats (e.g, transaction RAD-28 Structured Report Export) therefore it may be beneficial to provide both text and PDF documents in certain scenarios. 410 18.3 Image Information Sharing Process Flow 415 The sharing of imaging related information among different health professionals and facilities, even across administrative and geographic boundaries can lead to a large variety of information flows. Typical imaging information sets used in healthcare settings are well known, but the challenge is to distill the “exchange” scenarios to drive the sharing of imaging information across enterprises distributed over a community, region or nation. 18.3.1 Overview of Imaging Information Sharing Use Cases The following use case scenarios express the core imaging information sharing common to most clinical settings. They cover: 420 425 430 1. Routine imaging referral. The referring physician in his office requests that a patient have an examination done at an imaging facility. The physician expects to have electronic access to the imaging report and to the images if needed after the examination has been performed on his patient. This use case is further analyzed in this profile. 2. Course of Treatment Consult. An emergency physician orders an imaging examination for a patient at his hospital. After reviewing the preliminary report the ER physician decides to consult a surgical specialist at the regional hospital for advice on a course of action. For this, the surgical specialist accesses the images and preliminary report and reviews them in order to propose, on the phone, a course of action for the patient. This use case is further analyzed in this profile. 3. Clinical Consult. A general practitioner performs a routine imaging referral, reviews the shared imaging report and chooses to send the patient for evaluation by a specialist (e.g. an oncologist). The specialist needs access to the imaging report and full image set produced at the imaging facility where the patient had been sent by his general practitioner to perform the examination. This use case is further analyzed in this profile. __________________________________________________________________________ 19 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 435 440 4. General imaging record access. A patient relocates or decides to change her physician. The new physician needs to retrieve relevant information from the patient record, review its content, including recent labs and imaging studies. A similar situation occurs when a patient is admitted for an emergency and timely access to the patient’s past information is required, including prior imaging studies. This use case is further analyzed in this profile. This profile describes the information sharing transactions for care-delivering systems to publish patient’s imaging diagnostic documents (EHR-CR) for sharing across enterprises as longitudinal patient care records (HER-LR). The policies or administrative details regarding the sharing of imaging information are for the most part not explicitly discussed so as not to obscure clinical needs. Administrative variations between countries and regions are expected, and can be added or modified without losing the clinical information-sharing context. 445 Since the focus is on the sharing and access to patients imaging records rather than the entire workflow in which such information sharing takes place, other activities are described as though they are being done by telephone, paper mail, fax, etc. In an integrated electronic environment these other activities may be more automated, but those details are separate from the records access/sharing and are to be addressed by separate Integration Profiles. 450 18.3.2 Assumptions The imaging information needs to be shared between multiple care delivery organizations (information sources and consumers), each (typically) with its own RIS and PACS. The point of service (“POS”) for physicians may be supported by a variety of systems: hospital EMR, physician practice system, PACS viewers, EHR web application, etc. 455 460 The concept of sharing information across enterprises that have agreed to join in such a health information network is based on basic design principles that can be summarized in the following points: 1. A group of healthcare enterprises have agreed to work together using a common set of policies and to share a common infrastructure of repositories and a registry for an affinity domain. 2. Information sources (e.g. EHR, lab system, PACS) select the “documents” they wish to share. 3. Documents may include any information in an agreed format (e.g. a PDF document, a DICOM manifest, etc.). Documents are stored in multiple document repositories. 465 470 4. Shared documents are registered with a central service called a document registry that tracks only indexing information and the location from which documents may be retrieved. 5. Information consumers may query this well-defined unique/singular indexing service (document registry) to find the document index information for any patient and the location from which documents may be retrieved (document repositories). __________________________________________________________________________ 20 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 6. Information sources remain the owner of the documents shared in repositories and, thereby, remain responsible for replacing or deprecating its documents if necessary. 475 480 In each one of the use cases, it is assumed that the people and the information systems that participate in a single “Affinity Domain” have agreed upon mechanisms to address: • Governance: operational structure, data stewardship, etc. • Privacy: consent management and data masking controls • Security: Authorization and authentication, network security, audit trails, etc. • Normalized patient ID schemes: MPI (Master Patient Index), unique information IDs, etc. • Coded Vocabularies used for registry information 18.3.3 Use cases 18.3.3.1 Routine Imaging Referral Use Case 485 490 This scenario describes imaging information sharing in a typical patient referral and reporting use case where: • An examination is performed upon the request of a referring physician: • The referring physician accesses the regional health information network and reviews the report along with the key images and may optionally access the full image set that made the study. This scenario is characterized by all the information being provided for sharing at one time, as a single logical unit, when the imaging study is completed by the radiology enterprise (i.e., a single “document submission set”). 18.3.3.1.1 Process Flow 495 500 Figure 18.3.3-1 highlights the people and systems participating in this regional health information network, including: • Physician Office: A referring physician working out of a private office with a physician practice system for access to information • RIS/PACS Enterprise A: A radiology enterprise with modality equipment and a RIS/PACS to manage report and imaging information: Radiology Enterprise A • RIS/PACS Enterprise B: Another radiology enterprise with a RIS/PACS to manage report and imaging information: Radiology Enterprise B • Document Registry: A document registry that serves as the information index for the regional health information network __________________________________________________________________________ 21 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 505 In the process flow description, steps that pertain to information sharing are shown in bold (and numbered). In contrast, the steps that do not pertain to the focus of information sharing are shown in italic (and not numbered). These steps are expressed to ensure a more complete context. Figure 18.3.3-2 shows the transaction diagram for this process flow. 510 Exam is ordered The Referring Physician orders the examination and the patient goes to the Imaging Department: Radiology Enterprise A. 515 This is well-understood workflow that may be executed using any combination of paper, faxes, telephone, and electronic communications. It may or may not be addressed using the IHE Scheduled Workflow Integration Profile. Although this step is part of the use case, it is peripheral to the specific steps for sharing of imaging of information. 520 525 Step 1: Obtain Relevant Prior Imaging Information • The PACS at Radiology Enterprise A, where the acquisition and reporting is performed, does a query of the Document Registry to identify relevant prior images and reports. It should be noted that the determination of what is relevant is the responsibility of the consumer and not the registry. • The PACS at Radiology Enterprise A retrieves prior imaging information from a repository in another radiology enterprise within the regional health network: Radiology Enterprise B, in preparation for study acquisition and subsequent reporting __________________________________________________________________________ 22 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Radiology Enterprise B Prior imaging studies Query document Prior imaging studies Registry Query document Query document Provide Imaging Information for sharing Imaging Study Radiology Enterprise A Affinity Domain Physician Office Figure 18.3.3-1 Data Flow within the Regional Health Network for a Routine Imaging Referral 530 Exam is Acquired and Reported Images are sent from the modality to the PACS. This is well-understood workflow described in IHE SWF. 535 540 The study is reported. This is well understood workflow that is managed by systems within Radiology Enterprise A Step 2: Share Imaging Information within the Regional Health Network (Affinity Domain) • The PACS at Radiology Enterprise A, serving as a “Imaging Document Source”, provides imaging information to the document repository, which register the document in the registry, for sharing, including: o Acquired DICOM study o Final report __________________________________________________________________________ 23 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ o Key images along with annotations 545 550 555 Step 3: Obtain and Display Study Results • A physician practice system in the Physician’s office, serving as a document consumer, queries the Document Registry in the regional health network. This query may be triggered by the patient’s next appointment, a call from the patient to the physician’s secretary, an electronic notification that the examination’s result is available (using the IHE ITI Notification for Document Availability profile), etc. • The physician practice system presents a list of imaging information available for the patient • The referring physician selects the study results and relevant prior studies and reports • The physician practice system in the Physicians office, serving as an Imaging Document Consumer, retrieves the selected documents from the RIS/PACS Document Repositories in the regional health network and displays them to the referring physician. Referring Physician reviews the results 560 The Referring Physician reviews the results of the examination: the report and images from the RIS/PACS in Radiology Enterprise A, and the results of prior examinations: reports and images from the RIS/PACS in Radiology Enterprise B Radiology Enterprise A (Document Consumer) Radiology Enterprise A (Document Source) Radiology Enterprise A (Document Repository) Radiology Enterprise B (Document Repository) Document Registry Document Consumer (Physician Office) Step 1 - Query for relevant priors Step 1 - Retrieve relevant prior images and reports Step 2 - Share Images and Final Report Step 2 - Register Images and Final Report Step 3 - Query for Exam Step 3 - Retrieve Final Report and Images, Relevant prior images and reports 565 Figure 18.3.3-2 Process Flow – Routine Imaging Referral Use Case __________________________________________________________________________ 24 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 18.3.3.2 Course of Treatment Consult Use Case 570 575 580 585 This scenario is a variation on the routine imaging referral use case in that an addendum is generated after completion of the final report. As such, this scenario is characterized by information being provided for sharing at two separate times while ensuring that the initial information is supplemented by the addendum report. The use of addendum reports is commonly encountered in a course of treatment consultation where: • An ER physician orders an exam, and the study is acquired in the affiliated radiology department. • A department radiologist creates and shares a report as well as identifies key images and annotations. • A remotely located surgical specialist, at the request of the ER physician, reviews the report along with key images and the full study, and provides a consult to the ER physician (this use case does not constrain the method for communicating the results of the consult, e.g. phone, fax, etc). • The radiologist identifies additional information and completes an addendum to the initial report. Note that the scenario where the radiologist seeks an opinion from a more senior radiologist is similar to this use case. 18.3.3.2.1 Process Flow The process flow description and steps are as for the routine imaging referral, but with the following variations (shown in bold): 590 Exam is ordered Step 1: Obtain Relevant Prior Imaging Information Exam Acquisition and Reporting 595 600 Step 2: Share Imaging Information within the Regional Health Network (Affinity Domain) • The PACS at Enterprise A, serving as a “Imaging Document Source”, provides imaging information to the document repository, which register the document in the registry, for sharing, including: o Acquired DICOM study o Report o Key images along with annotations Step 3: Obtain and Display Study Results ER Physician reviews the results __________________________________________________________________________ 25 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 605 610 Step 4: Share Addendum to Report within the Regional Health Network (Affinity Domain) • Sometime later on, the radiologist creates an addendum to the initial report. This addendum is transcribed into the RIS at Enterprise A and signed off by the radiologist. This addendum must now supplement the initial report. • The RIS at Enterprise A performs a document query of the document registry for the first submission set • The RIS at Enterprise A, serving as a “Imaging Document Source”, provides the addendum for sharing to the document registry including the content of the first submission set and declaring the new document as an addendum to the initial report Figure 18.3.3-3 shows the transaction diagram for this process flow. Rad. Enterprise A Rad. Enterprise A: PACS (Document Consumer) (Document Source) Rad. Enterprise A: RIS (Document Source) Rad. Enterprise A (Document Repository) Rad. Enterprise B (Document Repository) Document Registry Orthopaedic Centre (Document Consumer) Step 1 - Query or relevant prior exams Step 1 - Retrieve relevant prior images and reports Step 2 - Share images and Initial Report (Submission Set 1) Step 2 - Register images and report Step 3 - Query for exam Step 3 - Retrieve images and report for new exam Step 4 - Query for new exam (associated submission set) Step 4 - Register Addendum Step 4 - Share Addendum (Submission Set 2) 615 Figure 18.3.3-3 Process Flow – Course of Treatment Consult Use Case 18.3.3.3 Clinical Consult Use Case 620 This scenario is an extension of the routine imaging referral use case in that a consult report is generated based from the original imaging exam and radiologist report. As such, this scenario is characterized by information being provided for sharing at two separate times by two separate source systems. __________________________________________________________________________ 26 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ The reports shared in this use case are based on the same initial imaging exam. However the reports are generated by different people and registered by different systems. 