Answers to the Respiration Study Guide
advertisement
.:
Name
:~
Date
Class
-----
CHAPTER
8
Study Guide
Section3: Cellular Respiration
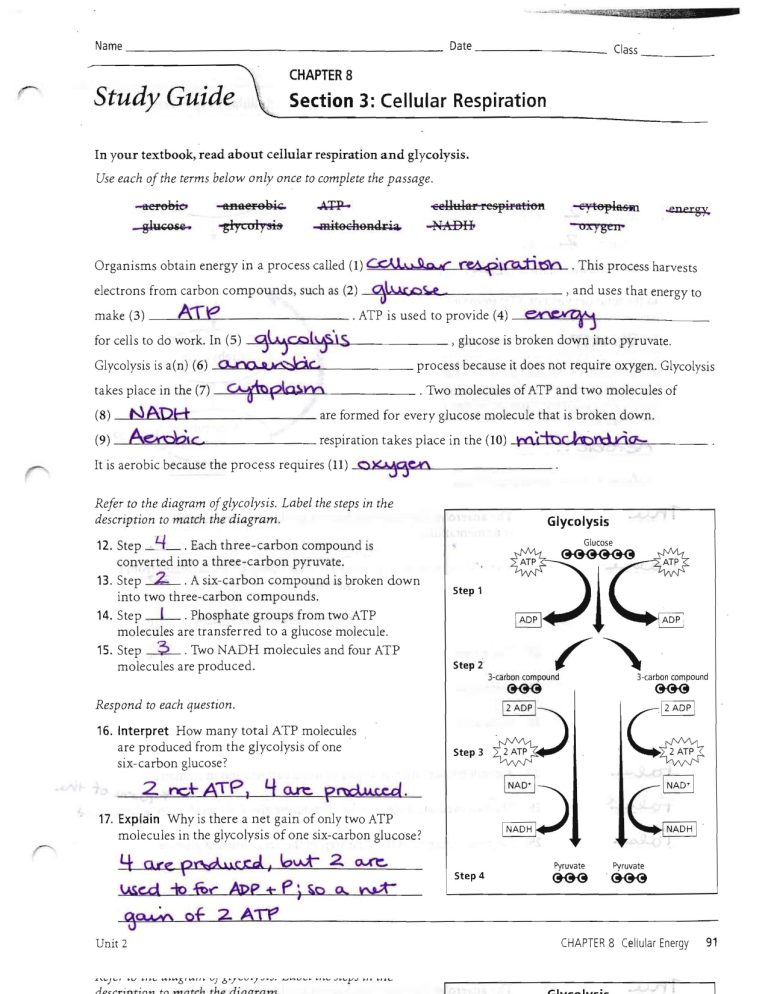
In your textbook, read about cellular respiration and glycolysis.
Use each of the terms below only once to complete the passage .
aer6bi eo
aflfteF89i""
shl,gie .
-glrco1r Mtt
eelh:tlar resf)if'ltti6ft
.A+P
electrons from carbon compounds,
..Sl.p oC C~H1;d;r)y'\
. AT P is used
u ses that ener gy to
-
_
­
is broken down into pyruvate.
process because it doe s not require oxygen . Glycolysis
¥plo:.m
takes place in the (7)
) and
, glucose
o.....no.--a
~
Glycolysis is a(n ) (6)
. This process har vest s
to pro vide (4) ----"oo£1.....-:::.....Io<P'\-~
__
~l'"5>'\S
for cells to do work. In (5)
oxrgen "
~Lv.eos.t
such as (2)
AT\?
make (3)
~tADI:Iv
....mitecheHdria.
Organi sms obtain energy in a process called (1) caL
eperg+:,
.Two molecules
of ATP and two molecule s of
(8)
NADH
are formed for ever y glucose molecule that is br oken down .
(9)
Af!:N'dti,
c.
respiration takes place in the (10)
P'\«mckl:>cJ....)n:1'--"'"'Yl
w'...
