This flow chart outlines both the anaerobic and aerobic catabolism
advertisement
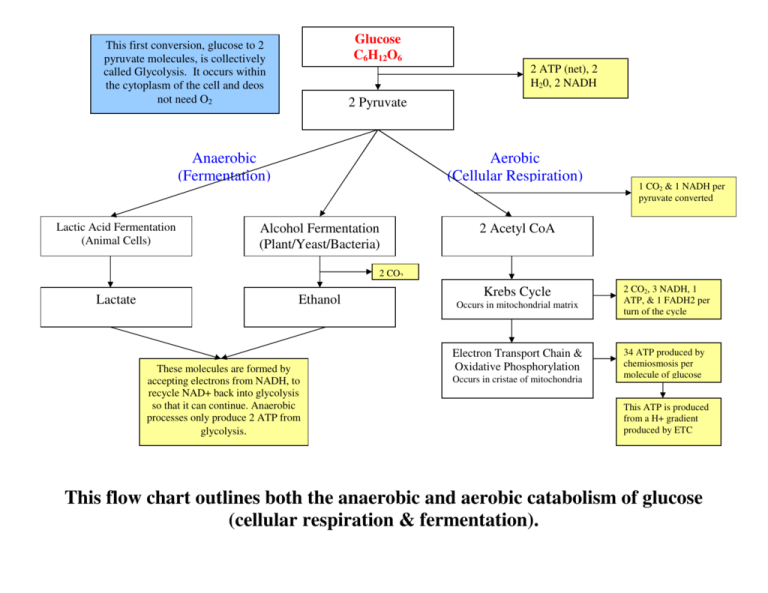
Glucose C6H12O6 This first conversion, glucose to 2 pyruvate molecules, is collectively called Glycolysis. It occurs within the cytoplasm of the cell and deos not need O2 2 ATP (net), 2 H20, 2 NADH 2 Pyruvate Anaerobic (Fermentation) Lactic Acid Fermentation (Animal Cells) Aerobic (Cellular Respiration) Alcohol Fermentation (Plant/Yeast/Bacteria) 1 CO2 & 1 NADH per pyruvate converted 2 Acetyl CoA 2 CO2 Lactate Ethanol These molecules are formed by accepting electrons from NADH, to recycle NAD+ back into glycolysis so that it can continue. Anaerobic processes only produce 2 ATP from glycolysis. Occurs in mitochondrial matrix 2 CO2, 3 NADH, 1 ATP, & 1 FADH2 per turn of the cycle Electron Transport Chain & Oxidative Phosphorylation 34 ATP produced by chemiosmosis per molecule of glucose Krebs Cycle Occurs in cristae of mitochondria This ATP is produced from a H+ gradient produced by ETC This flow chart outlines both the anaerobic and aerobic catabolism of glucose (cellular respiration & fermentation).