625 630 635 640 645 The generation of consult reports is commonly encountered in cancer treatment. As such, the following clinical consult use case is used to describe the scenario: • A general practitioner performs a routine imaging referral (as per Use Case 1). • In reviewing the imaging exam report from the radiologist, the practitioner chooses to send the patient to an oncologist for a consultation. • The oncologist, located at a Cancer Center, reviews the report along with key images, the full study, and past imaging information records for the patient • The oncologist generates an additional report that is made available to the general practitioner • The general practitioner reviews the oncologists report and takes appropriate treatment action 18.3.3.3.1 Process Flow Figure 18.3.3-4 highlights the people and systems participating in this regional health information network. These are the same as for the routine imaging referral but with one additional participant: • Physician Office • RIS/PACS Enterprise A • RIS/PACS Enterprise B • Document Registry • Oncologist: An oncologist working out of a cancer center: Cancer Center. This center has an Electronic Health Record (EHR) application that serves as the POS application for reviewing imaging information within the regional health network. The EHR application has DICOM Viewing capabilities 650 __________________________________________________________________________ 27 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Radiology Enterprise B Physician’s Office Prior imaging studies Prior imaging studies Query document New Exam Query document Registry Prior imaging studies Query document Provide Imaging Information for sharing Provide Imaging Information for sharing Query document Imaging Study Radiology Enterprise A Affinity Domain Cancer Center Figure 18.3.3-4 Data Flow within the Regional Health Network for a Clinical Consult 655 The process flow description and steps are as for the routine imaging referral, but with certain variations. The variations that pertain to information sharing are shown in bold (and numbered). In contrast, the variations that do not pertain to the focus of information sharing are shown in italic (and not numbered). Exam is ordered 660 Step 1: Obtain Relevant Prior Imaging Information Exam Acquisition and Reporting Step 2: Share Imaging Information within the Regional Health Network (Affinity Domain) 665 Step 3: Obtain and Display Study Results (General Practitioner) • This is identical to Step 3 in the routine imaging referral use case • Based on the radiology report, the general practitioner determines that a consult with an oncologist is required __________________________________________________________________________ 28 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 670 675 680 Step 4: Obtain and Display Study Results (Oncologist) • The EHR application in the oncologist’s office, serving as a document consumer, queries the document registry in the regional health network. This query is triggered by a consult request from the general practitioner via paper, fax, phone, and/or electronic notification. The EHR application presents a list of imaging information available for the patient, including the most recent exam completed at Radiology Enterprise A • The oncologist selects the exam reported by the radiologist as well as a number of relevant prior exams • The EHR application in the oncologist’s office, serving as an Imaging Document Consumer, retrieves the documents selected from the RIS/PACS document repositories in the regional health network and displays them to the oncologist • The oncologist reviews the images using image manipulation tools such as window level, zoom, pan, invert, measurement, etc. The oncologist may also apply 3D rendering such as multi-planar reformatting Oncologist Generates Consult Report • The oncologist reviews the results of the examination along with prior exams • The oncologist generates a consult report 685 Step 5: Share Consult Report within the Regional Health Network (Affinity Domain) • The EHR application in the oncologist’s office, serving as a “Imaging Document Source”, provides the consult report to the document registry for sharing. This has reference to the original imaging exam, which was used during the consult. Figure 18.3.3-5 shows the transaction diagram for this process flow. 690 __________________________________________________________________________ 29 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Rad. Enterprise A Rad. Enterprise A Rad. Enterprise A Cancer Centre Cancer Centre Rad. Enterprise B (Document Consumer) (Document Source) (Document Repository) (Document Repository) (Document Consumer)(Document Source) Document Registry GP Office (Document Consumer) Step 1 - Query for relevant priors Step 1 - Retrieve relevant prior images and reports Step 2 - Register images and report Step 2 - Share Images and FInal Report Step 3 - Query for new exam Step 3 - Retrieve new exam Step 4 - Retrieve new exam & relevant priors Step 4 - Query for new exam and relevant priors Step 5 - Query new exam (associated submission set) Step 5 - Share Consult Report Step 5 - Register consult report Figure 18.3.3-5 Process Flow – Clinical Consult Use Case 18.3.4 Queries 695 As presented in the use cases, human or machine users may query the Registry in order to retrieve documents in a subsequent step, based on the query result. The type of query attributes my vary between users or query scenarios, depending on the intent of the query. For instance, human users often wish to query specifically, restricting the search by several query attributes and values. 700 The following query attributes are relevant (but not exhaustive): • Patient Identity – The patient is expected to be identified by Patient ID • Exam Identity – The physician is looking for a specific exam. The attributes used to identify the exam may include one or more of the following: o Date 705 o Modality o Body part/anatomical region o Document type – images, diagnosis, progress report, preliminary report, etc. o Author – in the case of reports, the physician may well identify the report by its author i.e. the radiologist and / or specialist __________________________________________________________________________ 30 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 710 715 The metadata in the query response needs to be sufficient to allow the system consumer to parse the response and identify relevant priors. Relevant metadata includes (but is not limited to): • Exam date • Modality • Body part/anatomical region • Procedure code 18.4 Consumer Processing 18.4.1 Consumer Processing – Set of DICOM Instances 720 725 When the Imaging Document Consumer retrieves a manifest from the Document Repository, it is expected to decode the Key Object Selection Document Instance in order to find the references to DICOM objects. The Imaging Document Consumer is also expected to retrieve the referenced DICOM objects using DICOM retrieve or WADO. It should not make any assumptions about whether one or more studies are referenced within the Key Object Selection Document. 18.5 Patient Information Reconciliation These considerations can be found in appendix X1. 18.6 Security considerations These considerations can be found in appendix X2. __________________________________________________________________________ 31 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 730 Add the following appendices (X1 and X2) after the last appendix, but before the glossary in Volume 1 Appendix X1: Patient Information Reconciliation (INFORMATIVE) 735 740 Patient Information Reconciliation (PIR) workflow within a local domain is well understood and addressed within the IHE PIR Integration Profile. However, within an XDS affinity domain, there is the added complexity of managing patient information within the XDS Registry and synchronizing data between the document sources, repository and registry. The XDS Profile does not address the challenges of PIR. The reason for this is scope management (at the time of writing the initial XDS Profile) as well as a lack of content profiles to stress the PIR issue. It is the intent of the ITI Technical Committee to address the issue of PIR within XDS in due course. Given that PIR will be addressed within the XDS Profile, this Appendix is considered informative and serves to demonstrate that imaging informatin content does not introduce any new or imaging information content specific PIR issues. X1.1 Context and Assumptions 745 X1.1.1 XDS Affinity Domain Assumptions • The Document Registry assumes that all documents have a normalized patient ID pertaining to the XDS Affinity Domain. Therefore: o The XDS Affinity Domain must have a Patient Identification Domain in order to realize normalized patient IDs. o The XDS Affinity Domain must have a Patient Identity Source Actor 750 • 755 • 760 • • o To simplify description in this section, the nomenclature for the XDS Affinity Domain will be “XAD”. A Document Source is responsible for obtaining the XAD patient ID for registering the document within the registry. The XAD patient ID that is obtained is only used for this purpose and is not used to update any patient ID’s within the document. Patient ID’s within the document shall remain unchanged by the registration process A Document Consumer is expected to query the Document Registry using the XAD patient ID The Registry can only accept a document if the document has a valid XAD patient ID The Registry must check to see if the XAD patient ID is valid. This can be done in two ways: __________________________________________________________________________ 32 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ o Query the XAD Patient Identity Source to see if the XAD patient ID exists – not supported at this time 765 • o Maintain all XAD patient IDs in the registry irrespective of whether there are documents for that patient i.e. keep in synch with the XAD Patient Identity Source – this is the expected model The Registry cannot accept a document with an OID that is already registered o If a document is submitted that has the OID of a document already registered, the Registry will reject the submission 770 o If a document is re-submitted and, thereby, is identical to a document already submitted, the Registry will reject the submission X1.1.2 Meta-Data in the Registry • 775 • The XAD patient ID is the only piece of metadata that can be reliably used to query for a patient The Registry maintains supporting patient information such as Name, Sex, DoB, etc. but is NOT obligated to ensure the referential integrity of this data. Therefore: o This information is NOT used for query matching (but is only used for audits and potential verification of Document Consumers) 780 • o There is no requirement for the XDS Document Registry to verify that the metadata in the Registry corresponds to the patient information in the document itself The Registry does track the local domain source patient ID, but this is not used for query matching X1.1.3 Patient Identity Management in the XDS Registry 785 790 • • • • • • The Registry keeps a list of known XAD patient IDs The Registry associates documents with the patient IDs The Registry receives patient “merge” notifications from the XAD Patient Identity Source The Registry is responsible for updating XAD patient IDs associated with documents The Registry does not update metadata nor document content If the clinical content of a document has changed, the Document Source is responsible for updating the Repository and Registry X1.1.4 Expected Implementation Models for Patient Identity Management In a cross enterprise scenario, we assume that there are multiple patient identity domains __________________________________________________________________________ 33 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ • 795 • Local patient identity domains that support one or more enterprises. These pertain to Document Sources and Document Consumers Affinity Domain patient identity domain Each patient identity domain has a Patient Identity Source. In the case of local domains, this is likely to be an ADT system. For the Affinity Domain, this is yet another patient registry. 800 805 810 A participating enterprise may deploy a Patient Identifier Cross-Referencing (PIX) Manager to cross-map Patient ID in the local domain to Patient ID in XAD domain. In such cases, the Cross Reference Manager will interact with the Affinity Domain Patient Identity Source. Document sources and consumers are required to obtain a normalized XAD patient ID. The mechanism for achieving this is dependent on the implementation of patient identity feeds and patient identity cross reference manages within the Affinity Domain. For example, where local domains have Patient Identity X-ref managers, the document sources and consumers obtain the normalized XAD patient ID from the Affinity Domain patient identity source via the X-ref managers. The document sources and consumers can also obtain the XAD patient ID using other methods such as IHE PDQ or non- IHE approaches. This is shown in Figure X1.1-1 For the sake of discussion, no assumptions are made on how document sources and consumers interact with the XAD patient identity domain – it could be directly or through a local domain Xref manager. __________________________________________________________________________ 34 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Patient Identity Source Patient Identity Feed Patient Identity X-Ref Mgr Patient Identification Domain C Patient Identification Domain XAD XDS Document Source Patient ID Consumer Dm=C Dm=XAD PID=Px Patient Identity X-Ref Mgr Patient Identification Domain D2 XDS Document Registry Document Entry Dm=XAD PID=Px Query Docs Dm=XAD PID=Px Provide&Register Doc Set XDS Doc PID=Pc XDS Doc XDS Document Consumer Dm=D2 XDS Document Repository Patient ID PID=Pd Consumer 815 Figure X1.1-1 – Patient Identity Management using PIX Cross Referencing 820 X1.2 Patient Information Reconciliation (PIR) in an Affinity Domain PIR workflow within a local domain is well understood and addressed within the IHE PIR Integration Profile. However, within an XDS affinity domain, there is the added complexity of managing patient information within the XDS Registry and synchronizing data between the document sources, repository and registry. 825 X1.2.1 Patient Merge within XAD Patient Identity Domain • • 830 XAD patient identity domain merges two patients Document sources are unaware of the merge transaction within XAD patient identity domain In this situation: __________________________________________________________________________ 35 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ • • 835 • 840 XDS Registry receives a merge notification from the XAD patient identity source and applies merge logic to the registry Document consumers have continued access to documents pertaining to the patient since consumers are expected to obtain the XAD patient ID for the patient at the time of querying the Registry Document sources are unaware of the merge transaction that occurred in the XDS registry and do not need to be made aware of this merge. The reasons for this are: o Consumers have continued access to the document o The document source must query for the XAD patient ID before attempting to interact with the repository and registry. As such, the document source will have an updated XAD patient ID at the time of interacting with the registry. o When a document source wishes to submit a change to the document: o The document source must query for the XAD patient ID before registering the new document 845 o The document source must register the new document with a request to deprecate the old document. From the document source’s perspective, the old document is still associated with the original XAD patient ID. By virtue of obtaining a new XAD patient ID for the patient, the document source must assume that a patient merge has taken place and use the new XAD patient ID to deprecate the old document 850 The process flow is described in more detail as follows: 855 Scenario: • Key identifier for a patient within the XAD patient identity domain changes, such as health number • The XAD patient identity source merges two patients Process Steps: 1. The XAD patient identity source sends a “merge” notification to the XDS Registry 860 2. XDS Registry applies merge logic to the patients within the merge notification • The metadata in the registry will be accurate with the exception of the source patient ID X1.2.2 Local Domain Patient Update - XAD Domain Patient ID does not change 865 • Demographics for the patient change __________________________________________________________________________ 36 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ • • 870 875 Local domain patient ID does NOT change XAD patient ID does NOT change In this scenario: • XDS Registry does nothing since the XAD patient ID has not changed • If a document source changes the patient demographics content of a document and a new document is created then this document should be registered with the XDS repository/registry as