<br..=..
_
It is aerobic because the pro ce ss require s (ll) ---'
O
........
~Oo<ll"\'P.)"'¥'e.n
.a...J'----~---Refer to the diagram of glycolysis. Label the steps in the
description to match the diagram.
Glycolysis
-:..
4._.
12. Step
Each three-carbon compound is
converted into a three -carbon pyruvate.
13. Step ~ . A six-ca rbo n compound is broken down
into two three-carbon compounds .
14. Step ~ . Phosphate groups from tw o ATP
molecules are transferred to a gluc ose molecule.
15. Step .2. Two NADH m ole cule s and four AT P
molecules are produ ced .
Step 1
Step 2
Respond to each question.
Step 3
-rorApp
~c:uM of
2
+
e) £.0
0...
o.A1:.
Y'Wt
J- V
Step 4
l 2 ADP I
Ce
INADT I
c~
Pyruvate
Pyruvate
~
~
An"
CHAPTER
8 Cellular Energ
y
Unit 2
.I.'\.'­ )'-J
0'
~
17. Explain Wh y is there a net gain of only two ATP
molecules in the glycolysis of one six-carbon glucose ?
~e.et io
~
~,
4 a.n:. pnclu c.uL.­
.!:l-ace {'M-HCerJ.., lov..;t-2.
3-carbon compound
~
. ~)
16. Interpret How many total ATP molecules
are produced from the glycolysi s of one
six-c arbon glucose?
2 nc.+-ATP J
3-carboncompound
J-'~'-
J.
O/
,f~
V)
6 ..j'
V
.. f
o.l J. ..,J ·
A oc rr ;n+ ;I"'IYJ tl"'l .,.".,ntrl-t tl-t o r!; nrrrnYYr
,J.
0.1
" '-1' .,) "/J
J-Jf. .....
91
Study Guide, Section 3: CellularRespirationcontinued
In your textbook, read about the Krebs cycle, electron
transport , and anaerobic respiration .
Refer to the diagram of cellular respiration. Respond to
each question and stat em ent .
Cellular Respiration
Glucose
~ without oxygen
18. Recall What is the net yield of ATP produced by
each of the circled processe s in the diagram?
Glycolysis =
2
Krebs cycle =
2.
2ATP
ATP
ATP
Electron transport chain
= "3.2-
Pyruvate
ATP
19. Findthe total net yield of ATP from one
molecule of glucose.
~ with oxygen
Acetyl-CoA
2ATP
20. Specify Based on the diagram and your
calcul ations, which pro cess produces more
energy-the anaerobic pathway or the
aerobic pathwa y?
32ATP
~blc.. ~~
For each statem en t below, write true or false.
-rJ"'.,»
21. The an aer obic pathwa y that follows glycolysis in the absence of oxygen
is fermentation.
n
'"F~
~
-rY'-U­
0
'<
-e
,.
22. The hydrogen necessary in the electron tran sport chain come s from the
splitting of carbon dioxide molecule s.
~
e
0
g
23. Cellular respir ation in eukaryotes is slightly more efficient than in prokaryotes .
~z
0
~
24. The Krebs cycle is sometime s called the TCA cycle or the citri c acid cycle.
~
Q,
~:
-.:F~
-r~
g.
25. Fermentation occurs in the mitochondria.
!2,
tz
c,
26. Skeletal muscle produces lactic acid when the body cannot suppl y
enough oxygen.
~
~
n
0
~
92
3
27. Alcohol fermentation is found in some bact eria and in humans .
~
*~W\S. <Sf
-r~*
28. The two pyruvate molecules formed during glycolysis result in tw<}\Krebscyclefl
"F~,.A.
29. Electron transport is the first step in the breakdown of glucose.
CellularEnerg
y CHAPTER
8
Unit 2
~
Jr
=
n