a replacement to the old document The process flow is described in more detail as follows: Scenario: • Patient first name is corrected from “Jamie” to “James” in the local domain patient identity source 880 Process Steps: 1. Update information flows from the local domain patient identity source (i.e. ADT) to the document source: image manager/archive. • Document source updates its database to correct demographics • Either: Document source does not change the document 885 • o The Document Source does not update the repository/registry. In this scenario, the patient demographics: Name, Dob, Sex, etc.; in the Document Source do not match those in the XDS Registry. This is acceptable in the XDS framework Or: Document source changes the document o The Document Source updates the repository/registry with an addendum 890 2. The Registry takes no action as the XAD patient ID has not changed X1.2.3 Local Domain Patient Update - XAD Domain Patient Merge 895 • • • • Demographics for the patient change Local domain patient ID does NOT change XAD patient ID does change and triggers a merge within XAD domain Document sources are unaware of the merge transaction within XAD patient identity domain __________________________________________________________________________ 37 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 900 In this scenario: • See “X1.2.1 Patient Merge within XAD Patient Identity Domain” The process flow is described in more detail as follows: 905 Scenario: • Patient last name is corrected from “Alfonsp” to “Alfonso” within local domain patient identity source • XAD domain patient identity source merges “Alfonsp: XAD-Pp” into “Alfonso: XAD-Pa” – patient “Alfonso” was already registered within the XAD domain with patient ID XAD-Pa 910 Process Steps: • See “X1.2.1 Patient Merge within XAD Patient Identity Domain” X1.2.4 Local Domain Patient Merge – XAD Domain Patient ID does not change • • • 915 920 925 Demographics for the patient changes Local domain patient identity source merges patient A with patient B XAD patient ID for patient A and patient B are the same In this scenario: • XDS Registry does nothing since the XAD patient ID for patient A and patient B is the same • Document sources apply merge logic to the documents within their database i.e. documents are now associated with a new local domain patient ID • Document sources must now query XAD patient identity source 1 to obtain the XAD patient ID for the merged patient • The XAD patient ID is the same as already associated with the document: o If the document source does not change the document content, the document source does not need to interact with XDS Repository/Registry – status quo 1 How the document source queries the XAD patient identity source is not prescribed as this may be directly or via a local domain x-ref manager __________________________________________________________________________ 38 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ o 930 If the document source changes the patient demographics content of a document and a new document is created, then this document should be registered with the XDS repository/registry as a replacement to the existing document. The process flow is described in more detail as follows: 935 940 Scenario: • Patient last name is corrected from “Smythe” to “Smyth” • ADT already has an entry for “Smyth” • “Smythe” with local domain patient ID D-123 is merged with Smyth with local domain patient ID D-456 • XAD Patient Identity Source already recognized “Smythe: D-123” and “Smyth: D456” as the same patient and, therefore, assigned each with the same XAD patient ID: XAD-Px Process Steps: 945 1. Update information flows from the local domain patient identity source (i.e. ADT) to the document source: image manager/archive. • Document source applies merge logic to the database: documents for the merged patient are associated with the new patient ID 2. Document source queries the XAD patient identity domain to determine whether the XAD patient ID has changed for the merged documents. In this case the XAD patient ID does not change 950 3. Document source updates the demographics of the document • Either: Document source makes no changes to the document – demographics are in the database 955 • o The Document Source need not update the repository/registry. In this scenario, the patient demographics in the Document Source do not match those in the XDS Registry. This is acceptable in the XDS framework Or: Document source changes the document o The Document Source updates the repository/registry with an addendum 4. The Registry takes no action as the XAD patient ID has not changed 960 X1.2.5 Local Domain Patient Merge – XAD Domain Patient Merge • • Demographics for the patient changes Local domain patient identity source merges patient A with patient B __________________________________________________________________________ 39 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ • • XAD patient IDs for patient A and patient B are different Patient A is merged with patient B in the XAD domain patient identity source 965 There are three situations that can occur: 970 975 980 1. XDS Registry merge prior to Document Source merge • XDS Registry receives a merge notification from the XAD patient identity source and applies merge logic to the registry • Document sources are unaware of the merge transaction that occurred in the XDS registry and do not need to know about this transaction (see X1.2.1) • Document consumers have continued access to documents pertaining to the patient since consumers are expected to obtain the XAD patient ID for the patient at the time of querying the Registry • Document sources apply merge logic to the documents within their database i.e. documents are now associated with a new local domain patient ID • Document sources must now query XAD patient identity source to obtain the XAD patient ID for the merged patient • The XAD patient ID for the documents has changed: o The document source changes the XAD patient ID associated with the documents – it can assume that the Registry has made this change as well o If the document source does not change the document content, the document source does not need to interact with XDS Repository/Registry – status quo 985 990 995 o If the document source changes the patient demographics content of a document and a new document is created then this document should be registered with the XDS repository/registry – the existing document is deprecated. 2. Document Source merge prior to XDS Registry merge • Document sources apply merge logic to the documents within their database i.e. documents are now associated with a new local domain patient ID • Document sources must now query XAD patient identity source to obtain the XAD patient ID for the merged patient • The XAD patient ID is the same as already associated with the document: o If the document source does not change the document content, the document source does not need to interact with XDS Repository/Registry – status quo __________________________________________________________________________ 40 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ • 1000 • • 1005 1010 o If the document source changes the patient demographics content of a document and a new document is created, then this document should be registered with the XDS repository/registry as a replacement to the old document XDS Registry receives a merge notification from the XAD patient identity source and applies merge logic to the registry Document sources are unaware of the merge transaction that occurred in the XDS registry and do not need to know about this transaction Document consumers have continued access to documents pertaining to the patient since consumers are expected to obtain the XAD patient ID for the patient at the time of querying the Registry 3. Document Source merge at same time as XDS Registry merge • Document sources apply merge logic to the documents within their database i.e. documents are now associated with a new local domain patient ID • Document sources must now query XAD patient identity source 2 to obtain the XAD patient ID for the merged patient • • 1015 o The XAD patient ID is the same as already associated with the document XDS Registry receives a merge notification from the XAD patient identity source and applies merge logic to the registry Document source chooses to change the patient demographics content of a document and a new document is created. This document is registered with the XDS repository/registry: o The XAD patient ID for this document has now been merged in the XDS Registry and, therefore, is no longer valid 1020 o The Registry will reject the document registration transaction as the XAD patient ID used in the transaction is no longer valid. o Document sources must now query XAD patient identity source to obtain the XAD patient ID for the merged patient and re-register the document with the XDS repository/registry 1025 Scenario: • Patient last name is corrected from “Smythe” to “Smyth” • ADT already has an entry for “Smyth” 2 How the document source queries the XAD patient identity source is not prescribed as this may be directly or via a local domain x-ref manager __________________________________________________________________________ 41 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 1030 • • Smythe: patient ID D-123 is merged with Smyth: patient ID D-456 XAD Patient Identity Source has separate entries for both “Smythe: XAD-Pc” and “Smyth: XAD-Pf”. As such, it merges these two patients in to “Smyth: XAD-Pf”. Process Steps: 1035 The process flow is a combination of the previous scenario process flows and, thereby, not repeated here. __________________________________________________________________________ 42 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Appendix X2: Security considerations for XDS-I (informative) 1040 1045 This IHE profile does not specify all the details of the security environment for exchanging radiology information. The IHE includes several security profiles that apply to the XDS/ XDS-I use. The use of these security profiles in the first trial implementation for XDS-I will likely be optional. The security profiles make assumptions about the overall security environment and are configurable to adapt to different security requirements. Figure X2-1 shows typical transactions for XDS-I. Each transaction goes through security and privacy controls. This figure illustrates use of firewall access points and TLS controls for all XDS-I participants, including the Imaging Document Source. The firewalls may have simple easy to implement rules or more complex rules depending upon local policies. The flows shown in figure X2-1 are described in more detail below: Flow #1. The Store Images, etc. transactions: 1050 a) Internal firewall rules I: - Simple rules: “outgoing HTTP is OK” - Complex rules: examine source IP, destination IP, HTTP headers to decide whether to permit the connection. b) TLS within each actor: 1055 - IM/IA: Is this really the authorized Image Document Source that was requested? - Repository: Is this really an authorized IM/IA? c) Once the TLS connection is established there is further processing, generation of audit records, etc. 1060 Flow #2. The Provide and Register Imaging Document Set transaction: a) does not cross a firewall b, c) TLS, authorization, auditing as above. Flow #3. The Register transaction 1065 a) External firewall rules II: - Simple: Outgoing HTTP is OK - Complex: examine source IP, destination IP, HTTP headers to decide whether to permit the connection. __________________________________________________________________________ 43 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ b, c) TLS, authorization, auditing as above. 1070 Flow #4, Query Documents transaction: a) External firewall access rules II: - Simple: Incoming HTTP to the DMZ is OK 1075 - Complex: very tricky given many different uses for HTTP incoming by different web applications. b, c) TLS, authorization, auditing as above. Flow #5, Retrieve Images, etc. transactions: a) External firewall access rules III: 1080 - Simple: Incoming DICOM is only permitted from authorized affinity domain IP blocks. - Complex: Examine the DICOM retrieve connection initiator and the targeting acceptor IP addresses, and permit only connections between a priori authorized pairs of initiator and acceptor. b, c) TLS, authorization, auditing as above. 1085 This example shows access for both HTTP and DICOM traffic. It is easier to get multi-layer protection for the DICOM traffic because it is easily differentiated from the many diverse uses of HTTP for web applications and services. Then the TLS security, actor authorization rules, and auditing are applied to all traffic regardless of type. __________________________________________________________________________ 44 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Inside the Enterprise Outside the Enterprise (Affinity Domain and the rest of the world.) Affinity Domain Zone (Part of DMZ) II Registry 3 4 Repository Image Manager/ Image Archive Internet TLS Authentication, Affinity Authorization 1 2 I III 5 Imaging Document Source Internal Firewall Document Consumer External Firewall 1090 Figure X2-1 Security Environment 1095 IHE assumes that there will be some form of external control point. This usually involves technologies like VPNs, firewalls, routers, etc. IHE does not specify what is necessary here, and the IHE profiles will operate and provide a good level of security even when the external control point is missing. The purpose of having an external control point is: • To control the low level network access between the Internet and the Imaging Document Source and Document Repository. The precision of this control is up to the sites involved. One common configuration is to merely restrict the list of IP Ports that are permitted access. This simplifies the security requirements on the server. • Log and monitor all traffic for indications of hostile or abusive activity. This is usually a combination of logging and intrusion detection (IDS) activity that is oriented towards the overall IT organization requirements. 1100 __________________________________________________________________________ 45 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 1105 1110 1115 1120 This kind of protection is useful and complements the encryption and access controls defined as part of IHE’s Audit Trail and Node Authentication (ATNA) Profile and its Radiology Option. The internal network is probably divided into two or more zones that are isolated by internal control points. These internal control points are similar to the external control point, but usually are much more permissive in terms of the traffic that they allow. They exist both to detect problems and to provide a means of rapidly isolating portions of the network in the event of a security breach. The Imaging Document Source is assumed to be located in the zone labeled the “Affinity Domain Zone”. This might also be part of a general DMZ (De-Militarized Zone) for the organization or it might be a special zone reserved exclusively for Affinity Domain activities. There are cost and functionality tradeoffs involved in making that decision and the IHE profiles support both approaches. IHE will specify the minimum-security requirements for the Imaging Document Source. It will be expected to comply with the IHE ITI ATNA (Audit Trail and Node Authentication) Integration Profile. There may be multiple Imaging Document Sources in the Affinity Domain Zone and they will all be expected to comply with the ATNA profile. This profile mandates: • All connections that might transfer protected health information (PHI) must utilize TLS configured to: o Authenticate both machines involved o Ensure that all traffic is encrypted, either directly by TLS or by means of equivalent protection such as VPN. 1125 • Enforce access control to the system • Provide a detailed security audit trail for all PHI related activity and information transfers The TLS protocol is also widely known as HTTPS. The ATNA profile mandates this protection for any DICOM, HL7, HTTP or other protocols. 1130 1135 There may be special auditing requirements for an XDS-I actor. For example, in the US there are HIPAA requirements for disclosure logs. Only the sites themselves can determine what belongs in a disclosure log. The ATNA logs were not directly intended for this purpose. The Imaging Document Source may be a system that is complete with its own image archive, or it may be a proxy machine that relays information to another machine, perhaps located in a private zone. This is considered an internal design issue by IHE. The IHE XDS-I profile specifies that the Imaging Document Source must support the XDS-I transactions, and does not specify the internal design. There are several important design considerations for securing XDS-I networks that must be made by the affinity domain and its members. These are: __________________________________________________________________________ 46 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 1140 1. What kind of external control points are used. IHE recommends that they be present, but does not profile them. 2. How to subdivide the enterprise network and whether to establish a dedicated Affinity Domain Zone. There is an advantage to creating a Affinity Domain Zone with just a few servers located in it: 1145 a. The log analysis is easier b. The certificate and TLS management for node authentication is easier c. The preparation of disclosure logs and the equivalent is easier. d. The internal control point reduces the risks from a breach of the Affinity Domain Zone. 1150 1155 1160 3. Whether User Authentication is needed. IHE provides both the Enterprise User Authentication (EUA) and Cross Enterprise User Authentication (XUA) profiles. Use of user authentication permits additional information to be captured in the audit logs (e.g., the identity of the user) and permits additional access control in some situations. The issues that the affinity domain and sites must address are: a. What to do about automated processes, such as pre-fetch and email. These can be identified using node authentication via TLS as specified in ATNA, by using simple identity assertions. b. How to handle delegation. Often it is clerks, nurses, etc. that are actually operating the computer to obtain the records for a patient, and it is someone else that will actually be examining the records. So the user authentication might not provide any further useful information. The IHE profiles do not determine these choices. Some reasonable selections include: 1165 1170 1175 1. Not using user authentication. The ATNA ensures that the enterprise and the machine are authenticated. These machines are already authenticated and trusted to protect PHI information. It may be impractical to track and coordinate the personnel activities across all the different organizations. 2. Though not specifically designed for this purpose, it is also possible that the XDSI profile is being used internally within a centrally controlled large organization, where the Kerberos based identity management of EUA is available. EUA can be used in such an intra-enterprise environment. EUA supports simple identity assertions. These are based on trusting the authenticated node to provide the correct identity of its user. 3. The use of XUA is optional. Where a human user is involved, XUA can be employed for cross-enterprise user identity assertion. If only machines are involved, the node authentication provided by ATNA should be sufficient. The use of XUA requires that the affinity domain establish the authentication policies, __________________________________________________________________________ 47 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 1180 1185 procedures, and have a supporting infrastructure of servers, etc. (This infrastructure may be provided by the local government or might need to be provided by the affinity domain.). Note: In order to use the IHE XUA Integration Profile, the underlying application protocol must be able to carry a user identity assertion in its payload. While such a mechanism has been established in HL7 and HTTP/S, the mechanism to provide this for DICOM messages is still under development. Thus, XUA profile cannot (yet) be employed when retrieving DICOM SOP Instances referenced in the manifest document. The affinity domain and individual site policies will determine the choices made. There are IHE profiles defined to address these alternatives. __________________________________________________________________________ 48 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ GLOSSARY Add the following to glossary entries to the Glossary in Volume one Affinity Domain Refer to the IHE ITI Technical Framework Glossary. Care Delivery Organization/Enterprise An organization that provides medical services at one or more physical locations XDS Document Refer to the IHE ITI Technical Framework Glossary Point of Service (POS) Application An application used by physicians to access patient information and perform work. Examples of a POS include EMR, EHR, physician practice system, PACS, etc. Regional Health Information Network An implementation of an affinity domain serving a number of care delivery organizations in a region. Submission Set Refer to the IHE ITI Technical Framework Glossary URI Unique Resource Identifier DMZ De-Militarized Zone. A computer or small sub-network that sits between a trusted internal network, such as a corporate private LAN, and an un-trusted external network, such as the public Internet. Typically, the DMZ contains devices accessible to Internet traffic, such as Web (HTTP) servers, FTP servers, SMTP (e-mail) servers and DNS servers. Manifest Document A Manifest Document is an instance of DICOM Key Object Selection SOP Class, which describes and collects a set of DICOM SOP Instances that are intended for sharing. 1190 __________________________________________________________________________ 49 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Volume 2 - Transactions 4. IHE Transactions Update the following existing transaction 16 1195 4.16 Retrieve Images This section corresponds to Transaction RAD-16 of the IHE Technical Framework. Transaction RAD-16 is used by an Image Display actor to request and retrieve images from an Image Archive and the Imaging Document Consumer to request and retrieve documents from an Imaging Document Source actor. the Image Archive, and Image Display actors. 1200 4.16.1 Scope After the Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer request for image retrieval, the requested DICOM Images are transferred from the Image Archive to the Image Display or from the Imaging Document Source to the Imaging Document Consumer for viewing. 4.16.2 Use Case Roles Image Archive Imaging Document Source Imaging Document Consumer Image Display Retrieve Images 1205 Actor: Image Archive: Role: Sends requested images to the Image Display Actor. Actor: Imaging Document Source: Role: Sends requested images to the Imaging Document Consumer Actor. 1210 Actor: Image Display Role: Receives requested images from the Image Archive Actor. Actor: Imaging Document Consumer Role: Receives requested images from the Imaging Document Source Actor. __________________________________________________________________________ 50 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 4.16. 4 Interaction Diagram Image Display Image Archive Retrieve Images (C-MOVE) Store Images (C-STORE) View Images 1215 Imagig Document Source Imaging Document Consumer Retrieve Images (C-MOVE) Store Images (C-STORE) View Images 4.16.4.1 Retrieve Images 1220 1225 The Retrieve (Study Root – MOVE and optionally Patient Root – MOVE) SOP Classes shall be supported. The DICOM Image Storage SOP Classes will be supported by the Image Archive or Imaging Document Source as an SCU. Refer to DICOM 2003 PS 3.4, Annex C, for detailed descriptive semantics. In the case of retrieving images in a Cross-Enterprise, imaging document sharing (XDS-I) network environment, a configuration of mapping the AE Titles to DICOM AE Network Addresses (IP Address and Port number) is needed to be exchanged between the Imaging __________________________________________________________________________ 51 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Document Source and the Imaging Document Consumer. Appendix Y describes in details the AE Title mapping to the DICOM AE Network Addresses. 4.16.4.1.1 Trigger Events Images are selected for viewing at the Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer. 1230 4.16.4.1.2 Message Semantics The message semantics are defined by the DICOM Query/Retrieve SOP Classes and the DICOM Image Storage SOP Classes. 1235 A C-MOVE Request from the DICOM Study Root Query/Retrieve Information Model – MOVE SOP Class or the DICOM Patient Root Query/Retrieve Information Model – MOVE SOP Class shall be sent from the Image Display to the Image Archive or from the Imaging Document Consumer to the Imaging Document Source. 4.16.4.1.3 Expected Actions 1240 1245 The Image Archive or Imaging Document Source receives the C-MOVE request, establishes a DICOM association with the Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer, respectively, and uses the appropriate DICOM Image Storage SOP Classes to transfer the requested images. The Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer is expected to support at least one of the SOP Classes specified in table 4.8-1. It is assumed that support of retrieval for a SOP Class also means support for display. 4.16.4.1.3.1 NM Image Profile Image Manager/Image Archive, Imaging Document Source, Image Displays and Imaging Document Consumer actors that claim support of the NM Image Profile shall support all the SOP Classes specified in Table 4.8-3 in section 4.8. 1250 4.16.4.2 View Images This transaction relates to the “View Images” event of the above interaction diagram. 4.16.4.2.1 Trigger Events 1255 The Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer is requested to be capable to display the images. __________________________________________________________________________ 52 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 4.16.4.2.2 Invocation Semantics This is a local invocation of functions at the Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer. 4.16.4.2.2.1 Display of Digital X-Ray, Mammo and Intra-Oral Images 1260 1265 1270 For the “For Presentation” variant of the Digital X-Ray Image, the Digital Mammography Image, and the Digital Intra-oral X-Ray Image, the Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer actor shall have both the capability to apply the transformations specified by the VOI LUT Sequence (0028,3010) and the capability to apply the transformations specified by the Window Width (0028,1051)/Window Center (0028,1050) attributes in the DX Image Module (although not simultaneously). The Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer actor must also support pixel rendering according to the Grayscale Standard Display Function (GSDF) defined in DICOM 2003 PS 3.14, because the output values of these images are always P-Values. If the DICOM image is referenced by other DICOM composite objects, such as Grayscale Softcopy Presentation States, it is optional for the Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer to actually retrieve and display/apply these objects. 4.16.4.2.2.2 Display of Localizer Lines Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer actors that want to show the localizer lines, if visible, will be able to calculate the position of these lines of intersection based on the information recorded in the images by the Acquisition Modality actor (See 4.8.4.1.2.1). 1275 Section 4.16.4.2.2.3 remains unchanged. 4.16.4.2.3 1280 1285 Expected Actions The Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer presents to the user a DICOM Image. The Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer may receive patient data inconsistent with those received from a previously issued query or retrieve operation. For example, in the event that a patient has been renamed, the Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer will receive images with the same Study Instance UID, Series Instance UID and SOP Instance UIDs, but with a different patient name. The Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer shall use the just queried information or the most recently received instances to ensure that the most recent patient data from the Image Manger/Archive or Imaging Document Source is displayed. __________________________________________________________________________ 53 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ The Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer shall be able to display the Series Description for each series displayed. 1290 Update the following existing transaction 17 4.17 Retrieve Presentation States 1295 This section corresponds to Transaction RAD-17 of the IHE Technical Framework. Transaction RAD-17 is used by the Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer to request and retrieve Presenttaion State from the Image Archive or Imaging Document Source actor. Image Archive and Image Display actors. 4.17.1 Scope 1300 1305 This section describes the sequence of messages required for the Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer to retrieve Grayscale Softcopy Presentation State Instances from the Image Archive or Imaging Document Source. The Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer will query and then retrieve Presentation State objects. The transformations will be applied by the Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer to the image data to assure the image display is consistent with the device that originally created and stored the Presentation State. The Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer will be required to support all transformations defined in DICOM 2003 PS 3.4: Grayscale Softcopy Presentation State Storage. In addition, multiple Presentation States may exist that reference the same image data. 4.17.2 Use Case Roles Image Archive Imaging Document Source Imaging Document Consumer Image Display Retrieve Presentation States 1310 Actor: Image Display 1315 Role: Retrieve Grayscale Softcopy Presentation State objects together with the referenced image data and apply the transformations specified by the Presentation State. This actor must support pixel rendering according to the Grayscale Standard Display Function (GSDF) defined in DICOM 2003 PS 3.14. This device will implement the Query/Retrieve SOP Classes in the role of an SCU. __________________________________________________________________________ 54 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Actor: Imaging Document Consumer 1320 Role: Retrieve Grayscale Softcopy Presentation State objects together with the referenced image data and apply the transformations specified by the Presentation State. This actor must support pixel rendering according to the Grayscale Standard Display Function (GSDF) defined in DICOM 2003 PS 3.14. This device will implement the Query/Retrieve SOP Classes in the role of an SCU. Actor: Image Archive 1325 Role: Respond to retrieve requests from the Image Display for Grayscale Softcopy Presentation States objects. Transmit requested Grayscale Softcopy Presentation State object(s) to the Image Display. This device will implement the Query/Retrieve SOP Classes in the role of an SCP. Actor: Imaging Document Source 1330 Role: Respond to retrieve requests from the Imaging Document Consumer for Grayscale Softcopy Presentation States objects. Transmit requested Grayscale Softcopy Presentation State object(s) to the Imaging Document Consumer. This device will implement the Query/Retrieve SOP Classes in the role of an SCP. 4.17.4 Interaction Diagram Image Display Image Archive Select Presentation States (C-MOVE) Store Presentation States (C-STORE) View Presentation States __________________________________________________________________________ 55 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Imaging Document Consumer Imaging Document Source Select Presentation States (C-MOVE) Store Presentation States (C-STORE) View Presentation States 1335 4.17.4.1 Retrieve Grayscale Softcopy Presentation State 1340 1345 This transaction refers to the “C-MOVE” and “C-STORE” messages between the Image Display and Image Archive or Imaging Document Consumer and Imaging Document Source actor in the above interaction diagram. The Retrieve (Study Root – MOVE and optionally Patient Root – MOVE) SOP Classes are supported. Refer to the DICOM 2003 PS 3.4 for detailed descriptive semantics. In the case of retrieving Grayscale Softcopy Presentation State in a Cross-Enterprise, imaging document sharing (XDS-I) network environment, a configuration of mapping the AE Titles to DICOM AE Network Addresses (IP Address and Port number) is needed to be exchanged between the Imaging Document Source and the Imaging Document Consumer. Appendix Y describes in details the AE Title mapping to the DICOM AE Network Addresses. 4.17.4.1.1 Trigger Events 1350 The Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer selects specific Grayscale Softcopy Presentation State objects to retrieve from the Image Archive. __________________________________________________________________________ 56 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 4.17.4.1.2 Message Semantics 1355 The message semantics are defined in the DICOM Query/Retrieve Service Class section of the DICOM 2003 PS 3.4: Query/Retrieve Service Class. It is the responsibility of the Image Manager or Imaging Document Source to assure that the patient and procedure information is current in the images and Softcopy Presentation State objects when they are retrieved from the Image Archive or Imaging Document Source. 4.17.4.1.3 Expected Actions 1360 The Image Archive or Imaging Document Source receives the C-MOVE request, establishes a DICOM association with the Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer actor, respectively, and uses the DICOM Grayscale Softcopy Presentation State Storage SOP Class to transfer the requested Presentation State objects. 4.17.4.2 View Presentation States 1365 This transaction relates to the “View Presentation States” event in the above interaction diagram. Presentation States cannot be viewed separately, but must be applied to an image. Refer to sec. 4.16 for a description of the transaction used to retrieve images to which Presentation States may be applied. 4.17.4.2.1 Trigger Events 1370 The Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer receives Presentation State instances from the Image Archive or Imaging Document Source actor, respectively. 4.17.4.2.2 Invocation Semantics 1375 This is a local invocation of functions resident within the Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer. The method used by the Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer to present images for viewing by the user after the Presentation State transformations have been applied is outside the scope of the IHE Technical Framework. 4.17.4.2.3 Expected Actions 1380 The Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer applies the transferred Grayscale Softcopy Presentation State to image data and renders it for viewing. The Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer may receive patient data inconsistent with those received from a previously issued query or retrieve operation. For example, in the event that a patient has been renamed, the Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer will receive Softcopy Presentation State objects with the same Study Instance UID, Series Instance UID and SOP Instance UIDs, but with a different patient name. The Image Display or Imaging Document __________________________________________________________________________ 57 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 1385 Consumer shall use the most recently queried information or the most recently received instances to ensure that the most recent patient data from the Image Manger/Archive or Imaging Document Source actor is displayed. Update the following existing transaction 27 1390 4.27 Retrieve Reports This section corresponds to Transaction RAD-27 of the IHE Technical Framework. Transaction RAD-27 is used by the Report Manager, Report Repository, Imaging Document Source, Report Reader, Imaging Document Reader, and External Report Repository Access actors. 4.27.1 Scope 1395 In the Retrieve Reports Transaction, the requested DICOM Structured Reports are transferred from the Report Manager, Report Repository, Imaging Document Source or External Report Repository Access to the Report Reader or Imaging Document Reader for viewing. 4.27.2 Use Case Roles R eport R epo sitory R ep o rt M anager Im a g in g D o cu m en t S o u rce R ep o rt R ead er R etrieve R ep o rts E xternal R ep o rt R ep o sito ry A cce ss Im a g in g D o cu m en t C o n su m er 1400 Actor: Report Repository Role: Sends requested DICOM Structured Reports to Report Reader. Actor: Imaging Document Source Role: Sends requested DICOM Structured Reports to the Imaging Document Consumer Actor. 1405 Actor: External Report Repository Access Role: Sends requested DICOM Structured Reports to Report Reader. Such a system may be required to convert reports of different formats (HL7) into DICOM Structured Reports (see appendix C). Actor: Report Reader __________________________________________________________________________ 58 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 1410 Role: Retrieves DICOM Structured Reports from Report Repository or External Report Repository Access and makes them available for viewing. Actor: Imaging Document Consumer Role: Retrieves DICOM Structured Reports from the Imaging Document Source Actor and makes them available for viewing. 1415 Actor: Report Manager Role: Sends requested DICOM Structured Reports to Report Reader. 4.27.3 Referenced Standards DICOM 2003 PS 3.4: Query/Retrieve Service Class 1420 DICOM 2003 PS 3.4: Storage SOP Class DICOM 2003 PS 3.16: Content Mapping Resource __________________________________________________________________________ 59 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 4.27.4 Interaction Diagram Report Repository Report Reader External Report Repository Access Retrieve Reports (C-MOVE) Store Reports (C-STORE) View Reports Retrieve Reports (C-MOVE) Store Reports (C-STORE) View Reports __________________________________________________________________________ 60 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 1425 Report Manager Report Reader Retrieve Reports (C-MOVE) Store Reports (C-STORE) Imaging Document Source Imaging Document Consumer Retrieve Reports (C-MOVE) Store Reports (C-STORE) View Reports 4.27.4.1 Retrieve Reports 1430 1435 This transaction relates to the retrieve section of the above interaction diagram. The Retrieve (Study Root – MOVE and optionally Patient Root – MOVE) SOP Classes shall be supported. The Report Reader and Imaging Document Consumer as an SCP shall support the DICOM Basic Text SR Storage SOP Class and optionally the DICOM Enhanced SR Storage SOP Class. The Report Manager, Imaging Document Source and the Report Repository as an SCU shall support both the DICOM Basic Text SR Storage SOP Class and the DICOM Enhanced SR Storage SOP Class. The External Report Repository Access as an SCU shall support the DICOM Basic Text SR Storage SOP Class and optionally the DICOM Enhanced SR Storage SOP Class. Refer to DICOM PS 3.4, Annex C, for detailed descriptive semantics. __________________________________________________________________________ 61 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 4.27.4.1.1 1440 Trigger Events The user at the Report Reader or Imaging Document Consumer selects specific reports to view. 4.27.4.1.2 Message Semantics The DICOM Query/Retrieve SOP Classes and the DICOM Structured Report Storage SOP Classes define the message semantics. 1445 A C-MOVE Request from the DICOM Study Root Query/Retrieve Information Model – MOVE SOP Class or the DICOM Patient Root Query/Retrieve Information Model – MOVE SOP Class shall be sent from the Report Reader to the Report Manager, Report Repository or External Report Repository Access, or from the Imaging Document Consumer to the Imaging Document Source. 4.27.4.1.3 Expected Actions 1450 The Report Manager, Report Repository, Imaging Document Source or External Report Repository Access receives the C-MOVE request, establishes a DICOM association with the Report Reader or Imaging Document Consumer and uses the appropriate DICOM Structured Report Storage SOP Classes (Basic Text SR Storage SOP Class and/or Enhanced SR Storage SOP Class) to transfer the requested reports. 1455 Report Repository responds to the queries with the information from the DICOM instances it received from the Report Manager. Typically, Report Manager will apply information updates to the instances of reports it holds and re-issue the reports to the Report Repository. To properly update the content of instances that are no longer present on the Report Manager, the update shall be performed by retrieval and re-submission of the report through the Report Manager. It may also be done by grouping the Report Repository and Report Manager. 1460 4.27.4.2 View Reports This transaction relates to the “View Reports” event of the above interaction diagram. 4.27.4.2.1 1465 The Report Reader or Imaging Document Consumer receives reports from the Report Repository, Imaging Document Source or External Report Repository Access. 4.27.4.2.2 1470 Trigger Events Invocation Semantics This is a local invocation of functions at the Report Reader or Imaging Document Consumer, and the method used by the Report Reader or Imaging Document Consumer to interpret and display the report data in a meaningful way is outside the scope of the IHE Technical Framework. At a minimum the Report Reader or Imaging Document Consumer shall be able __________________________________________________________________________ 62 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 1475 1480 to correctly display reports defined in RAD TF-1: 9.4. The Report Reader or Imaging Document Consumer shall be able to display reports based on the Simple Image Report (RAD TF-1: 9.4.1). If the Report Reader or Imaging Document Consumer supports the Enhanced SR Information Object Definition then it shall also support display of Simple Image and Numeric Reports (RAD TF-1: 9.4.2). Even though the IHE Technical Framework sets boundaries on the complexity of SR objects, the Report Reader or Imaging Document Consumer must still be able to receive, store and view any Basic Text SR object and optionally any Enhanced SR object in order to conform to the DICOM Standard. An implementation may not be able to render, in a meaningful way, reports more complex than those specified in RAD TF-1: 9.4. If a DICOM Structured Report references other DICOM composite objects, such as images, and softcopy presentation states, it is optional for the Report Reader or Imaging Document Consumer to actually retrieve and display/apply these objects, but the Report Reader or Imaging Document Consumer must convey to the user that such references exist in the report. 4.27.4.2.2.1 Retrieve AE Title 1485 If the Report Reader is grouped with an Image Display and capable of retrieving objects referenced in a DICOM Structured Report then the Report Reader shall retrieve these objects from the device matching the appropriate Retrieve AE Title attribute (0008,0054) included in the DICOM Structured Report. If the Retrieve AE Title attribute is not specified or configured, then the Report Reader may use some other configurable Retrieve AE Title. 1490 In the case of retrieving reports in a Cross-Enterprise, imaging document sharing (XDS-I) network environment, a configuration of mapping the AE Titles to DICOM AE Network Addresses (IP Address and Port number) is needed to be exchanged between the Imaging Document Source and the Imaging Document Consumer. Appendix Y describes in details the AE Title mapping to the DICOM AE Network Addresses. 1495 4.27.4.2.3 Expected Actions The Report Reader or Imaging Document Consumer presents to the user a DICOM Structured Report. Update the following existing transaction 31 1500 4.31 Retrieve Key Image Notes This section corresponds to Transaction RAD-31 of the IHE Technical Framework. Transaction RAD-31 is used by the Image Display and Image Archive actors. __________________________________________________________________________ 63 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 4.31.1 Scope 1505 In the Retrieve Key Image Notes Transaction, the requested DICOM Key Image Notes are transferred from the Image Manager or Imaging Document Source to the Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer for viewing along with the images flagged by the Key Image Note. 4.31.2 Use Case Roles Image Archive Imaging Document Source Imaging Document Consumer Image Display Retrieve Key Image Notes 1510 Actor: Image Archive: Role: Sends requested Key Image Notes to the Image Display Actor. Actor: Imaging Document Source Role: Sends requested Key Image Notes to the Imaging Document Consumer Actor. 1515 Actor: Image Display Role: Receives requested Key Image Notes from the Image Archive Actor. Actor: Imaging Document Consumer Role: Receives requested Key Images Notes from the Imaging Document Source Actor. 1520 4.31.3 Referenced Standards DICOM 2003 PS 3.4: Query/Retrieve Service Class DICOM 2003 PS 3.4: Key Object Selection Document Storage SOP Class __________________________________________________________________________ 64 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 4.31.4 Interaction Diagram Image Display Image Archive Retrieve Key Image Notes (C-MOVE) Store Key Image Notes (C-STORE) Render Key Image Notes Imaging Document Source Imaging Document Consumer Retrieve Key Image Notes (C-MOVE) Store Key Image Notes (C-STORE) Render Key Image Notes 1525 4.31.4.1 Retrieve Key Image Notes The Retrieve (Study Root – MOVE and optionally Patient Root – MOVE) SOP Classes will be supported. The Image Archive and Imaging Document Source as an SCU shall support DICOM Image Storage SOP Classes. Refer to DICOM 2003 PS 3.4, Annex C, for detailed descriptive semantics. 1530 4.31.4.1.1 Trigger Events The Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer selects specific Key Image Note objects to retrieve from the Image Archive or Imaging Document Source. __________________________________________________________________________ 65 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 4.31.4.1.2 1535 1540 Message Semantics The message semantics are defined in the DICOM Query/Retrieve Service Class section of the DICOM 2003 PS 3.4: Query/Retrieve Service Class. It is the responsibility of the Image Manager to assure that the patient and procedure information is current in the images and Key Image Note objects when they are retrieved from the Image Archive. It is the responsibility of the Imaging Document Source to assure that the patient and procedure information is current in the Key Image Note objects when they are retrieved from this Actor. 4.31.4.1.3 Expected Actions The Image Archive or Imaging Document Source receives the C-MOVE request, establishes a DICOM association with the Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer, and uses the DICOM Key Image Note Storage SOP Class to transfer the requested Key Image Note objects. 4.31.4.2 Render Key Image Notes 1545 1550 This transaction relates to the “Render Key Image Notes” event of the above interaction diagram. Key Image Notes cannot be rendered separately, but must be applied to images. Refer to sec. 4.16 for a description of the transaction used to retrieve images to which Key Image Notes may be applied. The Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer is not required to, but may choose to, support retrieval and display of images from other studies than the one to which the Key Image Note belongs 4.31.4.2.1 Trigger Events The Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer receives Key Image Note instances from the Image Archive or Imaging Document Source. 1555 4.31.4.2.2 Invocation Semantics This is a local invocation of functions resident within the Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer. The method used by the Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer to present images for viewing by the user flagged by the Key Image Notes is outside the scope of the IHE Technical Framework. 1560 4.31.4.2.2.1 Retrieve AE Title 1565 If the Image Display is capable of retrieving objects referenced in a DICOM Key Image Note then it shall retrieve these objects from the device matching the appropriate Retrieve AE Title attribute (0008,0054) included in the DICOM Key Image Note. If the Retrieve AE Title attribute is not specified or configured, then the Image Display shall use some other configurable Retrieve AE Title. __________________________________________________________________________ 66 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 1570 In the case of retrieving DICOM Key Image Notes in a Cross-Enterprise, imaging document sharing (XDS-I) network environment, a configuration of mapping the AE Titles to DICOM AE Network Addresses (IP Address and Port number) is needed to be exchanged between the Imaging Document Source and the Imaging Document Consumer. Appendix Y describes in details the AE Title mapping to the DICOM AE Network Addresses. 4.31.4.2.3 Expected Actions The Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer flags the images and renders the Key Image Note. 1575 Note: It is recommended to use the just retrieved instance of the Key Image Note to ensure that the most recent patient data be displayed to reflect possible patient merge and patient update in the Image Manager/Image Archive or Imaging Document Source. This patient data may be inconsistent with patient data contained in a previously retrieved copy of the same Key Image Note instance. 1580 Volume 3 begins here. Update the following existing transaction 45 4.45 Retrieve Evidence Documents 1585 This section corresponds to Transaction RAD-45 of the IHE Technical Framework. Transaction RAD-45 is used by the Image Archive, Image Display, Imaging Document Source and Imaging Document Consumer. 4.45.1 Scope 1590 In the Retrieve Evidence Documents Transaction, the requested DICOM Evidence Documents are transferred from the Imaging Archive to the Image Display, or from the Imaging Document Source to the Imaging Document Consumer. 4.45.2 Use Case Roles Actor: Image Archive __________________________________________________________________________ 67 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Role: Sends requested Evidence Documents to the Image Display Actor. 1595 Actor: Imaging Document Source Role: Sends requested Evidence Documents to the Imaging Document Consumer. Actor: Image Display Role: Receives requested Evidence Documents from the Image Archive Actor. Actor: Imaging Document Consumer 1600 Role: Receives requested Evidence Documents from the Imaging Document Source 4.45.4 Referenced Standards DICOM 2000 PS 3.4: Query/Retrieve Service Class, Storage SOP Class 4.45.4 Interaction Diagram Image Archive Image Display Retrieve Evidence Documents (C-MOVE) Store Evidence Documents (C-STORE) Render Evidence Documents 1605 __________________________________________________________________________ 68 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 4.45.4.1 1610 1615 The Retrieve (Study Root – MOVE and optionally Patient Root - MOVE) SOP Classes shall be supported. The Image Archive as an SCU shall support DICOM Storage SOP Classes that may be used as Evidence Documents. The Imaging Document Source as an SCU shall support DICOM Storage SOP Classes that may be used as Evidence Documents it published for sharing. Refer to DICOM 2003 PS 3.4, Annex C, for detailed descriptive semantics (see vol. III, table 4.38-1). In the case of retrieving Evidence Documents in a Cross-Enterprise, imaging document sharing (XDS-I) network environment, a configuration of mapping the AE Titles to DICOM AE Network Addresses (IP Address and Port number) is needed to be exchanged between the Imaging Document Source and the Imaging Document Consumer. Appendix Y describes in details the AE Title mapping to the DICOM AE Network Addresses. 4.45.4.1.1 1620 Trigger Events The Image Display or the Imaging Document Consumer selects specific Evidence Document objects to retrieve from the Image Archive or the Imaging Document Source. 4.45.4.1.2 1625 Retrieve Evidence Documents Message Semantics The message semantics are defined in the DICOM Query/Retrieve Service Class section of the DICOM 2000 PS 3.4: Query/Retrieve Service Class. It is the responsibility of the Image Manager or Imaging Document Source to assure that the patient and procedure information is current in the Evidence Document objects when they are retrieved from the Image Archive or Imaging Document Source. __________________________________________________________________________ 69 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 4.45.4.1.3 1630 1635 The Image Archive or the Imaging Document Source receives the C-MOVE request, establishes a DICOM association with the Image Display or the Imaging Document Consumer, and uses the DICOM C-STORE command to transfer the requested Evidence Document objects. Since the Image Display or the Imaging Document Consumer can select compatible documents based on the Template IDs returned in the query, the Image Display or the Imaging Document Consumer is required not to return an error to the Image Archive or the Imaging Document Source due to the retrieved document content. The retrieved results may simply be discarded instead. 4.45.4.2 1640 Expected Actions Render Evidence Documents This transaction relates to the “Render Evidence Documents” event of the above interaction diagram. 4.45.4.2.1 Trigger Events The Image Display or the Imaging Document Consumer receives Evidence Document instances from the Image Archive or the Imaging Document Source. 4.45.4.2.2 1645 1650 This is a local invocation of functions resident within the Image Display or the Imaging Document Consumer. Evidence Documents shall be displayed to the user of the Image Display or Imaging Document Consumer. The method used by the Image Display or the Imaging Document Consumer to present Evidence Documents for viewing by the user is outside the scope of the IHE Technical Framework. For example, in the case when an Image Display or an Imaging Document Consumer is grouped with an Evidence Creator, the Evidence Document may be rendered as input for further processing by the Evidence Creator. 4.45.4.2.3 1655 Invocation Semantics Expected Actions The Image Display or the Imaging Document Consumer renders the Evidence Documents retrieved. If the Image Display or the Imaging Document Consumer is unable to handle parts of the document, it may inform the user and offer the choice of doing a “low-grade” rendering or ignoring the data. Evidence Documents may contain references to other types of evidence objects. The Image Display or the Imaging Document Consumer shall always be able to render (or “low-grade” render) referenced Evidence Documents or to invoke other rendering display functionality. __________________________________________________________________________ 70 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 1660 If the Image Display also supports the Consistent Presentation of Images Profile, it is also required to apply any presentation states referenced in the Evidence Document for application to the relevant images. If the Image Display also supports the Key Image Notes Profile, it is also required to render any Key Image Notes referenced in the Evidence Document. 1665 Note: It is recommended to use the just retrieved instance of the Evidence Document to ensure that the most recent patient data be displayed to reflect possible patient merge and patient update in the Image Manager/Image Archive or the Imaging Document Source. This patient data may be inconsistent with patient data contained in a previously retrieved copy of the same Evidence Document instance. 1670 Add the following new transactions RAD-54 and RAD-55, as well as Appendix Y: Configuration for Accessing DICOM and WADO Retrieve Services 1675 1680 4.54 Provide and Register Imaging Document Set This section corresponds to Transaction RAD-54 of the IHE Technical Framework. Provide and Register Imaging Document Set is used by the Imaging Document Source to provide a set of imaging documents to the Document Repository, and to request that the repository store these documents and then register them with the Document Registry. This transaction is derived from the Transaction ITI-15 of the IHE IT Infrastructure Technical Framework. It adds new document content types as well as additional semantics and constraints on the metadata defined in Transaction ITI-15. 4.54.1 Scope 1685 The Provide and Register Imaging Document Set transaction passes a Submission Request from an Imaging Document Source to a Document Repository. A Provider and Register Document Set transaction carries: • Metadata describing zero or more new documents Submission Set definition along with the linkage to new documents and references to existing documents Zero or more XDS Folder definitions along with linkage to new or existing documents. • Zero or more documents 1690 __________________________________________________________________________ 71 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 4.54.2 Use Case Roles Document Repository Imaging Document Source Provide and Register Document Set 1695 Actor: Imaging Document Source Role: Creates (text and/or PDF) report and/or DICOM KOS Manifest documents, and submits the document(s) with associated metadata to a Document Repository. Actor: Document Repository 1700 1705 Role: receives documents and associated metadata and: • Stores the documents • Enhances submitted metadata with repository information to enable later retrieval of documents • Forwards the enhanced metadata to the Document Registry. 4.54.3 Referenced Standard ebMS OASIS/ebXML Messaging Services Specifications v2.0 ebRIM OASIS/ebXML Registry Information Model v2.0 1745 ebRS OASIS/ebXML Registry Services Specifications v2.0 HTTP HyperText Transfer Protocol HTTP/1.1 (IETF RFC2616) 1710 MIME Multipurpose Internet Message Extensions (RFC 2045 to RFC 2049) SMTP Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (RFC2821) multipart/related The MIME Multipart/Related Content-type (RFC2387) DICOM 2004 PS 3.18: Web Access to DICOM Persistent Objects (WADO) DICOM 2004 PS 3.3: Key Object Selection Document (KOS) __________________________________________________________________________ 72 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 1715 4.54.4 Interaction Diagram Document Repository Imaging Document Source Provide and Register Document Set Provide and Register Document Set acknowledgment 4.54.4.1 Provide & Register Document Set message 1720 1725 An Imaging Document Source sends documents and associated metadata to a Document Repository. This message corresponds to an ebRS SubmitObjectsRequest with associated documents, and is specified in Transaction ITI-15 of the IHE IT Infrastructure Technical Framework, Volume 2. 4.54.4.1.1 Trigger Events The Imaging Document Source Actor, based on a human decision or the application of a certain rule of automatic operation, wants to submit • A set of one or more new imaging documents for sharing, or • A set of one or more updated imaging documents which reflect the content correction / change of previously submitted documents. 4.54.4.1.2 Message Semantics 1730 This transaction extends the message semantics of the ITI-15 Provide and Register Document Set by specifying additional document content types, to allow the sharing of the following types of documents: 1. Sets of persistent DICOM SOP instances 2. Imaging diagnostic reports __________________________________________________________________________ 73 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 1735 To support these content types, additional requirements and constraints on the XDS document metadata are specified. The Imaging Document Source is required to include appropriate metadata for the shared documents. XDS-I Provide and Register Imaging Document Set message semantics are specified in the following subsections: 1740 1745 1. Sharing of Persistent DICOM Instances via a Manifest document 2. Sharing of radiology diagnostic report in PDF or Text formats 3. XDS-I document metadata specification 4. Use of XDS Submission Set concept in sharing of radiology imaging information. 4.54.4.1.2.1 Sharing of Set of DICOM Instances The Imaging Document Source creates a manifest that describes and collects references to DICOM SOP instances that are intended for sharing. The manifest, a Key Object Selection (KOS) Document Instance, is the actual document provided to the Document Repository and registered at the Document Registry. 1750 As specified in IHE ITI XDS Integration Profile, the structure of the message between the Imaging Document Source and the Document Repository is a MIME “multipart/related” message. The KOS Document Instance to be stored is attached as a part having a MIME type of “application/dicom”. The registration transaction to the Registry must contain an indication of the MIME type (e.g., “application/dicom”). 1755 The referenced DICOM instances are made available to be retrieved from the Imaging Document Source. The Imaging Document Source is required to ensure that the referenced DICOM SOP Instances from within a published manifest are available to be retrieved. 1760 The Imaging Document Source is responsible for replacing a previously submitted manifest document when a change occurs to the manifest content (e.g., Change of the DICOM SOP instances referenced within the manifest). 4.54.4.1.2.1.1 Manifest KOS Document The Imaging Document Source is required to include the references of the DICOM SOP Instances for sharing in Current Requested Procedure Evidence Sequence (0040,A375) of the KOS Manifest Document. 1765 In addition, the Imaging Document Source shall support a number of attributes in (0040,A375), which are represented in the SOP Instance Reference Macro, as described in the following table __________________________________________________________________________ 74 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Table 4.54-1. Attributes of SOP Instance Reference Macro in KOS Manifest Document Attribute Name 1770 Tag Imaging Document Source Study Instance UID (0020,000D) R Referenced Series Sequence (0008,1115) R > Series Instance UID (0020,000E) R > Retrieve AE Title (0008,0054) R+ > Stoarge Media File-Set ID (0088,0130) O > Storage Media File-Set UID (0088,0140) O > Referenced SOP Sequene (0008,1199) R >> Referenced SOP Class UID (0008,1150) R >> Referenced SOP Instance UID (0008,1155) R Some of these requirements build on attributes which are Type 2 or Type 3 in DICOM (such attributes are indicated with R+). 4.54.4.1.2.2 Sharing of Report Since text reports address many of the weaknesses of PDF reports and vice versa, it is required that the Imaging Document Source shall support shared reports in at least one of the following 3 different formats: 1775 • Text, • PDF, or • A single multipart MIME document with corresponding Text and PDF parts. It is likely that in a given Affinity Domain only a subset of these formats will be used based on Affinity Domain policy. 1780 To maximize interoperability of the chosen formats, the following restrictions shall be required: • 1785 • For PDF documents: Baseline PDF version shall be PDF 1.3 (see IANA registry for details about PDF MIME type, such as version). PDF versions below 1.3 shall be supported. PDF text encryption feature shall be disabled. The Affinity Domain will specify restrictions on text fonts and languages used in the PDF documents. For Plain Text Documents: Text shall be encoded with UTF-8 UNICODE format. __________________________________________________________________________ 75 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 1790 A report (no matter what document format is chosen) can be shared with or without image reference(s). If a shared report includes image reference(s), it can embed selected images in its PDF format or it can include fully resolved hyperlinks that point to the selected images; these hyperlinks can be interactively clickable (e.g. PDF) or can be processed or copied (e.g. text). 1795 The Imaging Document Source that provides and registers the shared report is responsible for formatting the hyperlink to reference relevant images. The referenced images within a shared imaging report are meant to be accessed without the need for specialized (e.g., DICOM) viewing applications. The hyperlink that reference the selected image shall be formatted as a DICOM WADO URI. The Imaging Document Source is required to ensure that image references are valid links. 1800 Even though significant images can be shared as non-DICOM format (embedded picture in PDF report or hyperlinks in PDF or Text report), it is required that sharing of a large set of DICOM images be achieved by sharing a set of DICOM SOP instances by providing and registering a manifest document. This is to avoid registration of a large number of individual documents in the XDS Document Registry. 1805 4.54.4.1.2.3 Metadata The Register Document Set message shall include the metadata attributes that will be forwarded by the XDS Document Repository Actor to the Registry Actor using the Register Document Set Transaction (ITI-14). 1810 The Imaging Document Source supplies all necessary registry object attributes of an XDSDocumentEntry with the exception of the following attributes: XDSDocument.URI XDSDocument.hash XDSDocument.size 1815 This is the legend for the metadata tables that follow: • Optional - required status of the XDS attribute, one of R, R2, or O (optional). • Constrained – does this Content Profile further constrain this attribute. • Source Type – one of the following values: 1820 Source Type SA Description Source document Attribute – value is copied directly from source __________________________________________________________________________ 76 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ SAT FM FAD CAD CADT n/a DS O Cg Cp document. The Source/Value column identifies where in the source document this attribute comes from. Specify the location in XPath when possible. Source document Attribute with Transformation – value is copied from source document and transformed. The Source/Value column identifies where in the source document this attribute comes from. Specify the location in XPath when possible. Extended Discussion column must be ‘yes’ and the transform must be defined in the extended discussion Fixed (constant) by Mapping - for all source documents. Source/Value column contains the value to be used in all documents. Fixed by Affinity Domain – value configured into Affinity Domain, all documents will use this value. Coded in Affinity Domain – a list of acceptable codes are to be configured into Affinity Domain. The value for this attribute shall be taken from this list. Coded in Affinity Domain with Transform - a list of acceptable codes are to be configured into Affinity Domain. The value for this attribute shall be taken from this list. Not Applicable – may be used with an optionality R2 or O attribute to indicate it is not to be used. Document Source – value comes from the Document Source actor. Use Source/Value column or Extended Discussion to give details. Other – Extended Discussion must be ‘yes’ and details given in an Extended Discussion. Computed by Repository Computed by Registry 4.54.4.1.2.3.1 Metadata Attributes of Author Information and Document Creation Time 1825 1830 In XDS, a registered document directly contains the clinical information of interest for sharing. Therefore, its metadata for registration can be populated directly from the document content. For example, a discharge letter is submitted to the Document Repository, so its author and creation information is populated into the XDS Document metadata. In XDS-I, the Manifest document submitted to the Document Repository usually does not directly constitute clinical information of interest for sharing, but rather is a set of references to such clinical information. Thus, the metadata of the Manifest document should be related to the __________________________________________________________________________ 77 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ referenced source content or its creation process, to reflect the clinical nature of the shared information. This affects the metadata attributes including authorSpecialty, authorInstitution, authorPerson, authorRole, creationTime, title. 1835 1840 If the manifest references source data from multiple authors, then one primary author, source data creation time and document title need to be chosen. Note that this metadata needs to be populated from this part of the source data that represents the main content for sharing most closely, in order to best support a user query to the Registry for finding this data. For example, a manifest referencing a current report, a current study as well as a prior report and study, will register metadata populated from the current report (which is the clinical content of interest for sharing). In case where data to be shared is transformed from its original format (e.g. DICOM) to another format (e.g. PDF) in advance to sending it to the Repository, the metadata of such newly generated shared information must be populated from the original source data (e.g. DICOM data) 1845 In summary, XDS-I metadata always reflects the main clinical content of a shared document, which may be described directly in the document, or in the source data referenced within the document, or in the source data from which the document is transformed. 4.54.4.1.2.3.2 XDSDocumentEntry XDSDocumentEntry Metadata Optional Attribute Constrained Extended Discussion Source Type Source/ Value authorSpecialty R2 DS This attribute value shall be populated by the source actor from local configuration available to its software application. Usually, this value is not taken directly from a DICOM information object. authorInstitution R2 DS This attribute value shall be populated by the source actor from local configuration available to its software application. Usually, this value is not taken directly from a DICOM information object. authorPerson R2 DS This attribute value represents the person or the machine who authored the document, and shall be populated by the Imaging Document Source from information about the user who authored the clinical content that is intended for sharing in the document (either the person who is logged in or the software application). Note: this attribute does not necessarily represent the person who digitally signed __________________________________________________________________________ 78 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ XDSDocumentEntry Optional Constrained Attribute Extended Discussion Source Type Source/ Value the document. authorRole R CAD This Attribute value shall be populated by the Imaging Document Source from a list of codes designated by the Affinity Domain, to describe the clinical role of the author. authorRoleDisplayNa me R CAD The name of the authorRole code to be displayed. classCode R CAD This attribute value shall be populated by the Imaging Document Source from a list of codes designated by the affinity domain. It is a coarse classification of the documents such as Result. classCodeDisplayNa me R CAD The name of the class code to be displayed. confidentialityCode R CAD This attribute value shall be populated by the source system from a list of codes designated by the affinity domain. creationTime R SA This attribute value shall be populated by the source actor to record the date and time at which the clinical content conveyed in the shared document is created. If the published document is a DICOM object or is transformed from a DICOM information object, this attribute value should be taken from the tags Instance Creation Date (0008,0012) and Instance Creation Time (0008,0013) of the DICOM object. eventCodeList O R2 SA This attribute shall be populated by the Imaging Document Source from code(s) in DCMR Context Group CID 29 for Acquisition Modality and from code(s) in DCMR Context Group CID 4 for Anatomic Region This attribute can contain multiple codes and there is not any specific ordering assumed in these codes. For DCMR Context Groups, see DICOM PS 3.16-2004.The presence of this attribute is strongly recommended. eventCodeDisplay R R2 SA This attribute contains the Code Meaning __________________________________________________________________________ 79 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ XDSDocumentEntry Optional Attribute NameList Constrained Extended Discussion Source Type (if event Code is valued) Source/ Value text(s) of the code(s) for Acquisition Modality and for Anatomic Region valued in eventCodeList, from DCMR Context Group CID 29 and from DCMR Context Group CID 4, respectively. Note that the ordering of the Code Meaning texts populated in this attribute shall be sorted in the same order of the corresponding codes in eventCodeList. For DCMR Context Groups, see DICOM PS 3.16-2004. formatCode R FM This attribute shall be populated by the Imaging Document Source from one of the following values: “1.2.840.10008.5.1.4.1.1.88.59” (DICOM KOS SOP Class UID) as the Format Code Value and “1.2.840.10008.2.6.1” (DICOM UID Registry UID) as the Format Coding Scheme OID for a DICOM Manifest document. “TEXT” for a TEXT report document “PDF” for a PDF report document “PDF/TEXT” for a PDF and Text Multipart document. healthcareFacility TypeCode R CAD This attribute shall be populated by the source from a configured list that is defined by the affinity domain healthcareFacility TypeCodeDisplay Name R CAD The display name of the healthcare facility. languageCode R CAD This attribute shall be populated by the source by taking a value from the language tags specified in RFC 3066 Example: “en-us” for English in the United States. legalAuthenticator O If information about the legal authenticator is unknown, no value shall be filled in this attribute. Otherwise, this attribute can be populated by the Imaging Document Source to __________________________________________________________________________ 80 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ XDSDocumentEntry Optional Attribute Constrained Extended Discussion Source Type Source/ Value indicate the legal authenticator of the shared document. mimeType R FM This attribute shall be populated by the Imaging Document Source from one of the following values: “application/dicom” for a DICOM Manifest document “text/plain” for a TEXT report. “application/pdf” for a PDF report “multipart/related” and parts shall be “text/plain” and :application/pdf” for a multipart report parentDocument Relationship parentDocumentId R (when applicable) R (when parent Document Relationship is present) patientId DS R DS DS This attribute value shall be populated by the source actor by taking one of the three values defined in the IHE ITI XDS Integration Profile to describe the relationship of this document and previously published document(s), if the current document updates, amends or deprecates those documents. If the parentDocumentRelationship is present, this attribute shall contain the OID of the parent Document This attribute shall contain the Patient ID of the patient, who is the subject of the document, and shall be populated by the Imaging Document Source. The Assigning Authority of this Patient ID shall be the Affinity Domain. practiceSettingCode R FAD This attribute shall be populated by the Imaging Document Source by taking a fixed code defined by the affinity domain to designate “Radiology” practiceSettingCode DisplayName R FAD The display name of the practice setting code. serviceStartTime R2 DS This attribute shall be populated by the Imaging Document Source for a date and time that indicates the imaging service start time. __________________________________________________________________________ 81 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ XDSDocumentEntry Optional Attribute Constrained Extended Discussion Source Type Source/ Value As an example, the Imaging Document Source could take the value of Study Date (0008,0020) and Study Time (0008,0030) from the associated DICOM study serviceStopTime R2 N/a sourcePatientId R SA This attribute shall represent the Patient ID of the patient, issued from a local domain used in the Imaging Document Source, who is the subject of the document, and shall be populated by the Imaging Document Source The Assigning Authority of Patient ID shall represent the local patient identification domain. sourcePatientInfo R DS This attribute shall represent the Patient demographics information used in the Imaging Document Source actor system to identify the patient. This attribute allows multiple values for different pieces of patient demographics, see metadata specification of the IHE ITI XDS Integration Profile. As an example, this information can be transformed from DICOM Patient’s Name (0010,0010), Patient’s Birth Date (0010,0030), and Patient’s Sex (0010,0040). title O DS This attribute can be populated by the Imaging Document Source application for the text title of the document. Example: CT of the head typeCode R SA This attribute shall be populated by the source actor from a coding system of the Requested Procedure Code of the Requested Procedure, to which the document is associated. The coding system of the Radiology Imaging Requested Procedure Code will be designated by the affinity domain and shared by all Imaging Document Sources in the affinity domain. __________________________________________________________________________ 82 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ XDSDocumentEntry Optional Constrained Attribute Extended Discussion Source Type Source/ Value typeCodeDisplay Name R SA This attribute shall be filled by the source actor using the code meaning text of the corresponding Requested Procedure Code valued in typeCode. uniqueId R SA This attribute shall contain the Document unique ID generated by the source actor. It shall be an ISO OID. For a DICOM Manifest document, this attribute value shall be the same as the SOP Instance UID of the corresponding DICOM KOS object. 1850 entryUUID R Cg This attribute shall be computed and populated by the Document Registry. Size R Cp This attribute shall be computed and populated by the Document Repository. Hash R Cp This attribute shall be computed and populated by the Document Repository. availablityStatus R Cg This attribute shall be computed and populated by the Document Registry. 4.54.4.1.2.3.3 XDSSubmissionSet XDSSubmissionSet Metadata Optional attribute Constrained Extended Discussion Source Type Source/ Value authorDepartment R2 DS This attribute shall be populated by the source actor from local configuration available to its software application. authorInstitution R2 DS This attribute shall be populated by the source actor from local configuration available to its software application. authorPerson O DS This attribute can be populated by the source based on the information about the person who is logged in the software application and who is taken the decision to publish the Submission Set. comments R2 DS This attribute shall contain free text entered by a human user or generated by the source actor to describe this Submission Set. __________________________________________________________________________ 83 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ XDSSubmissionSet Optional Constrained attribute Extended Discussion Source Type Source/ Value contentTypeCode R CAD This attribute shall be populated by the source from a configured list of codes defined by the affinity domain contentTypeCode DisplayName R CAD The display name of the Type Code. patientId R CAD This attribute shall contain the Patient ID of the patient, who is the subject of the Submission Set, and shall be populated by the Imaging Document Source. The Assigning Authority of this Patient ID shall be the Affinity Domain. sourceId R DS This attribute shall be populated by the source actor from local configuration available to its software application submissionTime R DS This attribute shall be populated by the source actor to record the date and time, at which the Submission Set is sent to the Document Repository uniqueId R DS This attribute shall contain UID of the Submission Set generated by the source actor 4.54.4.1.2.3.4 Types 1855 1860 Transformation of DICOM VR to XDS Document Metadata Data A number of XDS document metadata attributes use HL7 data types for value representation. Some of the metadata attributes may be transformed from data elements of the corresponding DICOM SOP Instance. In this section, transformations of DICOM VR (Value Representation) to the HL7 data types used in XDS metadata are described. Note that term HL7 Data Type in the following transformations refers to their specified usage in XDS document metadata as defined in IHE ITI XDS Integration Profile. 4.54.4.1.2.3.4.1 CX – Extended Composite ID The following table describes the transformation of data element of DICOM VR to CX data type as specified in IHE XDS Integration Profile: CX Data Component 1 Component Name ID Number DICOM VR LO Comment This attribute represent the value of __________________________________________________________________________ 84 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Patient ID issued by an Assiging Authority as indicated in component 3. In DICOM, it is data element (0010,0020). 3.2 Assigning Authority – Universal ID Assigning Authority information is not required in DICOM instance. The Imaging Document Source must use its local configuration to populate this subcomponent, to inidcate the Patient ID Domain, from which the Patient ID value in component 1 has been issued. This must be an ISO OID 3.3 Assigning Authority – Universal ID Type This must be “ISO” Identifier Type Patient ID Type information is not required in DICOM instance. The Imaging Document Source can use its local configuration to populate this component, to inidcate the type of the Patient ID value in component 1. 5 1865 HL7 CX data components not listed in the table are not used in XDS document metadata and shall be left empty. 4.54.4.1.2.3.4.2 DTM – Date / Time HL7 DTM Data Type can be represented in the following regular expression: YYYY[MM[DD[HH[MM[SS]]]]] 1870 This can be transformed from DICOM elements of VR DA (format: YYYYMMDD) and TM (format: HHMMSS.fraction). 4.54.4.1.2.3.4.3 XCN – Extended Composite ID Number and Name for Person The following table describes the transformation of DICOM VR to XCN data type as specified in IHE XDS Integration Profile: XCN Data Component Component Name 1 ID Number 2 Family Name DICOM Data Element Comment This attribute component is not required in DICOM. Imaging Document Source must use its local configuration or personnel direcotory service to populate this component. Is this the patient ID for a patient or the performer id , this is not clear 1st Component of PN A data element of VR PN, like (0010,0010) for Patient Name. __________________________________________________________________________ 85 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 1875 3 Given Name 2nd Component of PN 4 Second or Further Given Names or Initials Thereof 3rd Component of PN 5 Suffix 5th Component of PN 6 Prefix 4th Component of PN 7 Degree This attribute component is not required in DICOM. HL7 XCN data components not listed in the table are not used in XDS document metadata and shall be left empty. 4.54.4.1.2.3.4.4 for Organization XON – Extended Composite Name and Identification Number The following table describes the transformation of DICOM VR to XON data type as specified in IHE XDS Integration Profile: XON Data Component 1 1880 Component Name Organization Name DICOM Data Element LO Comment A data element of VR LO, like (0008,0080) for institution name. HL7 XON data components not listed in the table are not used in XDS document metadata and shall be left empty. 4.54.4.1.2.4 Use of XDS Submission Set 4.54.4.1.2.4.1 1885 1890 Linking Report to Set of DICOM Instances Figure 4.45.4 -1 shows examples of three Submission Sets: • Submission Set 1 includes a report and a Manifest that are stored in the Document Repository. The manifest references DICOM instances that are archived in the IM/IA. • Submission Set 2 includes one single manifest. • Submission Set 3 includes a report and references the manifest from Submission Set 2 since it was generated by interpreting the images referenced by that manifest. Submission Set 3 also references the report and the manifest form Submission Set 1 since that report and images that are referenced by that manifest were used for the interpretation. __________________________________________________________________________ 86 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Figure 4.45.4 -1 Imaging Information Sharing Submission Set 1895 4.45.4.1.2.2.2 Linking Report to prior report The Report Submission Set can reference the manifest for a set of prior images published if the prior images were used in creating the interpretation. Likewise the report submission set can reference a report from a previous submission. 1900 4.54.4.1.3 Expected Actions The Document Repository Actor will receive this message. Each document within the message will be stored into the repository. A detected failure will result in an error result message being returned to the Imaging Document Source Actor thus terminating this transaction. 1905 If there is no error detected, as each document is stored into the repository, one URI must be created for the document, to reference it via an HTTP service. 1910 The Document Repository Actor will complete the received document metadata, to prepare these for document registration, as specified in transaction ITI-15. The Document URI created above, will be added in the metadata for each document deposited in the repository via an ebRIM object ExtrinsicObject (see IHE ITI XDS Integration Profile). The Document Repository Actor must also add the attributes discussed in Section 4.54.4.1.2.1, to the metadata. __________________________________________________________________________ 87 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ The Document Repository will initiate a Register Document Set transaction with the completed document metadata to the XDS Document Registry. __________________________________________________________________________ 88 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 4.55 WADO Retrieve 1915 This section corresponds to Transaction RAD-55 of the IHE Technical Framework. Transaction RAD-55 is used by the Imaging Document Consumer and the Image Manager/ Image Archive actors. 4.55.1 Scope 1920 The WADO Retrieve transaction enables an Imaging Document Consumer to access DICOM SOP Instances with a web-based service through HTTP/HTTPS protocol. 4.55.2 Use Case Roles Imaging Document Consumer Imaging Document Source WADO Retrieve Actor: Imaging Document Consumer 1925 Role: Issues an HTTP Get Request to access a DICOM instance. Actor: Imaging Document Source Role: Receives an HTTP Get Request for accessing a DICOM instance and generates the HTTP response with the appropriate content. 4.55.3 Referenced Standard 1930 DICOM 2004 PS 3.18: Web Access to DICOM Persistent Objects (WADO) __________________________________________________________________________ 89 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 4.55.4 Interaction Diagram Imaging Document Source Imaging Document Consumer Object(s) request (GET HTTP Request) Object(s) send (HTTP Response to the GET Request) 4.55.4.1 WADO Retrieve 1935 The Imaging Document Consumer issues an HTTP Get to request a specific DICOM instance from the Imaging Document Source. The Imaging Document Source receives the request, generates the response with the appropriate content and sends an HTTP Response to the Imaging Document Consumer. 4.55.4.1.1 Trigger Events 1940 The Imaging Document Consumer wishes to retrieve a DICOM instance that is referenced within a DICOM Manifest. 4.55.4.1.2 Message Semantics The message semantics are defined by the DICOM Web Access to DICOM Persistent Objects (WADO), PS 3.18. 1945 The WADO Retrieve transaction is performed by the Imaging Document Consumer to send a HTTP Request-URI to the web server of the Imaging Document Source. The Imaging Document Consumer generates the HTTP Request-URI to retrieve a DICOM instance. The DICOM instance shall be specified with its Study Instance UID, Series Instance UID, and SOP Instance UID in the HTTP Request-URI. The Imaging Document Consumer must obtain the host information (e.g., web server location, and script language) of the web server to perform this __________________________________________________________________________ 90 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 1950 transaction. The Imaging Document Consumer can map the Retrieve AE Title of the SOP Instance to the web server host information based on its local configuration (see Appendix Y). In addition, the Imaging Document Consumer shall support the following fields in the HTTP request: Table 4.55-1. WADO HTTP Request Fields HTTP Field Accept REQ Description Values R This field is used to specify MIME types which are acceptable for the response At least one of the following values: application/dicom image/jpeg application/text application/html */* Other values may be included as well AcceptLanguage 1955 This field specifies the language of the object to be retrieved. O Any valid value according to RFC2616 The Imaging Document Source shall list all media types it supports in the Accept field of the HTTP request, and shall use WADO HTTP parameter contentType to request the desired media type of the object to be retrieved in the HTTP response (see Table 4.55-2). The Imaging Document Source and the Imaging Document Consumer are required to support a number of parameters in the WADO HTTP Request-URI, as described in the following table. 1960 Table 4.55-2. WADO HTTP Request Parameters Parameter Name Parameter Description Requirement Imaging Document Source Imaging Document Consumer requestType Type of the HTTP request performed. It must be “WADO” R R studyUID Unique identifier of the study R R seriesUID Unique identifier of the series R R objectUID Unique identifier of the object R R contentType MIME type of the pesponse R+ R+ Note IHE-1 IHE-2 charset Charset of the response O O anonymize Anonymize object O O annotation Annotation of the object O O IHE-3 __________________________________________________________________________ 91 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 1965 rows Number of pixel rows O O IHE-3 columns Number of pixel columns O O IHE-3 region Region of image O O IHE-3 windowCenter Window center of the image O O IHE-3 windowWidth Window width of the image O O IHE-3 frameNumber Frame number of the single frame in a multi-frame image O O IHE-3 imageQuality Image quality factor O O IHE-3 presentationUID Unique identifier of the presentation object O O IHE-3 presentationSeriesUID Uniquer identifier of the series containing the presentation object O O IHE-3 transferSyntax Transfer syntax UID used with DICOM image object returned in the response O O IHE-3 IHE-1: The Imaging Document Consumer must use the value “application/dicom” to retrieve a DICOM SOP Instance in the DICOM Part 10 File Format. This allows the Imaging Document Consumer to receive a SOP Instance in the native DICOM format for full data manipulation. The Imaging Document Consumer can also use the value “application/jpeg” to retrieve an image encoded in JPEG baseline format if it is a single frame DICOM image object or a single frame image encoded in a multi-frame DICOM image object. 1970 1975 The Imaging Document Consumer can also use the values “application/text” or “application/html” to retrieve a DICOM SR object represented in the text or html format. The Imaging Document Consumer can also use other values for this parameter as specified in DICOM PS 3.18, if they are supported by the Imaging Document Source. This parameter is optional in DICOM PS 3.18. Because the default format of the DICOM persistent object returned in the HTTP Get response in the absence of a value in this parameter varies depending on the SOP Class of the retrieved object, this profile requires that the parameter is supported, to improve interoperability. 1980 IHE-2: This parameter must be compatible to the value(s) that the Imaging Document Consumer placed in the Accept field of the HTTP Request-URI. IHE-3: The parameter applies only to a DICOM SOP Instance if it is an image object. __________________________________________________________________________ 92 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ 4.55.4.1.2.1 Example of WADO Request-URI 1985 The following is an example of HTTP Request-URI for retrieving a persistent DICOM object using WADO: http://www.hospital/radiology/wado.php?requestType=WADO&studyUID=1.2.250.1.59. 40211.12345678.678910&seriesUID=1.2.250.1.59.40211.789001276.14556172.67789& objectUID=1.2.250.1.59.40211.2678810.87991027.899772.2&contentType=application %2Fdicom 1990 This example uses reponse MIME type application/dicom to request the DICOM SOP Instance returned in the native DICOM Part 10 file format. 4.55.4.1.3 Expected Actions 1995 Upon reception of the WADO HTTP Request, the Imaging Document Source shall parse the request and if there are no errors, shall construct an HTTP Get Response with the requested DICOM instance content and return the response as specified by the DICOM WADO standard, with HTTP response code 200 (OK). The Imaging Document Source shall return HTTP response code 406 (Not Acceptable), if it cannot serve the requested response MIME type(s) in parameter contentType and/or Accept Field. 2000 2005 The Imaging Document Source shall return HTTP response code 404 (Not Found) if it cannot locate the requested DICOM SOP Instance or cannot recognize the UID values specified in the received HTTP Request-URI. The Imaging Document Source shall return HTTP response code 400 (Bad Request) if any required HTTP field or required WADO HTTP parameters are missing in the received HTTP Request-URI, or any other syntactic error is detected in the HTTP Request-URI (e.g., media type in contentType parameter conflicts with media types in Accept field). 4.55.4.1.4 Audit Trial Trigger Events 2010 IHE specifies a number of events that shall be reportable by means of the IHE Audit Trail (ITI TF-II 3.20). IHE Radiology Audit Trial Option further defines a subset of these events, which are particularly applicable to the radiology transactions. Table 4.55-3 lists all the radiology audit trial trigger events applied to transaction RAD-55. The last column specifies whether the sender or receiver side of the transaction is required to audit the event. 2015 Table 4.55-3. Audit Record Trigger Events IHE Radiology Transaction WADO Retrieve [55] ATNA Trigger Event(s) Instance-Stored Audit Recording Requirements Imaging Document Source shall __________________________________________________________________________ 93 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ audit Study Used Imaging Document Consumer shall audit __________________________________________________________________________ 94 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Appendix Y. Configuration for Accessing DICOM and WADO Retrieve Services Y.1 Mapping DICOM AE Title to DICOM AE Network Address 2020 2025 2030 2035 2040 When an Imaging Document Consumer wants to retrieve DICOM instances that are referenced within a shared manifest Document using DICOM C-Move/C-Store, the following configuration is necessary. The Key Object Selection Document Instance includes an AE Title but does not include any IP address or any port number. As AE Title alone is not sufficient to retrieve DICOM objects, the Imaging Document Consumer needs to get the IP address and the port number of the Imaging Document Source from its local configuration file. Similarly, the Imaging Document Source needs to know the AE Title, the IP address and the port number of the Imaging Document Consumer in order to store the DICOM objects. The Imaging Document Source needs to get the IP address, the AE Title, the port number of the Imaging Document Consumer from its local configuration file. In this profile, it is assumed that mapping of AE Titles of Imaging Document Source and Imaging Document Source to their network presentation addresses (IP and port) is supported by exchanging configuration files of the related actors, under the guidance of affinity domain policies and processes. The method of configuration file exchange is out of the scope of this profile. In the future, DICOM Supplement 67 (Configuration Management) and its proper extension in cross-enterprise use can be employed to automate this mapping. This may be a future Integration Profile candidate of IHE IT Infrastructure. As IP addresses and port numbers need to be resolved from AE titles, a special attention is required to ensure that AE titles of actors that are involved in this profile are uniquely allocated in an affinity domain. Y.2 Mapping DICOM AE Title to WADO Service Network Address 2045 2050 In order for an Imaging Document Consumer to retrieve DICOM instances referenced within a shared Manifest Document using WADO Access transaction (RAD-55), it needs to build a WADO HTTP Request-URI for the SOP instance. Though SOP instance identification information is fully specified in the Manifest, the Imaging Document Consumer needs an auxiliary method to map the Retrieve AE Title specified for a referenced SOP Instance in the Manifest to the server network address, which supports the WADO retrieve service. The Imaging Document Consumer needs to maintain a mapping configuration of the server network addresses of all Imaging Document Source in the Affinity Domain, and their Retrieve AE Titles. Using this mapping, the Retrieve AE Title of a referenced SOP instance in the __________________________________________________________________________ 95 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA IHE Technical Framework Supplement - Cross-enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging Profile ______________________________________________________________________________ Manifest can be translated to WADO service server address, which is then used to build the WADO HTTP Request-URI together with SOP instance identification information, and optionally other standard WADO HTTP parameters. 2055 To achieve an unambiguous, automated mapping of Retrieve AE Title and WADO access service server network address, some policy needs to be in place to ensure unique Retrieve AE Titles of Imaging Document Source in the entire Affinity Domain. __________________________________________________________________________ 96 Trial Implementation Version 2005-08-15 Copyright © 1997-2005: ACC/HIMSS/RSNA